The DVMS 3D Knowledge Model: A Multidimensional Approach to Cyber Resilience
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) provides organizations with an overlay model for managing digital business risk by linking value creation and protection as inseparable activities. One of its most innovative components is the 3D Knowledge Model, a conceptual model designed to ensure that cybersecurity is not treated as a siloed technical problem but as an integrated organizational responsibility. This model emphasizes the interaction between team knowledge, collaboration, and strategic alignment, ensuring that organizations can see the “whole” system, not just isolated parts.
By embedding the 3D Knowledge Model within the DVMS overlay, organizations gain a powerful tool for achieving cyber resilience. This essay explores the model’s structure, principles, and implications, showing how it contributes to creating, protecting, and delivering digital business value in complex environments.
The Purpose of the 3D Knowledge Model
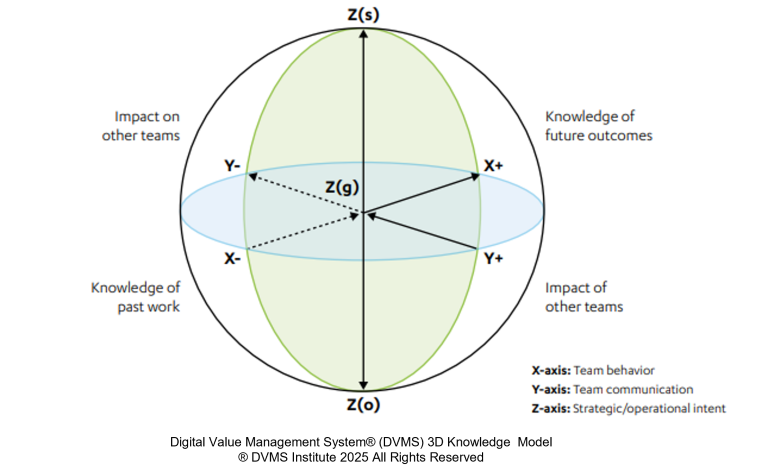
The 3D Knowledge Model is designed to uncover hidden vulnerabilities and strengthen resilience by framing team and organizational dynamics across three dimensions:
- Knowledge over Time (X-axis) – capturing lessons from the past, evaluating the present, and preparing for the future.
- Collaboration (Y-axis) – focusing on inter-team dependencies and cross-functional accountability.
- Strategic Alignment (Z-axis) – ensuring that every action contributes to the organizational mission and goals.
This multidimensional approach ensures that cybersecurity initiatives are not isolated technical fixes but embedded in the organization’s cultural, strategic, and operational fabric.
The X-Axis: Knowledge and Learning Over Time
The X-axis emphasizes the continuous learning cycle by leveraging past experiences, adapting present practices, and anticipating future challenges.
- Past: Teams must institutionalize lessons from incidents and successes to avoid repeating mistakes.
- Present: Current practices require constant evaluation to identify vulnerabilities and inefficiencies.
- Future: Teams must anticipate risks, emerging technologies, and evolving threats.
This temporal perspective ensures adaptability. For example, by analyzing a past data breach, teams can implement immediate controls while simultaneously using insights to prepare for more advanced attack vectors. The result is a proactive posture where learning is embedded into organizational routines.
The Y-Axis: Inter-Team Collaboration
The Y-axis captures how different teams interact and share knowledge. Cybersecurity failures often occur because departments operate in silos—IT may implement a control without HR understanding its role in insider threat management, or legal may overlook compliance implications of technical decisions.
The 3D Knowledge Model promotes cross-functional collaboration, where teams learn the impact of their work on others and develop mutual accountability. For instance, a vulnerability management team must understand how delayed patching impacts operations, while business units must grasp how their workflows affect overall risk posture. This cultural shift breaks down silos and fosters shared responsibility.
The Z-Axis: Strategic and Operational Alignment
The Z-axis ensures that team activities are technically sound and strategically relevant. Every cybersecurity effort must align with the organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
For example, if an organization’s mission emphasizes customer trust, its cybersecurity strategy must prioritize protecting personal data and transparent incident communication. The Z-axis ensures that security efforts advance these strategic objectives, preventing misalignment between operational activities and strategic intent.
This axis also introduces a maturity perspective: the better the alignment between operations and strategy, the more resilient and adaptive the organization becomes.
Context, Capability, and Maturity
Beyond the three axes, the 3D Knowledge Model incorporates three broader organizational dimensions:
- Context: Aligning knowledge and behavior with the organization’s unique mission, regulatory environment, and risk tolerance.
- Capability: Measuring the ability to collaborate across teams and effectively leverage resources.
- Maturity: Assessing how consistently strategic goals translate into operational execution.
These dimensions enable organizations to evolve from reactive cybersecurity measures to proactive and adaptive resilience.
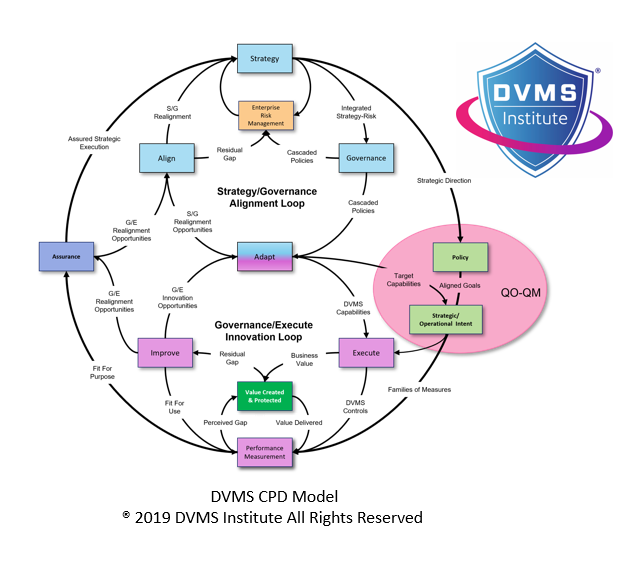
Integration with the DVMS Overlay
The 3D Knowledge Model is not standalone; it integrates directly with the DVMS overlay, which itself consists of three layers:
- What the organization already does (existing frameworks, methods, and processes).
- The Z-X Model defines the seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate).
- The CPD Model operationalizes the ability to create, protect, and deliver digital business value.
The 3D Knowledge Model enhances this structure by ensuring all three layers function cohesively. For example, when an organization uses the CPD Model to balance value creation with protection, the 3D Knowledge Model provides a lens for aligning knowledge (X), collaboration (Y), and strategy (Z) with those activities.
Practical Applications
Identifying Hidden Vulnerabilities
The model encourages organizations to ask better questions about their systems and assumptions. By mapping dependencies across the three axes, teams can reveal undocumented processes, cultural blind spots, and overlooked risks. For instance, asking “How does this system impact other teams?” can uncover cascading effects of a change that might otherwise remain invisible.
Cultural Integration
Cybersecurity resilience is not just technical—it requires cultural integration. The 3D Knowledge Model supports this by encouraging shared accountability, fostering a questioning culture, and embedding resilience into daily operations.
Alignment with NIST CSF 2.0
The model also aligns with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, particularly its emphasis on governance, enterprise risk management, and outcomes. CSF’s GOVERN function naturally aligns with the Z-axis, ensuring strategic alignment, while IDENTIFY and PROTECT correspond to the knowledge and collaboration axes.
The Role of Systems Thinking
A defining characteristic of the 3D Knowledge Model is its foundation in systems thinking. By treating organizations as complex adaptive systems, the model acknowledges that no part can be improved in isolation. Instead, outcomes depend on the interactions among parts.
This holistic perspective means that cybersecurity cannot be reduced to checklists. Instead, resilience emerges from the coordinated interplay of teams, processes, and strategies across all three axes.
Benefits of the 3D Knowledge Model
The DVMS 3D Knowledge Model delivers several tangible benefits:
- Improved Awareness: Teams learn from past events while staying prepared for the future.
- Reduced Risks: Collaboration across functions prevents blind spots and reduces systemic vulnerabilities.
