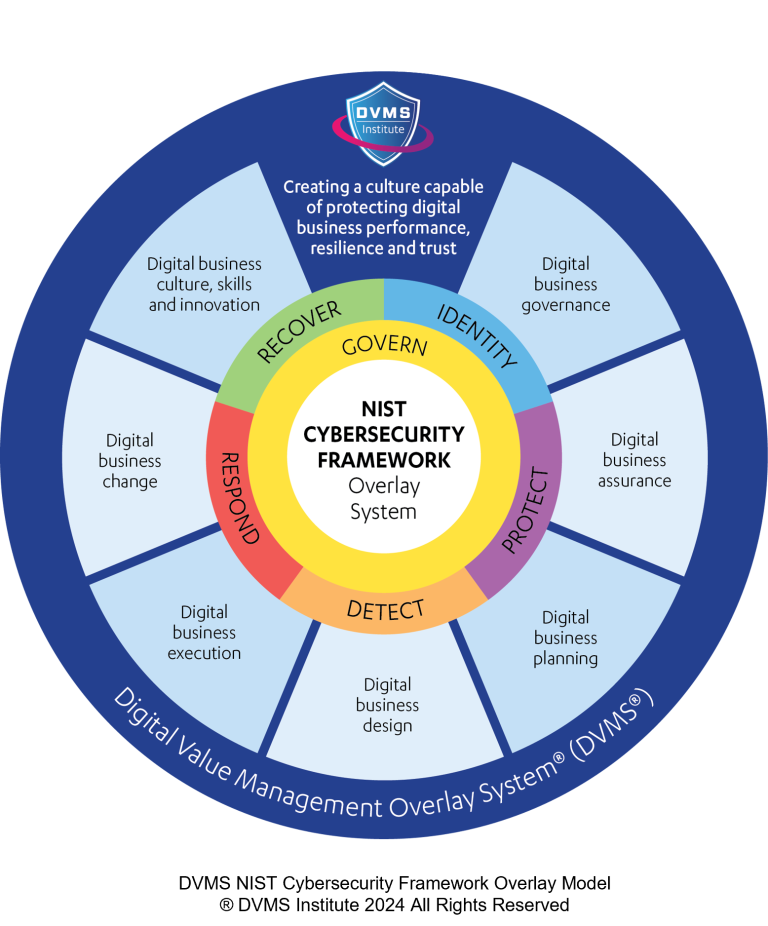
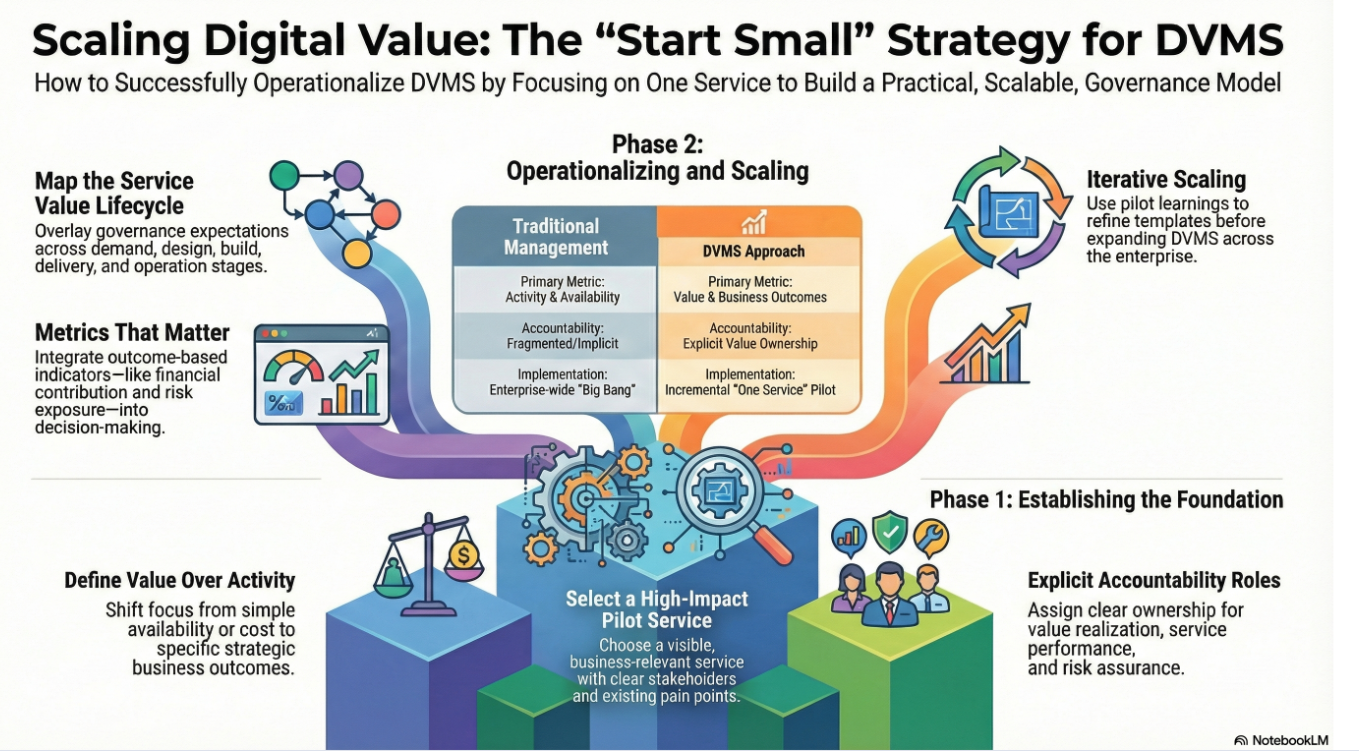
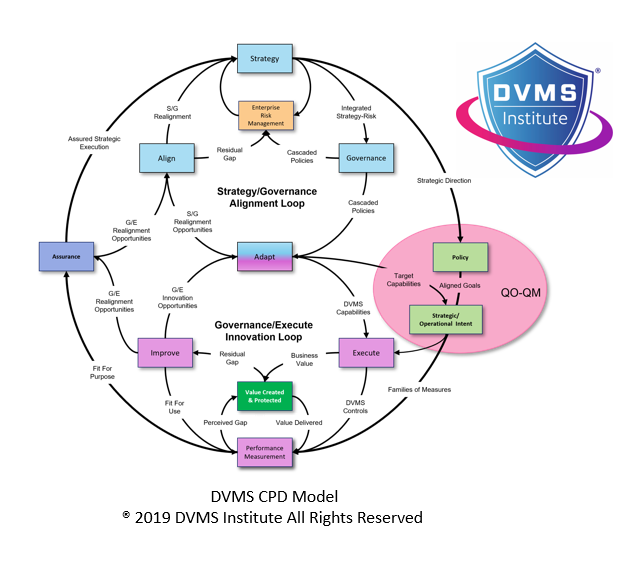
Culture as a Cornerstone of GRC: A Holistic Approach
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
The Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework has long been a cornerstone of effective organizational management, providing a structured approach to managing governance, mitigating risks, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. However, the evolving business landscape, characterized by increasing complexity, globalization, and rapid technological advancements, demands a more holistic and adaptive approach. One critical element often overlooked in traditional GRC models is organizational culture. Culture, as the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that shape an organizational identity and operations, is pivotal in determining its success or failure.
The Interconnectedness of Culture and GRC
Culture is not merely a soft, intangible factor that can be ignored or treated as an afterthought. It is deeply intertwined with the core elements of GRC: governance, risk, and compliance.
- Governance: Culture influences the way an organization is governed and managed. A culture of integrity, transparency, and accountability fosters effective governance practices, ensuring that the organization operates in alignment with its mission and values. Conversely, a culture of secrecy, fear, or complacency can undermine governance and create opportunities for misconduct.
- Risk: Culture shapes how an organization perceives and responds to risk. A culture of risk awareness and proactive management enables organizations to identify and address potential threats before they materialize. A culture of complacency or denial, on the other hand, can lead to blind spots and catastrophic consequences.
- Compliance: Culture is critical in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. A compliance culture characterized by a commitment to ethical behavior and adherence to laws and regulations helps organizations avoid costly penalties and reputational damage. However, a culture of shortcuts or disregard for rules can increase the risk of non-compliance and legal issues.
The Benefits of Integrating Culture into GRC
Integrating culture into the GRC framework offers numerous benefits for organizations:
- Enhanced Risk Management: A culture that values risk awareness and proactive management enables organizations to identify and mitigate risks more effectively. Employees empowered to speak up about potential issues and supported in taking proactive measures can help prevent costly incidents.
- Improved Governance: A culture of transparency, accountability, and integrity fosters effective governance practices, ensuring that the organization operates in alignment with its mission and values. Employees who feel empowered to challenge the status quo and rewarded for ethical behavior are more likely to contribute to good governance.
- Increased Compliance: A culture of compliance helps organizations avoid costly penalties and reputational damage. Employees who understand the importance of adhering to laws and regulations and are provided with the necessary training and resources are more likely to comply with regulatory requirements.
- Enhanced Reputation: A positive organizational culture can enhance an organizational reputation and attract top talent. Employees who feel valued, respected, and empowered are likelier to be loyal and committed to the organization.
Integrating Culture into GRC: Practical Considerations
Integrating culture into the GRC framework requires a deliberate and systematic approach. Here are some practical considerations:
- Define Cultural Values: Clearly articulate the organizational core values and ensure they align with its mission and vision.
- Communicate and Reinforce Culture: Develop effective communication channels to disseminate cultural values throughout the organization. Reinforce these values through policies, procedures, and reward systems.
- Measure Cultural Effectiveness: Assess the effectiveness of cultural initiatives through employee surveys, focus groups, and other qualitative and quantitative methods.
- Continuously Improve: Culture is an evolving entity. Regularly review and update cultural initiatives to remain relevant and practical.
By recognizing the critical role of culture in GRC, organizations can create a more resilient, ethical, and sustainable business environment. By integrating culture into their GRC framework, organizations can enhance risk management, improve governance, increase compliance, and build a more substantial reputation.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
The DVMS Institute teaches organizations of any size, scale, or complexity an affordable approach to mitigating cyber risk to protect digital business performance, resilience, and trust.
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
® DVMS Institute 2024 All Rights Reserved