How Internal Auditors Can Use A DVMS to Strengthen Cyber Risk Scoping and Testing
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Internal audit sits at a critical intersection in modern organizations. Cybersecurity threats are evolving, digital ecosystems are expanding, regulatory scrutiny is intensifying, and boards are demanding evidence of resilience rather than compliance theater.
Historically, technology audits have focused on control validation, framework mapping, and policy conformance. Those activities remain necessary, but they are no longer sufficient. The real question facing internal audit today is not whether controls exist, but whether the organization’s digital work system can reliably create, protect, and deliver value under normal and stressed conditions.
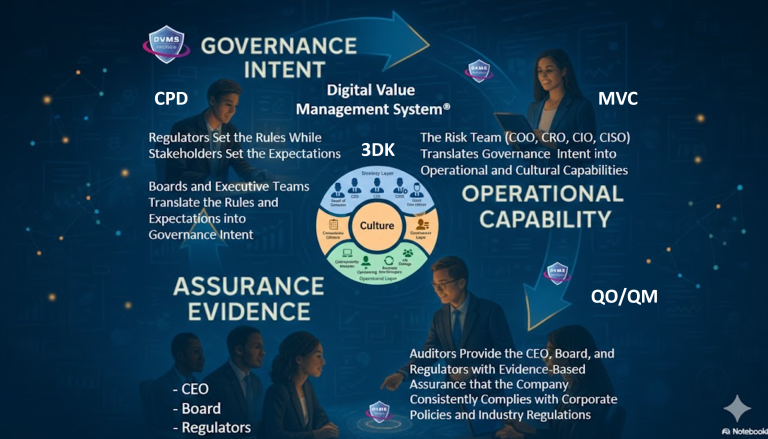
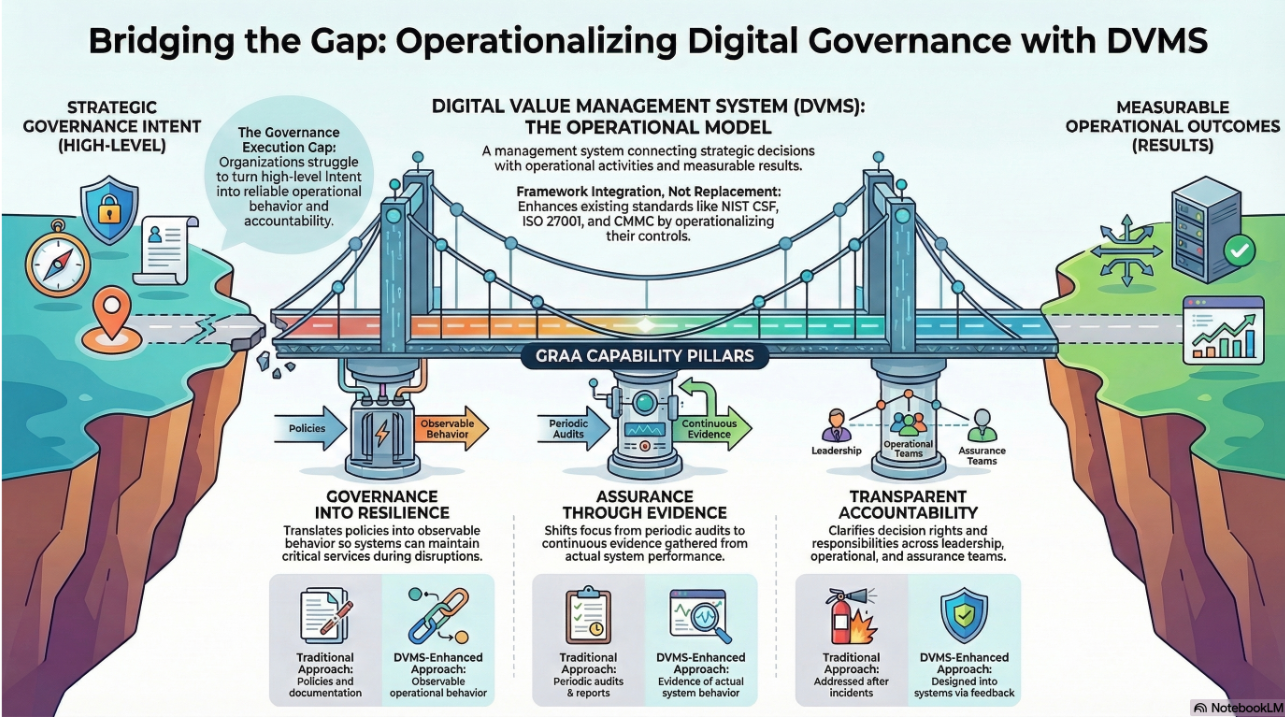
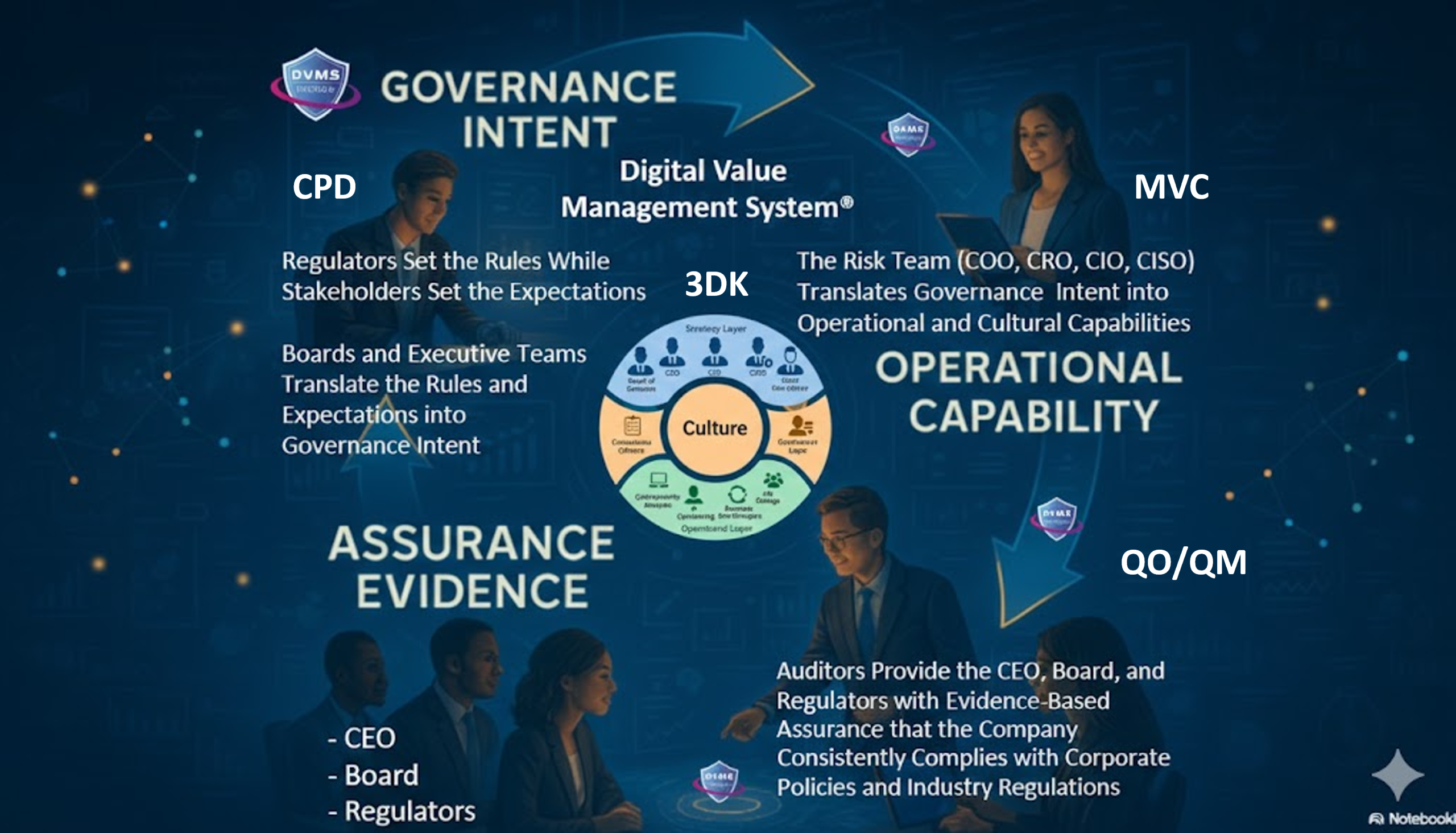
The Digital Value Management System (DVMS) offers an approach that enables internal auditors to scope and test digital programs in alignment with how value and risk are produced in the organization.
Starting With the CPD Model: Create, Protect, Deliver
At the heart of DVMS is the CPD Model: Create, Protect, Deliver. Every digital initiative, including cybersecurity, ITSM, GRC, AI, and transformation programs, exists to support one or more of these three value-producing motions.
- Create refers to innovation, growth, and the development of new capabilities.
- Protect ensures value is safeguarded against threats, volatility, and failure.
- Deliver ensures value is reliably produced and consumed as intended.
For internal auditors, CPD becomes a powerful lens for scoping. Rather than beginning with a framework checklist, auditors can start by asking:
- What value is this program intended to create, protect, or deliver?
- How does leadership define success?
- Where does imbalance across CPD create systemic risk?
Cybersecurity, for example, often overemphasizes Protect at the expense of Create and Deliver. Internal audit can reveal whether protection mechanisms unintentionally constrain innovation or operational flow, or whether delivery pressures erode protective discipline. This CPD imbalance frequently exposes risk concentrations that control catalogs do not reveal. Scoping through CPD ensures the audit begins with the inseparability of value and risk, not with control enumeration.
Using the MVC Capability Overlay to Structure Scope
The DVMS Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVC) provide the operational overlay that translates CPD intent into execution.
