How the DVMS FastTrack Model Supports a DVMS Program
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) is a systems-based overlay designed to help organizations create, protect, and deliver digital business value in an increasingly complex and volatile cyber landscape. While the DVMS provides the conceptual and structural foundation, the DVMS FastTrack™ Model offers a pragmatic pathway for implementation. FastTrack provides a phased, iterative approach that allows organizations to begin where they are, stabilize their environment, and progressively mature toward resilience and innovation. Rather than attempting a wholesale transformation, it emphasizes incremental, risk-informed, and adaptable progress, ensuring that organizations can align governance, culture, and execution with strategic objectives.
The Role of FastTrack in a DVMS Program
At its core, a DVMS program enables organizations to manage digital business risk through enterprise risk management, systems thinking, and cultural adaptation. The challenge is that many organizations struggle with the “how” of operationalizing such a holistic model. The DVMS FastTrack approach addresses this challenge by providing a phased adoption roadmap. It shifts the focus away from static compliance toward adaptive resilience, embedding cyber risk management into daily business practices. FastTrack ensures that organizations take manageable steps that build upon each other, creating tangible value while maintaining momentum.
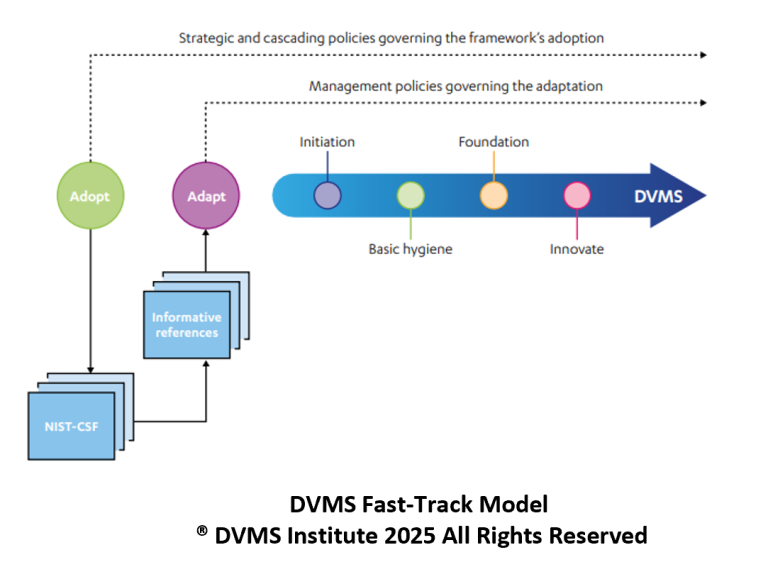
The Four Phases of FastTrack
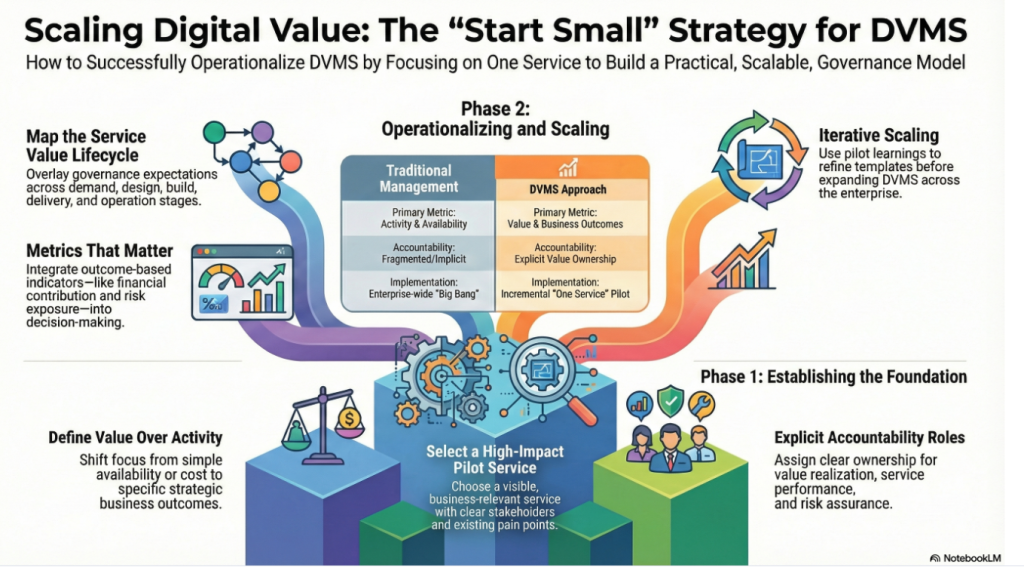
The FastTrack Model is structured into four iterative phases: Initiate, Basic Hygiene, Expand, and Innovate.
- Phase 0 – Initiate: Often called “getting ready to get ready,” this stage establishes the foundation for subsequent phases. It may require implementing early-stage controls, clarifying governance responsibilities, or conducting baseline risk assessments. It stabilizes organizational awareness of digital value and sets expectations for cultural and structural change.
- Phase 1 – Basic Hygiene: This phase focuses on stabilizing the environment. It includes essential cybersecurity practices such as patch management, identity controls, and ensuring critical assets are inventoried and protected. By securing the basics, the organization builds the confidence of stakeholders while reducing exposure to common, preventable risks.
- Phase 2—Expand: Once stability is achieved, organizations can expand by optimizing the environment. This may involve maturing assurance practices, strengthening risk governance, and broadening protective measures across more systems, processes, and supply chain elements. Expansion requires tighter integration of risk-informed governance with enterprise operations.
- Phase 3—Innovate: At this phase, the organization embeds continual innovation and adaptation into its culture. Innovation becomes a core capability, allowing the enterprise to protect value and create competitive advantage through resilience. Continuous feedback loops between governance, assurance, and execution ensure that learning and adaptation are institutionalized.
These phases are not strictly linear. Governance, assurance, and risk assessment occur across all stages, and improvements in one phase may cascade backward to strengthen earlier work. This cyclical nature reinforces the DVMS principle of treating organizations as complex adaptive systems.
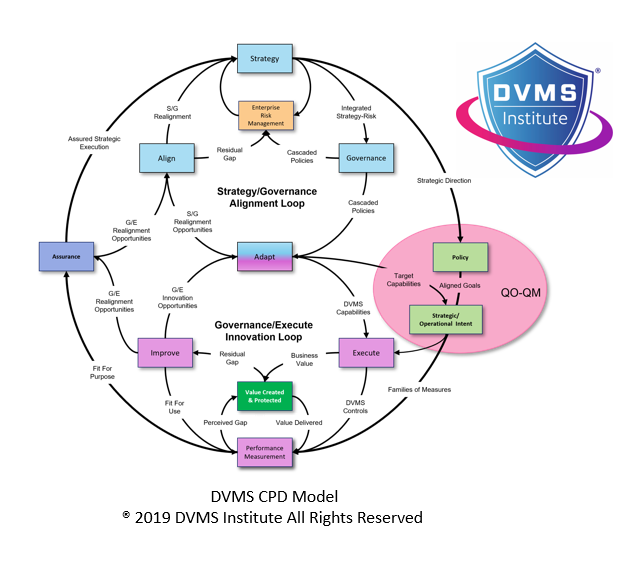
Aligning FastTrack with the DVMS Z-X and CPD Models
FastTrack is more than a stepwise checklist; it is embedded within the MVC–Z-X Model and the Create, Protect, Deliver (CPD) Model of the DVMS. The MVC-Z-X Model describes seven minimum viable capabilities (MVCs)—Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate—that every organization must master. FastTrack provides the temporal rhythm for maturing these capabilities. For example, the emphasis falls on Govern, Assure, and Plan in the Initiate and Basic Hygiene phases. When an organization reaches Innovate, the Execute and Innovate capabilities dominate, supported by continual governance and assurance.
The CPD Model reinforces that unprotected value has no value. FastTrack operationalizes this principle by ensuring that value creation and protection occur concurrently. Instead of a “create then protect” sequence, organizations learn to protect value as it is created, embedding resilience into processes from the outset.
Systems Thinking and FastTrack
One of the FastTrack Model’s most significant contributions to a DVMS program is its reliance on systems thinking. Organizations are not static entities but complex adaptive systems, where small changes in structure or culture can disproportionately impact behavior and outcomes. FastTrack encourages leaders to “see the whole, not the hole,” using iterative cycles to test and adapt. By applying leverage at critical points, organizations can coax systemic change without triggering destabilizing unintended consequences.
Embedding Culture and Leadership
A DVMS program succeeds or fails on culture, and FastTrack supports this by integrating cultural adaptation into each phase. In the Initiate stage, leadership signals accountability and aligns governance with enterprise risk management. In Basic Hygiene, employees across departments are engaged in establishing protective behaviors. By the Expand and Innovate phases, a questioning culture, continuous learning, and transparent accountability are institutionalized. FastTrack thus acts as a cultural scaffold, enabling leadership to cascade values, policies, and expectations from the boardroom to the front line.
Supporting Cyber Resilience and NIST CSF Adoption
The FastTrack Model is explicitly designed to help organizations operationalize the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0. The CSF provides the “what” and “why” of cybersecurity outcomes, but not the “how.” FastTrack fills this gap by giving organizations a practical, phased method to adopt CSF outcomes within their DVMS overlay. For example, the CSF’s GOVERN and IDENTIFY functions align naturally with the Initiate and Basic Hygiene phases. At the same time, PROTECT and DETECT are emphasized in Expand, and RESPOND and RECOVER are refined in Innovate.
In this way, FastTrack ensures that organizations do not treat the CSF as a compliance checklist but as a living, adaptive governance system integrated into strategy, risk, and culture.
Continuous Innovation and Competitive Advantage
The ultimate goal of FastTrack within a DVMS program is not mere compliance or even cybersecurity. It is operational resilience, sustainable digital business value, regulatory compliance, and client digital trust. By embedding a culture of continual innovation, FastTrack ensures that organizations can adapt to evolving threats, technological change, and shifting stakeholder expectations. The ability to create and protect digital business value concurrently becomes a source of competitive differentiation, allowing organizations to withstand disruption and thrive on the edge of chaos.
Conclusion
The DVMS FastTrack Model provides the structured, yet flexible path organizations need to implement a DVMS program effectively. It stabilizes environments by offering incremental, iterative phases, embeds cultural change, and enables continuous innovation. More importantly, FastTrack operationalizes the systems-based principles of the DVMS, aligning with the NIST CSF 2.0 and ensuring that value creation and value protection are inseparable. In doing so, it transforms cybersecurity from a technical silo into an enterprise-wide governance practice, fostering resilience, adaptability, and long-term success.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
DVMS Institute® Certified Training
Learn To Build a Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) for Assured and Accountable Cyber Resilience
Watch a Quick Paper to Practice Explainer Video
Despite abundant frameworks and dashboards, leaders still struggle to see how digital value streams actually perform under real-world stress.
Intent, structure, and day-to-day behavior are examined in isolation, creating flat views that hide how decisions and human responses interact in a living digital system.
The result is governance that appears robust on paper but breaks down in execution, forcing leaders to manage fragmented controls rather than assure and account for resilient, system-level performance
The Assurance Mandate White Paper Series
Watch a Quick Assurance Mandate Explainer Video
The whitepapers below present a clear progression from compliance-driven thinking to a modern system of Governance, Resilience, Assurance, and Accountability (GRAA). Together, they define an evidence-based approach to building and governing resilient digital enterprises.
The Assurance Mandate Paper explains why traditional GRC artifacts offer reassurance, not proof, and challenges boards to demand evidence that value can be created, protected, and delivered under stress.
The Assurance in Action Paper shows how DVMS turns intent into execution by translating outcomes into Minimum Viable Capabilities, aligning frameworks through the Create–Protect–Deliver model, and producing measurable assurance evidence of real performance.
The Governing by Assurance Paper extends this model to policy and regulation, positioning DVMS as a learning overlay that links governance intent, operational capability, and auditable evidence—enabling outcome-based governance and proof of resilience through measurable performance data.
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS)
Watch a Quick DVMS Explainer Video
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) training programs teach leadership, practitioners, and employees how to easily integrate fragmented frameworks and systems such as NISTCSF, GRC, ITSM, and AI into a unified, culture-driven governance and assurance system that enables organizations to manage the resilience of their living digital system by :
- Enabling Adaptive Governance through risk-informed decision-making
- Sustaining Operational Resilience through a proactive and adaptive culture
- Measuring Performance Assurance through evidence-based outcomes
- Ensuring Visible Accountability by making intent, execution, and evidence inseparable
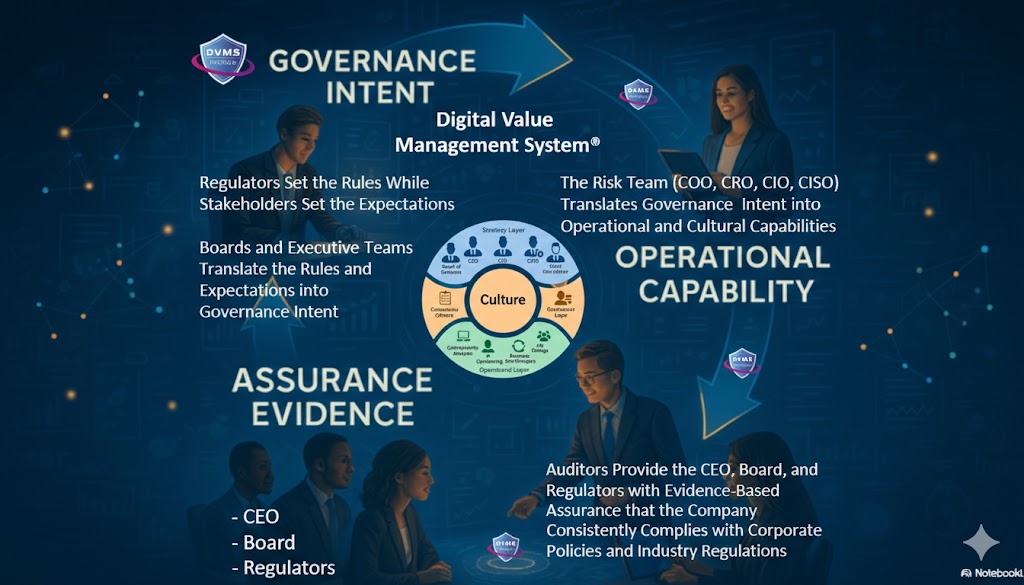
At its core, the DVMS is a simple but powerful integration of:
- Governance Intent – shared expectations and accountabilities
- Operational Capabilities – how the digital business actually performs
- Assurance Evidence – proof that outcomes are achieved and accountable
- Cultural Outcomes – that align people, decisions, and behaviors
Through its MVC, CPD, 3D Knowledge, and FastTrack Models, a DVMS turns this integration into three distinctive capabilities:
A Governance Overlay that replaces fragmentation with unity. The DVMS provides organizations with a structured way to connect strategy with day-to-day execution. Leaders gain a consistent mechanism to direct, measure, and validate performance—across every system responsible for digital value.
A Behavioral Engine that drives high-trust, high-velocity decision-making. The DVMS embeds decision models and behavioral patterns that help teams think clearly and act confidently, even in uncertain situations. It is engineered to reduce friction, prevent blame-based cultures, and strengthen organizational reliability.
A Learning System that makes culture measurable, adaptable, and scalable. Culture becomes a managed asset—not an abstract concept. The DVMS provides a repeatable way to observe behavior, collect evidence, learn from outcomes, and evolve faster than threats, disruptions, or market shifts.
The DVMS Team
Watch a Quick DVMS Explainer Video
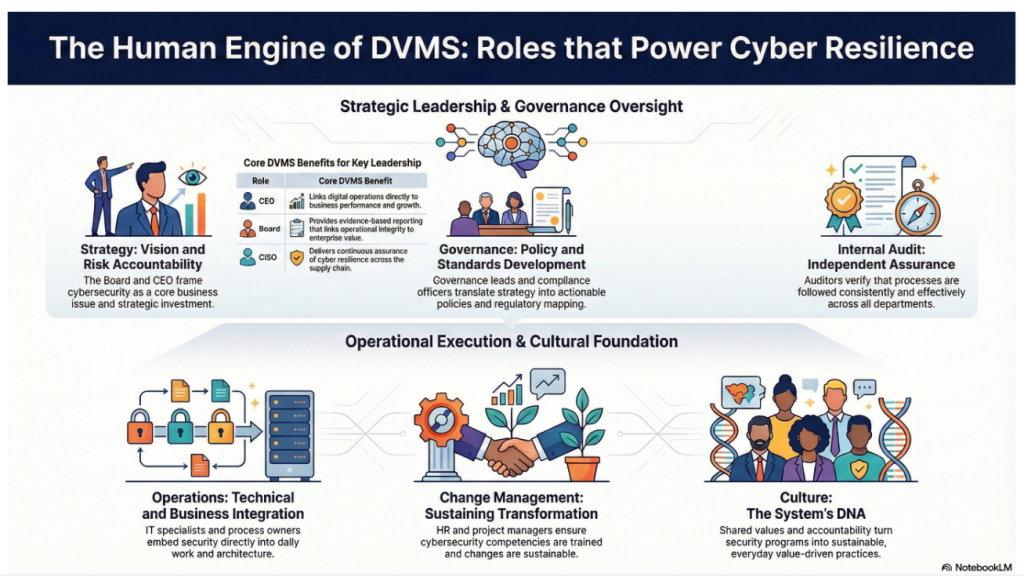
Delivering the outcomes of the DVMS integrated with the NIST CSF, ITSM, GRC, and AI systems requires coordinated action across an enterprise’s strategy, governance, and operational layers.
Each of these business layers contains unique roles that, when aligned and functioning cohesively, enable the organization to protect digital assets and adaptively manage digital business risks while delivering sustained digital value and resilience.
Together, these roles create an adaptive, risk-informed, and resilient organization capable of thriving in a complex, volatile digital environment.
The DVMS Training Pathway to Operational Resilience
Watch a Quick DVMS Training Explainer Video
The DVMS Institute’s certification training programs and publications equip leaders, practitioners, and organizations to govern operational cyber-resilience through an evidence-based system that assures and accounts for digital value outcomes.
Grounded in real-world governance challenges and aligned to NIST CSF 2.0, DVMS Institute offerings go beyond frameworks and compliance checklists to build measurable capability, clear accountability, and defensible confidence in decision-making.
Through structured learning, applied certification, and authoritative publications, the Institute advances a disciplined, outcome-driven approach to managing digital risk, performance, and resilience as an integrated system.
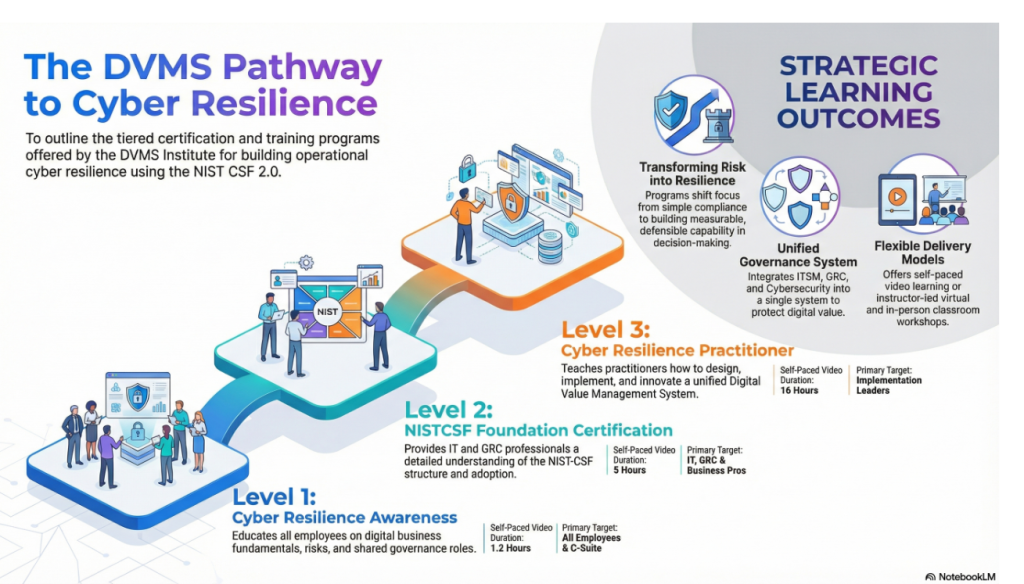
DVMS Cyber Resilience Awareness Training
The DVMS Cyber Resilience Awareness course and its accompanying body of knowledge publication educate all employees on the fundamentals of digital business, its associated risks, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and their role within a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
This investment fosters a culture that is prepared to operate within a system capable of transforming systemic cyber risks into operational resilience.
DVMS NISTCSF Foundation Certification Training
The DVMS NISTCSF Foundation certification training course and its accompanying body of knowledge publications provide ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business professionals with a detailed understanding of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and its role in a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
This investment fosters IT, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business professionals with the skills to operate within a system capable of transforming systemic cyber risks into operational resilience.
DVMS Cyber Resilience Practitioner Certification Training
The DVMS Practitioner certification training course and its accompanying body of knowledge publications teach ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business practitioners how to elevate investments in ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and AI business systems by integrating them into a unified governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability system designed to proactively identify and mitigate the cyber risks that could disrupt operations, erode resilience, or diminish client trust.
This investment fosters IT, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business practitioners with the skills to assess, design, implement, operationalize, and continually innovate a Digital Value Management System® program that operationalizes a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
A FastTrack Approach to Launching A DVMS Program
Watch a Quick DVMS FastTrack Explainer Video
The DVMS FastTrack Model is a phased, iterative approach that helps organizations adopt and mature their Digital Value Management System over time, rather than trying to do everything simultaneously. This approach breaks the DVMS journey into manageable phases of success.
DVMS Organizational Benefits
Instead of replacing existing operational frameworks, the DVMS elevates them—connecting and contextualizing their data into actionable intelligence that validates performance and exposes the reasons behind unmet outcomes.
By adopting a DVMS, organizations are positioned to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Deliver Digital Value and Trust Across A Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
DVMS Leadership Benefits
The Digital Value Management System (DVMS) provides leaders with a unified, evidence-based approach to governing and enhancing their digital enterprise, aligning with regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
For the CEO, the DVMS provides a clear line of sight between digital operations, business performance, and strategic outcomes—turning governance and resilience into enablers of growth and innovation rather than cost centers.
For the Board of Directors, the DVMS provides ongoing assurance that the organization’s digital assets, operations, and ecosystem are governed, protected, and resilient—supported by evidence-based reporting that directly links operational integrity to enterprise value and stakeholder trust.
For the CIO, CRO, CISO, and Auditors: an integrated, adaptive, and culture-driven governance and assurance management system that enhances digital business performance, resilience, trust, and accountability.
Company Brochures and Presentation
Explainer Videos
- DVMS Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- DVMS Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- DVMS Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- DVMS MVC ZX Model – Powers the CPD
- DVMS CPD Model – Powers DVMS Operations
- DVMS 3D Knowledge Model – Powers the DVMS Culture
- DVMS FastTrack Model – Enables A Phased DVMS Adoption
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved