The DVMS MVC Model – The Minimum Viable Business Capabilities that Power the DVMS-CPD Model
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
As presented in the DVMS Institute’s publications, the MVC Model is a structural visualization and operational strategy embedded within the Digital Value Management System (DVMS) overlay. This model represents a system-of-systems framework that equips organizations with the capability to navigate digital complexity and achieve cyber resilience by enabling the concurrent creation, protection, and delivery of digital business value.
The MVC Model: A Systemic Approach To Digital Business Operations
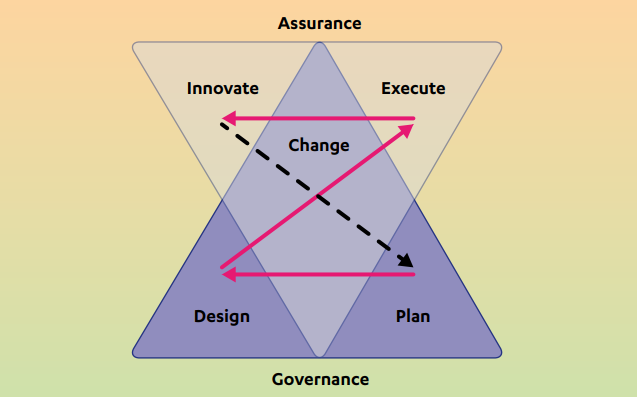
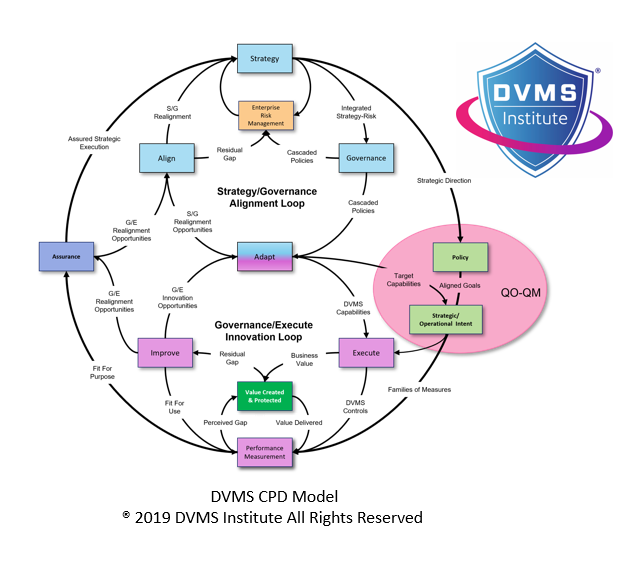
The MVC Model (often stylized as the Z-X Model) lies at the core of DVMS and represents the seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs) every organization must embody to function effectively in the digital landscape. The model is structured visually and reflects its systemic nature—its Z shape represents interconnected capabilities, and the X represents integration points across strategic and operational domains.
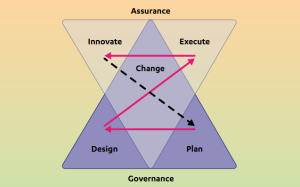
Each capability in the model encapsulates key operational dimensions of an organization, collectively ensuring that the organization is strategically aligned and operationally resilient. These capabilities are:
- Govern (GO) – Establishes the rules, policies, and boundaries of “how we conduct business.” It sets strategic direction, risk tolerance, and performance expectations through policy cascades that link boardroom intent to frontline execution.
- Assure (AS) – Ensures the right things are done correctly. This capability focuses on oversight, conformance to governance, and the feedback systems that validate outcomes and performance against expectations.
- Plan (PL)—This encompasses strategy formulation and tactical planning. It ensures that the organization can craft responsive strategies, aligning its goals and resources in anticipation of changes in its internal or external environment.
- Design (DE) – Orchestrates the structures, processes, and tools needed to implement the plans. It embodies the organization’s ability to experiment, innovate, and structure value creation and protection mechanisms.
- Change (CH) – Manages transitions within the organization. Whether introducing new technologies, policies, or behaviors, Change ensures adaptability by reducing resistance and embedding resilience.
- Execute (EX) – Delivers on the planned activities. It includes the processes and workflows that create, protect, and deliver value. Execution is where governance and planning are translated into action.
- Innovate (IN) – Pushes the boundaries of value creation through four lenses of innovation: incremental, sustaining, adaptive, and disruptive. This ensures the organization continually evolves and remains relevant in dynamic environments.
Together, these capabilities form the structure and behavior of a resilient organization. They offer a way to design organizational functions by recognizing that real performance and adaptability come not from isolated departments but from how their parts work together as a coherent whole.
Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs): Operational Implications
The term Minimum Viable Capabilities doesn’t imply minimal effort or lightweight activity. Rather, it designates the baseline competencies that must be in place for any organization, regardless of size, scale, or complexity, to function effectively and responsibly in today’s multi-vendor, risk-laden digital world.
Here’s a breakdown of what each capability entails in practice:
- Govern: Drives a culture of accountability. Policy cascades ensure everyone understands their role in risk management and performance expectations. Governance connects the boardroom’s strategic objectives with operational realities.
- Assure: Builds trust internally and externally. This capability enables internal audits, reviews, and performance monitoring. It closes the feedback loop between expected and actual results.
- Plan: Provides foresight. It allows organizations to allocate resources effectively, scenario-plan for crises, and align short-term actions with long-term goals.
- Design encourages systemic thinking. It integrates innovation, usability, and security into workflows, promoting functional and sustainable solutions.
- Change: Operationalizes adaptability. Whether it’s process reengineering or cultural transformation, the Change capability ensures disruptions are managed intentionally rather than reactively.
- Execute: Anchors delivery. It includes everything from service operations to customer support, ensuring the business meets its obligations and promises.
- Innovate: Embeds a learning culture. It encourages experimentation and celebrates curiosity as a strategic asset, enabling the organization to pivot when needed without losing focus.
Strategic Integration: From Overlay to Execution
A unique strength of the MVC Model is its overlay nature. It is not designed to replace existing frameworks or methods, like ITIL, COBIT, or ISO, but to integrate them into a coherent system that closes gaps between strategic goals and operational activities. This makes the MVC Model agnostic, allowing organizations to apply it atop their current systems while exposing performance and resilience gaps that otherwise go undetected.
By doing so, the model helps organizations:
- See and manage their whole system rather than just departmental fragments.
- Shift from a “create then protect” to a “create and protect” mode of operation.
- Understand and manage strategy-risk—the combination of value creation intent with risk-aware governance.
- Adopt adaptive working methods that are resilient to threats and aligned with opportunities.
Conclusion
The MVC Model is a cornerstone of the DVMS Institute’s approach to managing digital business risk. It provides a practical, systems-based approach for organizations to integrate strategic governance, operational assurance, adaptive planning, and innovation into a unified capability set. Far from being theoretical, it serves as a hands-on guide to achieving cyber operational resilience—not by merely deploying technical controls but by orchestrating the entire enterprise in pursuit of secure, sustainable value delivery. When applied rigorously, the MVC Model becomes more than just a model; it becomes a mindset.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
Digital Value Management System® (DVMS)
DVMS is a living management overlay system that governs digital value outcomes by ensuring operational resilience, performance assurance, and transparent accountability across complex digital ecosystems.
At its core, the DVMS is a simple but powerful integration of:
-
Governance Intent – shared expectations and accountabilities.
-
Operational Capability – how the business actually performs
-
Assurance Evidence – proof that outcomes are achieved and accountable
Rather than adding more complexity, a DVMS integrates Fragmented Frameworks and Practices such as NIST CSF, GRC, ITSM, DevOps, and AI into a unified overlay system that enables leaders and regulators to see, in real time, whether the digital business is working as intended—and whether the risks that matter most are being managed proactively.
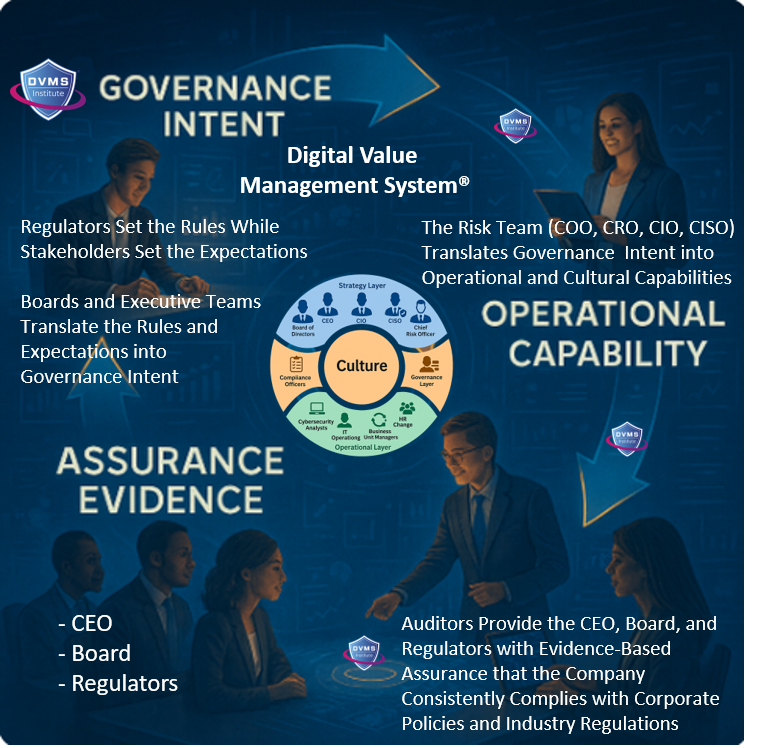
Through its MVC, CPD, 3D Knowledge, and FastTrack Models, a DVMS turns this integration into three distinctive capabilities:
A Governance Overlay that replaces fragmentation with unity. The DVMS provides organizations with a structured way to connect strategy with day-to-day execution. Leaders gain a consistent mechanism to direct, measure, and validate performance—across every system responsible for digital value.
A Behavioral Engine that drives high-trust, high-velocity decision-making. The DVMS embeds decision models and behavioral patterns that help teams think clearly and act confidently, even in uncertain situations. It is engineered to reduce friction, prevent blame-based cultures, and strengthen organizational reliability.
A Learning System that makes culture measurable, adaptable, and scalable. Culture becomes a managed asset—not an abstract concept. The DVMS provides a repeatable way to observe behavior, collect evidence, learn from outcomes, and evolve faster than threats, disruptions, or market shifts.
DVMS Organizational Benefits
Instead of replacing existing operational frameworks, the DVMS elevates them—connecting and contextualizing their data into actionable intelligence that validates performance and exposes the reasons behind unmet outcomes.
By adopting a DVMS, organizations are positioned to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Deliver Digital Value and Trust Across A Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
DVMS Leadership Benefits
The Digital Value Management System (DVMS) provides leaders with a unified, evidence-based approach to governing and enhancing their digital enterprise, aligning with regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
For the CEO, the DVMS provides a clear line of sight between digital operations, business performance, and strategic outcomes—turning governance and resilience into enablers of growth and innovation rather than cost centers.
For the Board of Directors, the DVMS provides ongoing assurance that the organization’s digital assets, operations, and ecosystem are governed, protected, and resilient—supported by evidence-based reporting that directly links operational integrity to enterprise value and stakeholder trust.
For the CIO, CRO, CISO, and Auditors: an integrated, adaptive, and culture-driven governance and assurance management system that enhances digital business performance, resilience, trust, and accountability
DVMS White Papers
The three whitepapers below present a coherent progression that shifts organizations from compliance-driven thinking to a modern system of Governance, Resilience, Assurance, and Accountability (GRAA). Collectively, the three papers define a comprehensive system for building and governing resilient digital enterprises, grounded in evidence rather than assumptions.
The Assurance Mandate Paper sets the stage by showing why traditional GRC artifacts provide only reassurance—not evidence—and calls boards to demand forward-looking proof that their organizations can continue to create, protect, and deliver value under stress.
The Assurance in Action Paper elevates the conversation from leadership intent to managerial execution, demonstrating how the DVMS operationalizes resilience by translating outcomes into Minimum Viable Capabilities, connecting frameworks through the Create–Protect–Deliver model, and generating measurable assurance evidence that managers can use to demonstrate real performance rather than activity.
The Governing by Assurance Paper elevates the approach to the policy and regulatory level, showing how DVMS functions as a learning overlay system that links governance intent, operational capability, and verifiable evidence into a continuous loop—enabling regulators, agencies, and enterprises to govern by outcomes rather than checklists and to prove capability with measurable, auditable performance data.
DVMS Cyber Resilience Certified Training Programs
DVMS Cyber Resilience Awareness Training
The DVMS Cyber Resilience Awareness course and its accompanying body of knowledge publication educate all employees on the fundamentals of digital business, its associated risks, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and their role within a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
This investment fosters a culture that is prepared to operate within a system capable of transforming systemic cyber risks into operational resilience.
DVMS NISTCSF Foundation Certification Training
The DVMS NISTCSF Foundation certification training course and its accompanying body of knowledge publications provide ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business professionals with a detailed understanding of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and its role in a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
This investment fosters IT, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business professionals with the skills to operate within a system capable of transforming systemic cyber risks into operational resilience.
DVMS Cyber Resilience Practitioner Certification Training
The DVMS Practitioner certification training course and its accompanying body of knowledge publications teach ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business practitioners how to elevate investments in ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and AI business systems by integrating them into a unified governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability system designed to proactively identify and mitigate the cyber risks that could disrupt operations, erode resilience, or diminish client trust.
This investment fosters IT, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business practitioners with the skills to assess, design, implement, operationalize, and continually innovate a Digital Value Management System® program that operationalizes a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
Company Brochures and Presentation
Explainer Videos
- DVMS Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- DVMS Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- DVMS Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- DVMS MVC ZX Model – Powers the CPD
- DVMS CPD Model – Powers DVMS Operations
- DVMS 3D Knowledge Model – Powers the DVMS Culture
- DVMS FastTrack Model – Enables A Phased DVMS Adoption
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved