Embedding CMMC Principles into the Structural and Cultural DNA of the Defense Industrial Base (DIB)
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) offers a groundbreaking approach that transforms how the Defense Industrial Base (DIB) perceives, implements, and sustains the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC).
Rather than positioning CMMC as a compliance burden or episodic requirement, the DVMS overlay system embeds CMMC principles into the structural and cultural DNA of DIB organizations. This transformation is achieved through systems thinking, continuous learning, governance integration, and a focus on protecting digital business value. By overlaying existing business operations with a holistic, risk-informed model, DVMS ensures that CMMC becomes not just a certification, but an essential, living component of organizational behavior and strategic execution.
CMMC a DIB Business Imperative
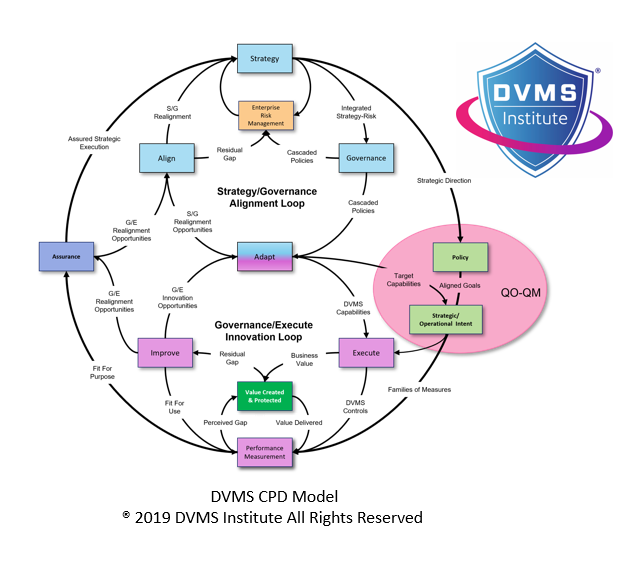
At the core of DVMS is a philosophy that cybersecurity is not merely a technical challenge but an enterprise-wide responsibility. This departure from conventional approaches is crucial to embedding CMMC into the DNA of the DIB. Traditionally, many organizations view CMMC as a standalone requirement, often relegated to IT departments. This fragmented view undermines the strategic significance of cybersecurity. DVMS shifts this perception by presenting cybersecurity as a dimension of value assurance—inseparable from value creation and delivery. The DVMS CPD Model (Create, Protect, and Deliver) captures this principle, illustrating how organizational resilience and digital value protection must happen concurrently, not sequentially. In this model, protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI)—the fundamental objective of CMMC—is no longer an isolated task but an intrinsic business imperative integrated into every operational layer.
CMMC – Central to The DIB Mission
The structure of the DVMS is anchored in seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs) within the Z-X Model: Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate. These capabilities offer a comprehensive scaffold for aligning organizational behavior with the principles underpinning CMMC. Governance and Assurance, in particular, are central to aligning strategic intent with cybersecurity practices. Governance ensures leadership ownership of CMMC obligations, embedding cybersecurity policy and accountability into the highest levels of the organization. Assurance provides the mechanisms to monitor, validate, and continuously improve compliance, ensuring that cybersecurity is not a once-a-year audit exercise, but a continuous organizational rhythm.
The concept of “strategy-risk” within the DVMS overlay system is especially critical for integrating CMMC into the DIB’s core operating model. Rather than treating strategy and risk as separate domains, strategy-risk combines them into a unified construct, acknowledging that all strategic objectives must be risk-informed. This approach is essential for DIB members because it aligns cybersecurity risk with broader mission outcomes. CMMC requirements become embedded in how organizations plan, execute, and govern their business. This alignment is reinforced through tools such as the Goal-Question-Metric (GQM) and Question Outcome–Question Metric (QO–QM) models, which help organizations derive measurable, contextual insights into their cybersecurity readiness. By connecting compliance outcomes directly to strategic objectives, these tools help ensure CMMC is no longer perceived as an external imposition but as an internal necessity.
CMMC Culture: The Force Multiplier
The DVMS Institute emphasizes the need to foster a security-conscious organizational culture. Culture, as DVMS literature repeatedly underscores, is a force multiplier—or inhibitor—of effective cybersecurity. Embedding CMMC into an organization’s DNA requires transforming culture from the top down and bottom up. Leaders must model risk-informed behavior and communicate the importance of protecting CUI as a shared responsibility. At the same time, staff at every level must understand how their daily actions relate to compliance and resilience. This is achieved through systemic cultural reinforcement mechanisms such as policy cascades, shared rituals and routines, and the use of visual symbols—all of which help engrain cybersecurity into the collective identity of the organization.
A particularly powerful enabler of embedding CMMC into the DIB’s DNA is the DVMS emphasis on continuous learning and adaptation through its application of systems thinking. Organizations are treated as complex adaptive systems (CAS), which evolve through the interactions between their structures, behaviors, and external environments. DVMS promotes the use of models such as the iceberg model and the 3D Knowledge Model to surface hidden patterns, feedback loops, and blind spots in cybersecurity practices. By visualizing and understanding these systemic dynamics, organizations can apply targeted leverage to shift culture, improve behavior, and ultimately institutionalize CMMC practices into daily operations. This results in a self-correcting, learning-centric organization that does not merely comply with CMMC but thrives through it.
CMMC Adoption and Adaption
The DVMS FastTrack™ approach facilitates practical implementation of CMMC-aligned capabilities across phases of organizational maturity. It provides a roadmap that begins with Phase 0 (Initiate) and progresses through Basic Hygiene, Expansion, and Innovation. These phases mirror the CMMC levels and provide a scalable, iterative model that supports organizations in stabilizing their environment, addressing gaps, and ultimately fostering continuous improvement. This phased approach ensures that even small organizations within the DIB can meaningfully begin their CMMC journey, and more importantly, sustain it. The FastTrack model eliminates the binary thinking of “certified or not” and instead emphasizes evolving capabilities in alignment with risk and mission priorities.
Conclusion
The DVMS provides the DIB with the mindset, structure, tools, and cultural integration necessary to make CMMC an organic, indispensable part of its operational DNA. Through systems thinking, strategic alignment, cultural transformation, and capability-based execution, the DVMS transforms CMMC from a compliance requirement into a dynamic capability. This capability enhances not only security and regulatory posture but also organizational performance, resilience, and mission assurance. In doing so, it empowers the DIB to not just meet the CMMC standard—but to embody it.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
The DVMS Institute’s NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System® certified training programs teach Internal or 3rd Party Digital Service Providers the skills to build a Holistic, Adaptive, and Culture-Powered Overlay System for Cyber Operational Resilience.
The NIST-CSF-DVMS positions cyber resilience not as a technical function but a strategic, enterprise-wide capability that mandates engagement from top Leadership to Frontline Employees, trained to proactively identify, classify, and mitigate the systemic cyber risks that impact cyber business operations.
Enabling organizational resilience requires a coordinated effort across an organization’s Strategy, Governance, and Operational business layers. When each layer is aligned and operating cohesively as an integrated system, service providers can proactively protect their cyber assets and ensure the continuity of cyber business operations.
This unique and innovative approach to Adaptive Governance, Resilience, and Assurance (GRA) also enables service providers to comply with any government-mandated cyber regulation (SEC, DORA, NIS2 etc.) or maturity model program (SCF, HITRUST, CMMC etc.).
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved