SAMA Compliance and the DVMS Institute NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System®
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
The Digital Value Management System™ (DVMS) offers a transformative model that enables companies in the Middle East to effectively operationalize the capabilities required by the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) Cybersecurity Framework. As digital transformation accelerates across the Gulf region and regulatory scrutiny sharpens, particularly within the financial sector, the need for a practical, scalable, and adaptive cybersecurity capability has never been more critical. SAMA’s framework, which applies to banks, insurance companies, financing institutions, and other regulated entities in Saudi Arabia, outlines comprehensive cybersecurity requirements across governance, defense, resilience, and third-party risk domains. The DVMS empowers organizations in the Middle East to implement these requirements not as isolated controls but as part of an integrated, business-aligned system that enhances strategic value, operational resilience, and regulatory readiness.
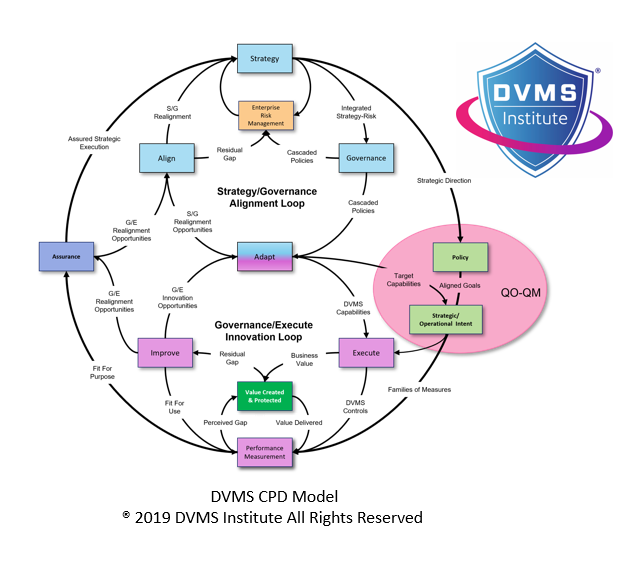
At the heart of the DVMS is recognizing that cybersecurity must be embedded within the broader context of digital business value. Rather than treating cybersecurity as a technical layer bolted onto the organization, the DVMS frames it as a set of interconnected capabilities that enable the secure creation, protection, and delivery of digital services. This perspective aligns closely with the intent of the SAMA Cybersecurity Framework, which emphasizes governance, leadership accountability, risk-driven decision-making, and continuous improvement. The DVMS achieves this alignment through its three-layered structure, with the CPD Model (Create–Protect–Deliver) at the foundation, the Z-X Model (seven minimal viable capabilities) at the middle, and the organizational operating model at the top. This structure helps companies in the Middle East integrate cybersecurity into strategic planning, operational execution, and innovation.
The SAMA Framework begins with Cybersecurity Governance, demanding that organizations establish board-level oversight, assign clear responsibilities, define cybersecurity policies, and integrate cybersecurity into enterprise risk management. The DVMS operationalizes these expectations by embedding governance and assurance as core capabilities. The Z-X Model ensures that governance is not a theoretical construct but a set of actual, measurable practices that guide cybersecurity investment, oversight, and decision-making. The DVMS concept of “strategy-risk” further aligns with SAMA’s governance intent by treating strategy and risk as a single construct. This encourages organizations to move away from the outdated view of cybersecurity as a risk-mitigation expense and instead embrace it as a key enabler of trust, innovation, and competitive advantage.
Leadership accountability is another area of alignment between SAMA and the DVMS. SAMA requires senior executives and boards to take ownership of cybersecurity, a concept reinforced in the DVMS through executive engagement in governance and planning capabilities. The DVMS provides the tools and models—such as the Question Outcome–Question Metric (QO-QM) approach—that help leaders translate strategic intent into actionable metrics and policies. This gives executive leadership visibility into cybersecurity posture, progress, and gaps, fulfilling regulatory expectations and building internal confidence.
SAMA’s Cybersecurity Defense domain focuses on protection, detection, and response capabilities. It outlines requirements for access control, network security, malware protection, data encryption, and secure software development. While these requirements are often implemented as technical controls, the DVMS frames them as part of a broader system that includes organizational behavior, cultural context, and operational dependencies. The 3D Knowledge Model of the DVMS helps organizations understand how people, teams, and systems interact—and where vulnerabilities might exist not just in software but in processes, communications, and shared assumptions. This model aligns with SAMA’s emphasis on defense-in-depth, ensuring that controls are not only in place but are context-aware, continuously validated, and strategically prioritized.
One of the defining strengths of the DVMS in supporting SAMA’s framework is its holistic treatment of Cybersecurity Resilience. SAMA strongly emphasizes business continuity, incident response, backup and recovery, and regular testing of contingency plans. The DVMS CPD Model makes resilience a continuous outcome of digital value delivery. Rather than treating incident response and continuity as separate disciplines, the DVMS integrates them into the organization’s core capabilities—ensuring that resilience is baked into every phase of business operation. Through its phased FastTrack™ implementation model, DVMS guides organizations through a maturity journey that begins with basic hygiene and stabilization and progresses toward innovation and adaptive resilience. This phased approach reflects SAMA’s emphasis on maturity progression and the need for organizations to evolve in response to emerging threats.
To meet SAMA’s expectations around incident response, the DVMS introduces a proactive mindset known as “being the menace.” This concept encourages organizations to adopt the perspective of threat actors—using red-teaming, adversarial simulations, and systems thinking to identify weaknesses before they are exploited. This aligns with SAMA’s requirement to detect and respond to threats promptly and regularly test incident response mechanisms. The DVMS reinforces this by linking detection and response capabilities directly to business value, ensuring that every cybersecurity function is measured by its technical precision and contribution to protecting stakeholder outcomes.
The DVMS also brings depth to Third-Party Cybersecurity, an increasingly important domain in the SAMA Framework. Middle Eastern financial institutions often rely on a diverse range of external vendors and cloud service providers, each of which introduces new layers of risk. SAMA requires organizations to identify critical third parties, conduct risk assessments, and establish contractual protections. The DVMS enhances these efforts by providing a systemic view of third-party interactions. The 3D Knowledge Model enables organizations to map out how third-party services integrate with internal systems and influence the flow of digital value. It helps identify dependencies, assess impact, and design assurance measures that are dynamic and sustainable. Rather than viewing vendor risk through a compliance lens, the DVMS treats it as a function of capability and alignment—making it easier for organizations to demonstrate to regulators that they have real control over their extended digital ecosystem.
Cultural integration is another crucial area where DVMS enhances SAMA compliance. The SAMA Framework requires cybersecurity awareness training and promotes a culture of shared responsibility. DVMS reinforces this through its emphasis on systems thinking and the development of a “questioning culture.” Tools such as the 5 Whys, misuse cases, and scenario-based planning encourage employees at all levels to think critically, question assumptions, and take ownership of their role in cybersecurity. This goes beyond traditional awareness training, cultivating an environment where resilience is a shared value and cybersecurity is integrated into everyday decision-making.
The DVMS also supports continuous improvement, a concept central to SAMA’s cybersecurity maturity model. Organizations are expected to assess their capabilities regularly and demonstrate progress over time, and the DVMS provides the mechanisms to do just that. Through its GQM and QO-QM methodologies, organizations can define strategic outcomes, generate relevant questions, and establish metrics that track progress across governance, defense, resilience, and vendor management. This continuous feedback loop ensures that evidence-based improvement is tied to operational goals, not just regulatory milestones.
Finally, the DVMS’s scalable overlay model makes it particularly well-suited to the Middle Eastern business environment. Many regional organizations operate across multiple jurisdictions and must align with various regulatory standards, including SAMA, NCA ECC, ISO/IEC 27001, and regional data protection laws. The DVMS does not require replacing existing frameworks—instead, it overlays and integrates with what already exists. This flexibility allows organizations to tailor their cybersecurity programs to meet SAMA’s requirements while aligning with other regional and global mandates, maximizing value from their investments, and ensuring consistency across diverse operating environments.
In conclusion, the DVMS provides Middle Eastern companies with a robust, adaptable, and business-aligned system to operationalize the capabilities required by the SAMA Cybersecurity Framework. Its foundation in systems thinking, strategic alignment, capability development, and continuous learning ensures that organizations can meet and exceed regulatory expectations while building lasting resilience. By embedding cybersecurity into governance, operations, culture, and value delivery, the DVMS transforms compliance into capability—and capability into competitive advantage.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
DVMS Institute is a renowned provider of accredited (APMG International), Assured (NCSC-GCHQ-UK), and Recognized (DHS-CISA-NICCS-USA) NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Digital Value Management System® body of knowledge publications, certification trainings, assessment platforms and real-life desktop simulation trainings.
The Institute’s NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System® certified training programs teach businesses of any size, scale, or complexity the skills to build a Performance Driven Overlay System for Cyber Resilience capable of anticipating and mitigating the systemic risk digital businesses face today.
By embedding systemic risk management into strategic decision-making and aligning it with employee cultural values, organizations can build resilience—a dynamic capability to withstand digital business disruption and comply with any cybersecurity regulation (SEC, UK, DORA, NIS2, SAMA, SOCI, IMO, etc.) or maturity model mandates (HITRUST, CMMC, C2M2 etc.).
® DVMS Institute 2024 All Rights Reserved