- Govern establishes direction, decision rights, and accountability.
- Assure validates the reliability of the outcomes with credible evidence.
- Plan and Design shape how value will be produced.
- Change and Execute operationalize intent.
- Innovate ensures adaptive capacity in dynamic environments.
These capabilities represent the organizational system required to sustain digital value production. Internal auditors provide a structured approach to scoping and segmenting testing. Instead of auditing “cybersecurity controls” as a monolith, internal auditors can ask:
- Where in the MVC sequence is risk most concentrated?
- Is governance intent clearly articulated and operationalized?
- Does the Assure capability generate reliable evidence tied to outcomes?
- Are Plan and Design producing resilient workflows?
- Can Change and Execute perform under stress?
- Does Innovate adapt based on learning?
This capability-based scoping often reveals that failures attributed to “control breakdowns” are actually design flaws, governance ambiguity, or weak assurance logic. By mapping audit scope to MVC, the internal audit evaluates the system rather than isolated components.
Reframing Assurance Through QO-QM Logic
In DVMS, assurance is not the accumulation of dashboards and artifacts. It is the disciplined validation of outcome reliability through Question Outcome and Question Metric logic.
A Question Outcome defines what leadership must know to determine whether value is being created, protected, or delivered.
A Question Metric defines the measurable indicator that answers that question.
Internal auditors can leverage QO-QM to evaluate whether the organization’s Assure capability is structurally sound. For example:
- What outcome is leadership attempting to assure?
- What question must be answered to validate that outcome?
- What metric provides reliable evidence?
- Is the metric complete, accurate, and decision-useful?
- Is the evidence traceable to execution?
Many organizations generate extensive data, but cannot clearly articulate the outcome questions those metrics answer. When QO-QM linkage is weak, assurance becomes performative rather than substantive.
Internal audit can test whether assurance evidence supports board-level decision-making or merely serves to populate reports. This shift elevates audit from control validation to outcome validation.
Scoping Based on Capability Alignment, Not Framework Coverage
Traditional scoping often begins with mapping controls to NIST, ISO, or regulatory standards. DVMS does not replace those frameworks, but it reframes how they are evaluated.
Instead of asking whether controls align with a framework, internal auditors can assess whether:
- CPD balance is maintained
- MVC capabilities are coherently aligned
- Governance direction translates into operational design
- Assurance evidence reliably reflects execution
Misalignment across these dimensions represents systemic risk.
For example:
- If governance intent emphasizes resilience but Change and Execute capabilities are under-resourced, resilience will not materialize.
- If Protect dominates without corresponding Innovate capability, adaptive capacity erodes.
- If Assure lacks QO-QM discipline, leadership decisions rest on unstable evidence.
These alignment gaps are audit priorities because they threaten the organization’s ability to produce reliable digital value.
Designing Tests That Evaluate System Reliability
Once scoped, testing under DVMS moves beyond existence checks. Internal auditors evaluate whether the system can reliably perform.
Testing can examine:
- Whether governance direction is operationally translated
- Whether capability design reflects intended outcomes
- Whether execution produces consistent results
- Whether assurance evidence validates performance
- Whether learning feeds back into innovation
- Resilience becomes observable when capabilities perform under variability and stress. Internal audit can assess whether scenario exercises, incident response simulations, and operational disruptions reveal design weaknesses or confirm reliability. This is not a “closed-loop compliance” exercise. It is a systemic reliability evaluation.
Structuring Audit Reporting Around DVMS
Audit reporting aligned to DVMS can be organized by capability impact rather than control deficiency. Findings may be framed as:
- Governance ambiguity affecting CPD balance
- Weak Assure capability reduces outcome confidence
- Design limitations constraining execution reliability
- Change management friction inhibiting Protect effectiveness
- Innovation gaps limiting adaptive resilience
This structure communicates risk in a language boards understand, reflecting the organization’s ability to reliably produce value. Rather than presenting isolated control gaps, the audit communicates how capability weaknesses affect Create, Protect, and Deliver outcomes.
Elevating Internal Audit’s Strategic Contribution
When the internal audit applies the DVMS approach, it transitions from verifying compliance to validating organizational reliability. It helps leadership understand:
- Whether governance intent is actionable
- Whether capabilities are coherent
- Whether assurance evidence is decision-grade
- Whether value and risk remain balanced
- Whether the organization can adapt under pressure
In dynamic digital environments, this level of insight is what boards increasingly expect. The DVMS approach does not replace existing audit methodologies. It strengthens them by anchoring scoping and testing in how digital value is created and protected.
By aligning audit work with CPD, structuring the scope around the MVC capability sequence, and testing assurance through QO-QM logic, internal audit becomes a strategic contributor to resilience rather than a retrospective validator of controls.
That shift is not cosmetic. It reflects a deeper recognition that in the digital era, assurance is not about artifacts. It is about confidence in the organization’s ability to consistently create, protect, and deliver value, even under stress.
And that is precisely where internal audit can have its greatest impact.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2026 All Rights Reserved