- Strategic Coherence: Cybersecurity efforts align with organizational goals, ensuring relevance and impact.
- Cultural Resilience: A questioning culture and leadership accountability embed security into daily routines.
- Adaptive Capacity: The model enables organizations to evolve continuously in response to dynamic threats.
Conclusion
The DVMS 3D Knowledge Model is a powerful innovation for managing digital business risk. Framing organizational behavior along the axes of knowledge, collaboration, and alignment ensures that cybersecurity is embedded in strategy, culture, and operations. Integrated into the DVMS overlay enables organizations to create, protect, and deliver digital value as concurrent, inseparable activities.
In an era of constant cyber threats and organizational complexity, the 3D Knowledge Model equips leaders and practitioners with a holistic, multidimensional lens to build resilience. By embracing this model, organizations can transform cybersecurity from a reactive technical function into a proactive driver of trust, adaptability, and long-term success.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
Digital Value Management System® (DVMS)
The DVMS is an adaptive, culture-enabled governance overlay designed to help organizations of any size, scale, or complexity transition from static, paper-based governance models to a living, evidence-based system of Governance, Resilience, Assurance, and Accountability (GRAA).
At its core, the DVMS is a simple but powerful integration of:
-
Governance Intent – shared expectations and accountabilities.
-
Operational Capability – how the business actually performs
-
Assurance Evidence – proof that intended outcomes are being achieved
Rather than adding more complexity, a DVMS integrates fragmented frameworks and practices such as NIST CSF, GRC, ITSM, DevOps, and AI into a unified overlay system that enables leaders and regulators to see, in real time, whether the digital business is working as intended—and whether the risks that matter most are being managed proactively.
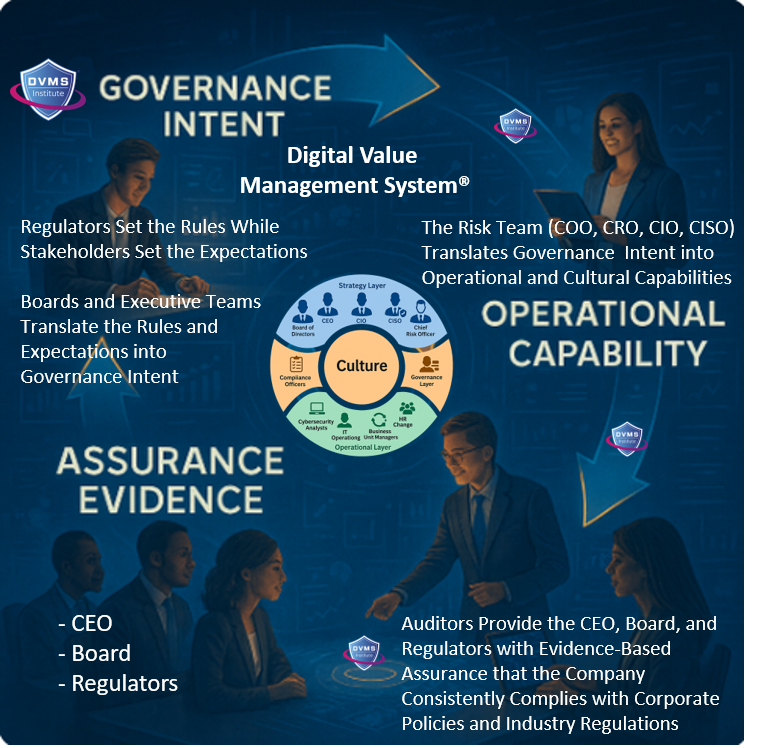
Through its MVC, CPD, 3D Knowledge, and FastTrack Models, a DVMS turns this integration into three distinctive capabilities:
A Governance Overlay that replaces fragmentation with unity. The DVMS provides organizations with a structured way to connect strategy with day-to-day execution. Leaders gain a consistent mechanism to direct, measure, and validate performance—across every system responsible for digital value.
A Behavioral Engine that drives high-trust, high-velocity decision-making. The DVMS embeds decision models and behavioral patterns that help teams think clearly and act confidently, even in uncertain situations. It is engineered to reduce friction, prevent blame-based cultures, and strengthen organizational reliability.
A Learning System that makes culture measurable, adaptable, and scalable. Culture becomes a managed asset—not an abstract concept. The DVMS provides a repeatable way to observe behavior, collect evidence, learn from outcomes, and evolve faster than threats, disruptions, or market shifts.
DVMS Organizational Benefits
Instead of replacing existing operational frameworks, the DVMS elevates them—connecting and contextualizing their data into actionable intelligence that validates performance and exposes the reasons behind unmet outcomes.
By adopting a DVMS, organizations are positioned to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Deliver Digital Value and Trust Across A Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
DVMS Leadership Benefits
The Digital Value Management System (DVMS) provides leaders with a unified, evidence-based approach to governing and enhancing their digital enterprise, aligning with regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
For the CEO, the DVMS provides a clear line of sight between digital operations, business performance, and strategic outcomes—turning governance and resilience into enablers of growth and innovation rather than cost centers.
For the Board of Directors, the DVMS provides ongoing assurance that the organization’s digital assets, operations, and ecosystem are governed, protected, and resilient—supported by evidence-based reporting that directly links operational integrity to enterprise value and stakeholder trust.
For the CIO, CRO, CISO, and Auditors: an integrated, adaptive, and culture-driven governance and assurance management system that enhances digital business performance, resilience, trust, and accountability
DVMS White Papers
The three whitepapers below present a coherent progression that shifts organizations from compliance-driven thinking to a modern system of Governance, Resilience, Assurance, and Accountability (GRAA). Collectively, the three papers define a comprehensive system for building and governing resilient digital enterprises, grounded in evidence rather than assumptions.
The Assurance Mandate Paper sets the stage by showing why traditional GRC artifacts provide only reassurance—not evidence—and calls boards to demand forward-looking proof that their organizations can continue to create, protect, and deliver value under stress.
The Assurance in Action Paper elevates the conversation from leadership intent to managerial execution, demonstrating how the DVMS operationalizes resilience by translating outcomes into Minimum Viable Capabilities, connecting frameworks through the Create–Protect–Deliver model, and generating measurable assurance evidence that managers can use to demonstrate real performance rather than activity.
The Governing by Assurance Paper elevates the approach to the policy and regulatory level, showing how DVMS functions as a learning overlay system that links governance intent, operational capability, and verifiable evidence into a continuous loop—enabling regulators, agencies, and enterprises to govern by outcomes rather than checklists and to prove capability with measurable, auditable performance data.
DVMS Cyber Resilience Certified Training Programs
DVMS Cyber Resilience Awareness Training
The DVMS Cyber Resilience Awareness course and its accompanying body of knowledge publication educate all employees on the fundamentals of digital business, its associated risks, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and their role within a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
This investment fosters a culture that is prepared to operate within a system capable of transforming systemic cyber risks into operational resilience.
DVMS NISTCSF Foundation Certification Training
The DVMS NISTCSF Foundation certification training course and its accompanying body of knowledge publications provide ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business professionals with a detailed understanding of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and its role in a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
This investment fosters IT, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business professionals with the skills to operate within a system capable of transforming systemic cyber risks into operational resilience.
DVMS Cyber Resilience Practitioner Certification Training
The DVMS Practitioner certification training course and its accompanying body of knowledge publications teach ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business practitioners how to elevate investments in ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and AI business systems by integrating them into a unified governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability system designed to proactively identify and mitigate the cyber risks that could disrupt operations, erode resilience, or diminish client trust.
This investment fosters IT, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business practitioners with the skills to assess, design, implement, operationalize, and continually innovate a Digital Value Management System® program that operationalizes a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
Company Brochures and Presentation
Explainer Videos
- DVMS Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- DVMS Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- DVMS Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- DVMS MVC ZX Model – Powers the CPD
- DVMS CPD Model – Powers DVMS Operations
- DVMS 3D Knowledge Model – Powers the DVMS Culture
- DVMS FastTrack Model – Enables A Phased DVMS Adoption
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved