Operationalizing a Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) One Service at a Time
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction: Starting Small to Govern Big
Organizations often struggle to operationalize enterprise frameworks because they attempt to deploy them all at once. Digital Value Management Systems (DVMS) are no exception. While DVMS is designed to govern digital value across the enterprise, its successful adoption does not require a large-scale transformation on day one.
In fact, the most effective way to operationalize a DVMS is to start with a single, well-chosen service. By focusing on one service, organizations can validate concepts, demonstrate measurable value, establish accountability, and build confidence before scaling. This incremental approach turns DVMS from an abstract governance concept into a practical, working system.
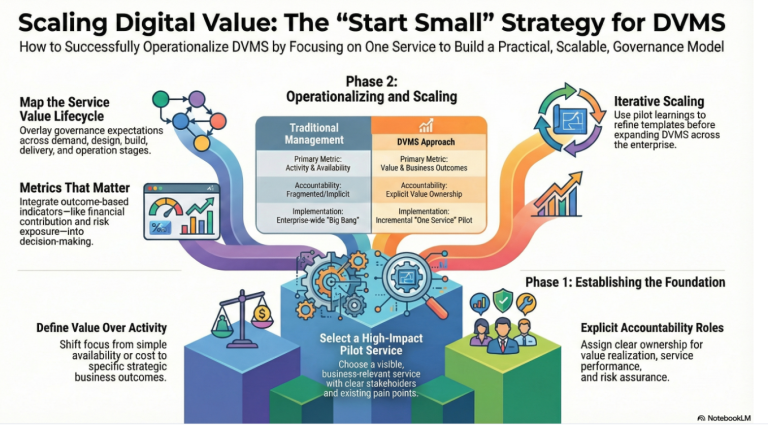
Selecting the Right Service as a DVMS Entry Point
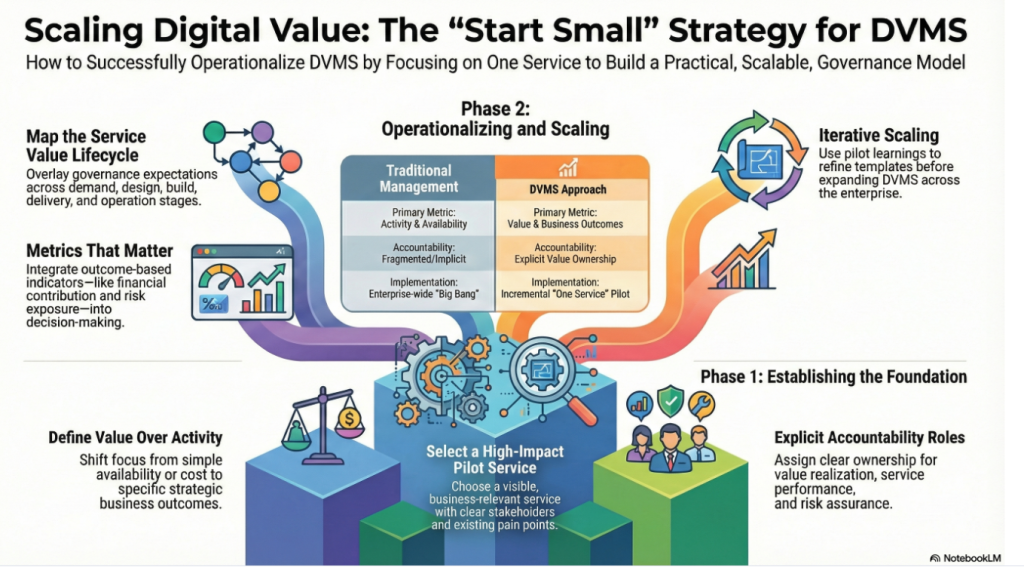
The first step in operationalizing DVMS is selecting the right service to pilot. The ideal service is business-relevant, visible, and meaningful, yet not so complex as to become unmanageable. It should have clear stakeholders, defined consumers, and measurable outcomes.
Services that support revenue generation, customer experience, regulatory compliance, or operational resilience are particularly effective starting points. Choosing a service that already has pain points or scrutiny can also accelerate adoption, as DVMS provides clarity and structure where ambiguity previously existed. The goal is not perfection, but relevance and learning.
Defining Digital Value at the Service Level
Once a service is selected, DVMS requires the organization to explicitly define what “value” means for that service. This is a critical shift away from traditional service management, which often focuses solely on activity, availability, or cost.
DVMS asks questions such as: What business outcomes does this service enable? How does it contribute to strategic objectives? What risks threaten its value? At this stage, value hypotheses are documented, benefits are articulated, and success criteria are agreed upon. This step anchors the service within the broader enterprise value context and ensures that all subsequent decisions are outcome-driven.
Assigning Ownership and Accountability
A defining characteristic of DVMS is accountability for value, not just delivery. Operationalizing DVMS through one service requires clearly assigning ownership roles. This includes a value owner responsible for benefits realization, a service owner accountable for performance, and risk and assurance responsibilities aligned with governance expectations.
These roles do not necessarily require new job titles; rather, they clarify accountability that often already exists but is implicit or fragmented. By making accountability explicit at the service level, DVMS creates transparency and eliminates ambiguity around who is responsible for outcomes.
Mapping the Service Value Lifecycle
With value defined and accountability established, the organization maps the service’s value lifecycle. This includes demand, design, build, delivery, operation, and improvement.
DVMS overlays governance expectations across this lifecycle, ensuring that value, risk, cost, and performance are considered at every stage. This mapping exercise reveals previously hidden gaps, redundancies, and misalignments. It also provides a structured view of how value is created, protected, and delivered through the service, making DVMS tangible and actionable.
Integrating Metrics That Matter
Operationalizing DVMS requires moving beyond traditional operational metrics to include value-based measures. For the selected service, the organization identifies a balanced set of indicators that cover outcomes, performance, risk, and assurance. These may include customer impact, financial contribution, service reliability, risk exposure, and compliance posture.
The key is alignment: every metric should connect back to the defined value objectives. By integrating these metrics into existing reporting and governance forums, DVMS becomes part of the decision-making process rather than an additional layer of bureaucracy.
Embedding Risk and Assurance Early
Starting with a single service enables organizations to embed risk management and assurance practices in a practical way. DVMS ensures that risks to value are identified, assessed, and monitored alongside performance. This includes operational risks, cybersecurity risks, third-party dependencies, and resilience concerns.
Assurance activities, such as controls validation and performance reviews, are aligned to value outcomes rather than checklist compliance. This approach demonstrates how DVMS proactively protects value, reinforcing trust among executives and stakeholders.
Enabling Decision-Making and Prioritization
As DVMS is operationalized through the service, it begins to inform real decisions. Investment requests, change approvals, and improvement initiatives are evaluated based on their impact on service value. Trade-offs between cost, risk, and performance become explicit rather than implicit. Leaders gain visibility into why certain decisions are made and how they support strategic objectives. This is often the moment when DVMS shifts from being perceived as a framework to being recognized as a decision-support system.
Learning, Improving, and Refining the Model
A single-service implementation provides a safe environment for learning. The organization can refine value definitions, governance workflows, metrics, and roles based on real experience. Feedback from stakeholders is used to improve clarity and usability.
DVMS is not treated as static; it evolves based on what works and what does not. This iterative approach builds organizational capability and confidence, ensuring that the system is practical and scalable.
Scaling DVMS Across the Organization
Once DVMS is operationalized successfully for one service, scaling becomes significantly easier. The patterns, templates, and governance mechanisms established during the pilot can be reused and adapted for additional services.
Leaders can point to tangible results, such as improved decision-making, clearer accountability, reduced risk exposure, or better value realization. Each new service added to the DVMS strengthens it, gradually transforming how the organization governs and delivers digital value without overwhelming teams.
Conclusion: One Service as the Catalyst for Enterprise Value Governance
Operationalizing a Digital Value Management System does not require an enterprise-wide overhaul. By starting with one service, organizations can bring DVMS to life in a controlled, meaningful way.
This approach allows value to be clearly defined, accountability to be established, risk to be managed, and performance to be assured. More importantly, it demonstrates that DVMS is not theoretical—it is operational. A single service becomes the catalyst for cultural change, governance maturity, and sustained digital value across the enterprise.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
DVMS Cyber Resilience Professional Accredited Certification Training
Enabling Enterprises to Govern, Assure, and Account for Digital Value, Operational Resilience, and Regulatory Outcomes in Living Digital Systems
Why Enterprises Must Move from Paper to Practice-Based Assurance
Explainer Video – Governing By Assurance
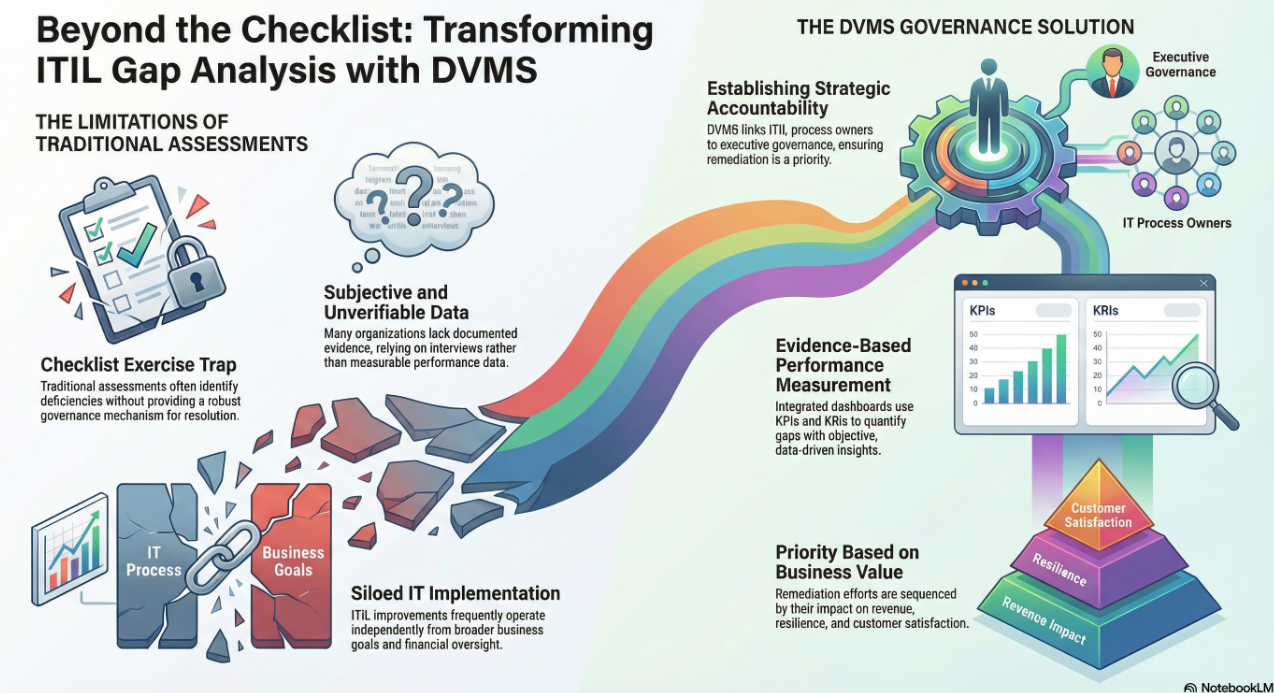
Despite an abundance of frameworks, metrics, and dashboards, many leaders still lack a clear line of sight into how their digital value streams perform when conditions deteriorate.
Strategic intent, organizational structures, and day-to-day behaviors are evaluated separately, producing static snapshots that fail to reveal how decisions, dependencies, and human actions interact within a dynamic digital system.
The result is governance that appears comprehensive in documentation yet proves fragile under pressure, leaving leaders to reconcile disconnected controls rather than systematically strengthen operational resilience.
What’s needed is a framework-agnostic operating overlay that enables digital value, operational resilience, and regulatory outcomes to be governed, assured, and accounted for coherently across living digital systems.
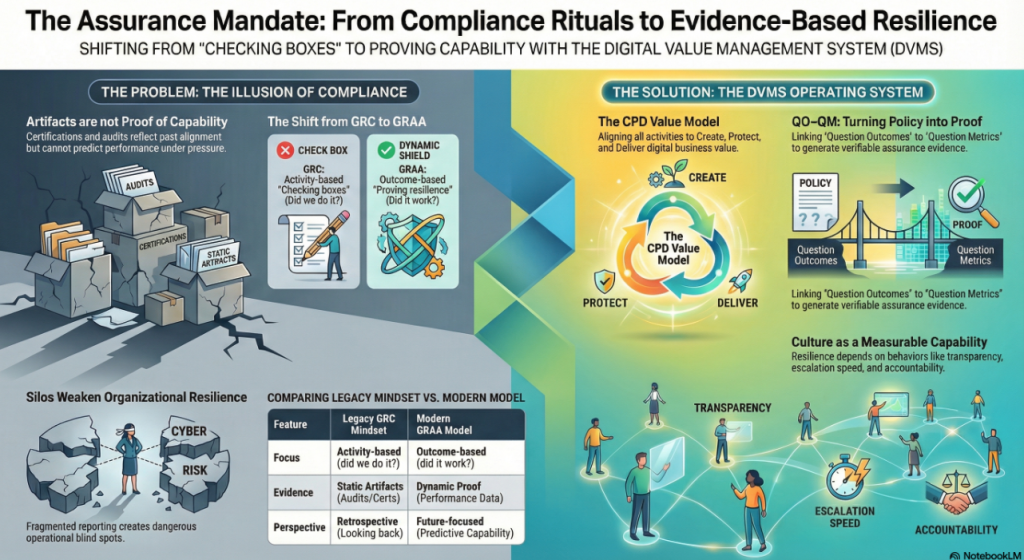
DVMS Institute White Papers – The Assurance Mandate Series
Explainer Video – From Compliance Rituals to Evidence-Based Resilience
The whitepapers below present a clear progression from compliance-driven thinking to a modern system of Governance, Resilience, Assurance, and Accountability (GRAA). Together, they define an evidence-based approach to building and governing resilient digital enterprises.
The Assurance Mandate Paper explains why traditional compliance artifacts offer reassurance, not proof, and challenges boards to demand evidence that value can be created, protected, and delivered under stress.
The Assurance in Action Paper shows how DVMS turns intent into execution by translating outcomes into Minimum Viable Capabilities, aligning frameworks through the Create–Protect–Deliver model, and producing measurable assurance evidence of real performance.
The Governing by Assurance Paper extends this model to policy and regulation, positioning DVMS as a learning overlay that links governance intent, operational capability, and auditable evidence—enabling outcome-based governance and proof of resilience through measurable performance data.
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS)
Explainer Video – What is a Digital Value Management System (DVMS)
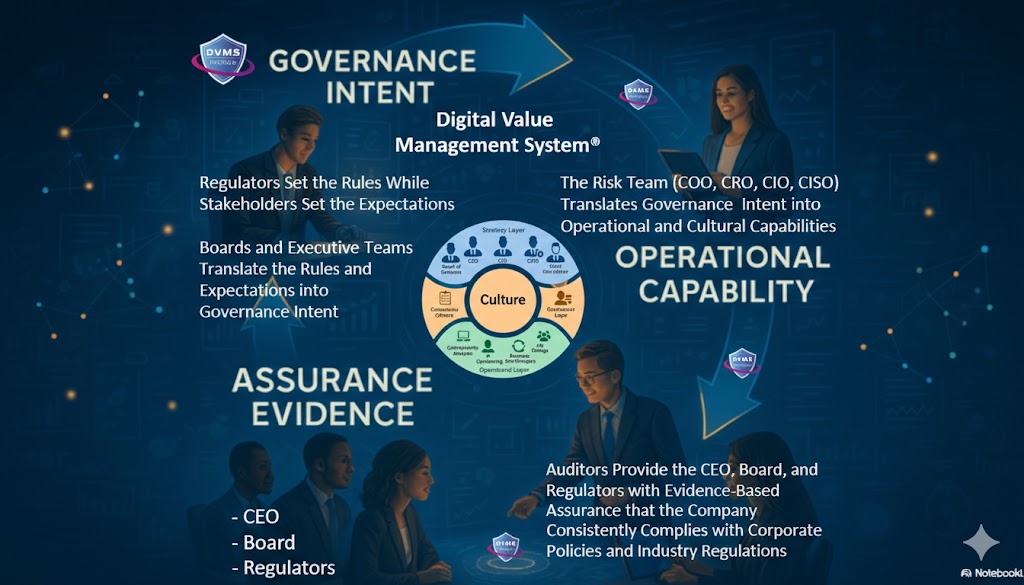
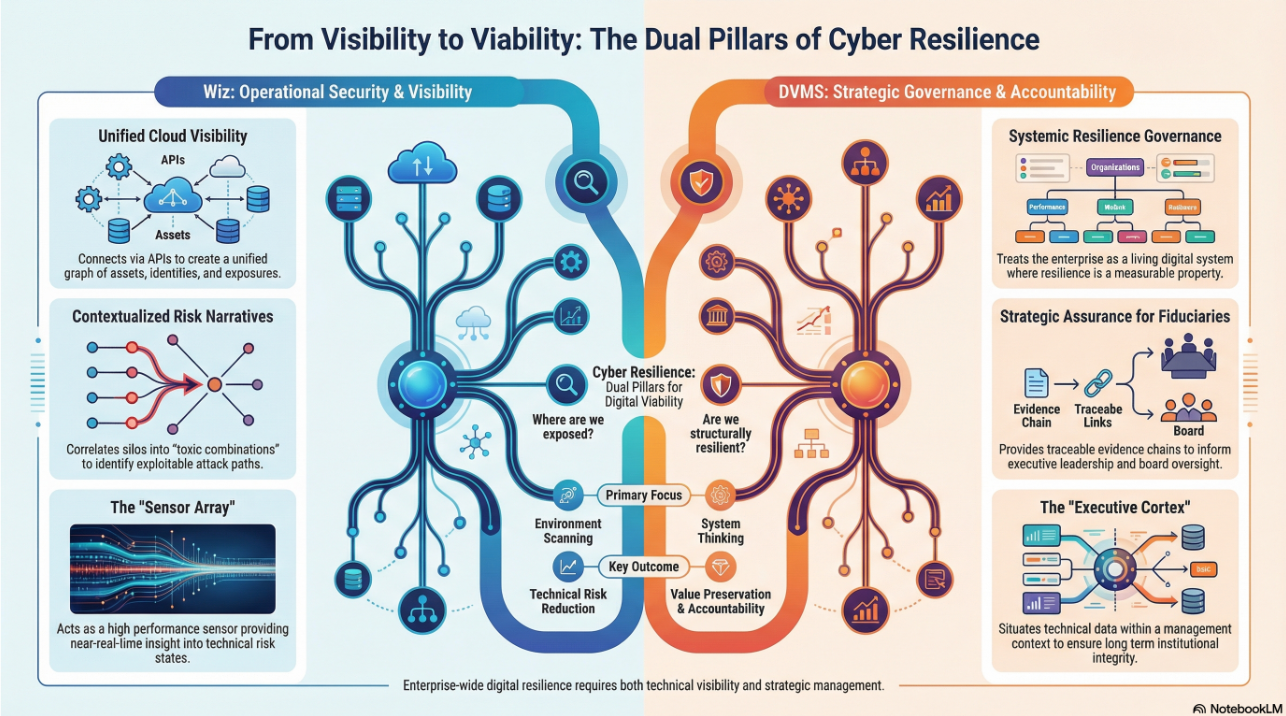
The DVMS is an overlay system that governs, assures, and accounts for digital value, operational resilience, and regulatory outcomes in living digital ecosystems.
At its core, the DVMS is a simple but powerful integration of:
- Governance Intent – shared expectations and accountabilities
- Operational Capabilities – how the digital business performs
- Assurance Evidence – proof that outcomes are achieved and accountable
- Cultural Learning – for governance intent and operational capability fine-tuning
Underpinning this integration are the following DVMS models and approaches:
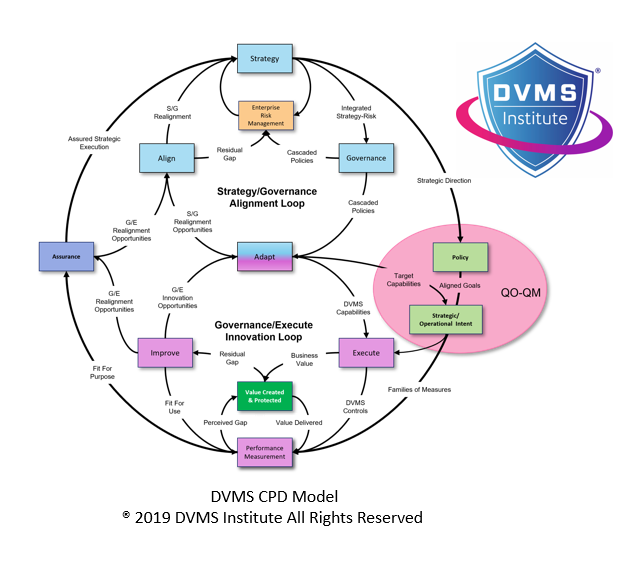
Create, Protect, and Deliver (CPD) – The CPD Model™ is a systems-based model within the DVMS that links strategy-risk and governance to execution to create, protect, and deliver digital business value as an integrated, continuously adaptive capability.
3D Knowledge (3DK) – The 3D Knowledge Model is a systems-thinking framework that maps team knowledge over time (past, present, future), cross-team collaboration, and alignment to strategic intent to ensure that organizational behavior, learning, and execution remain integrated and adaptive in delivering digital business value.
Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVC) – The Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs) model supports the seven essential, system-level organizational capabilities—Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate—required to reliably create, protect, and deliver digital business value in alignment with strategy-risk intent.
Question Outcome / Question Metric (QO/QM) – This approach supports governance as testable intent by defining a clear Question Outcome (QO), the specific value or resilience condition that must be true at a given boundary, and pairing it with one or more Question Metrics (QM) that provide observable, decision-relevant evidence that the system can actually create, protect, and deliver that outcome under complex, living system operating conditions
These models and approaches work together to enable three organizational capabilities:
A Governance Overlay that replaces fragmentation with unity. The DVMS provides organizations with a structured way to connect strategy with day-to-day execution. Leaders gain a consistent mechanism to direct, measure, and validate performance across every system responsible for digital value.
A Behavioral Engine that drives high-trust, high-velocity decision-making. The DVMS embeds decision models and behavioral patterns that help teams think clearly and act confidently, even in uncertain situations. It is engineered to reduce friction, prevent blame-based cultures, and strengthen organizational reliability.
A Learning System that makes culture measurable, adaptable, and scalable. Culture becomes a managed asset—not an abstract concept. The DVMS provides a repeatable way to observe behavior, collect evidence, learn from outcomes, and evolve faster than threats, disruptions, or market shifts.
DVMS Benefits – Organizational and Leadership
Explainer Video – DVMS Organization and Leadership Benefits
Instead of replacing existing operational frameworks and platforms, the DVMS elevates them, connecting and contextualizing their data into actionable intelligence that validates performance and exposes the reasons behind unmet outcomes.
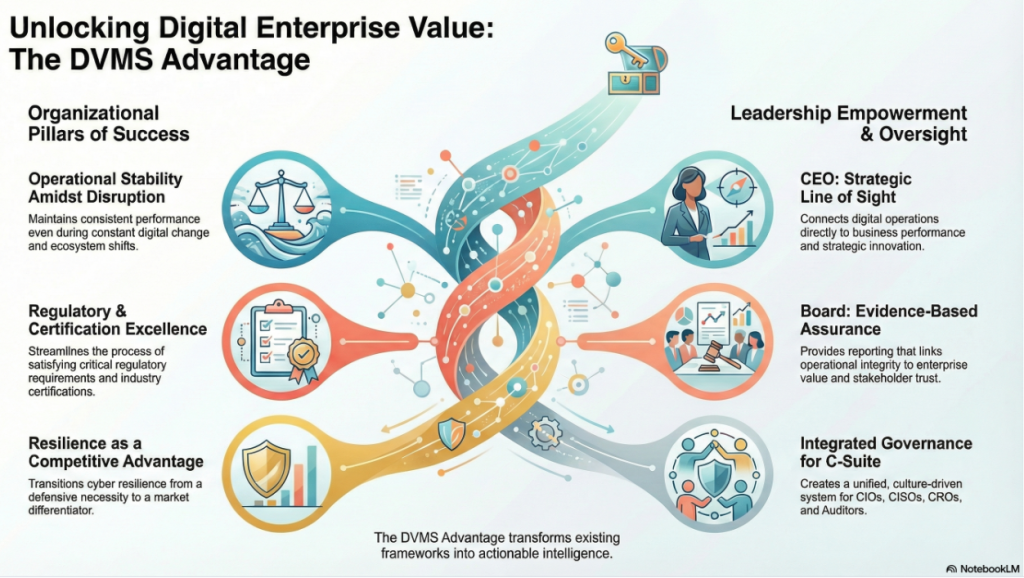
By adopting a DVMS, enterprises are positioned to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Deliver Digital Value and Trust Across A Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
The Digital Value Management System (DVMS) provides leaders with a unified, evidence-based approach to governing and enhancing their digital enterprise, aligning with regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
For the CEO, the DVMS provides a clear line of sight between digital operations, business performance, and strategic outcomes—turning governance and resilience into enablers of growth and innovation rather than cost centers.
For the Board of Directors, the DVMS provides ongoing assurance that the organization’s digital assets, operations, and ecosystem are governed, protected, and resilient—supported by evidence-based reporting that directly links operational integrity to enterprise value and stakeholder trust.
For the CIO, CRO, CISO, and Auditors, an integrated, adaptive, and culture-driven governance and assurance management system that enhances digital business performance, resilience, trust, and accountability.
DVMS – Accredited Certification Training Program
Explainer Video – The DVMS Training Pathway to Cyber Resilience
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) training programs teach leadership, practitioners, and employees how to integrate fragmented systems into a unified, culture-driven governance and assurance system that accounts for the resilience of digital value within a living digital ecosystem.
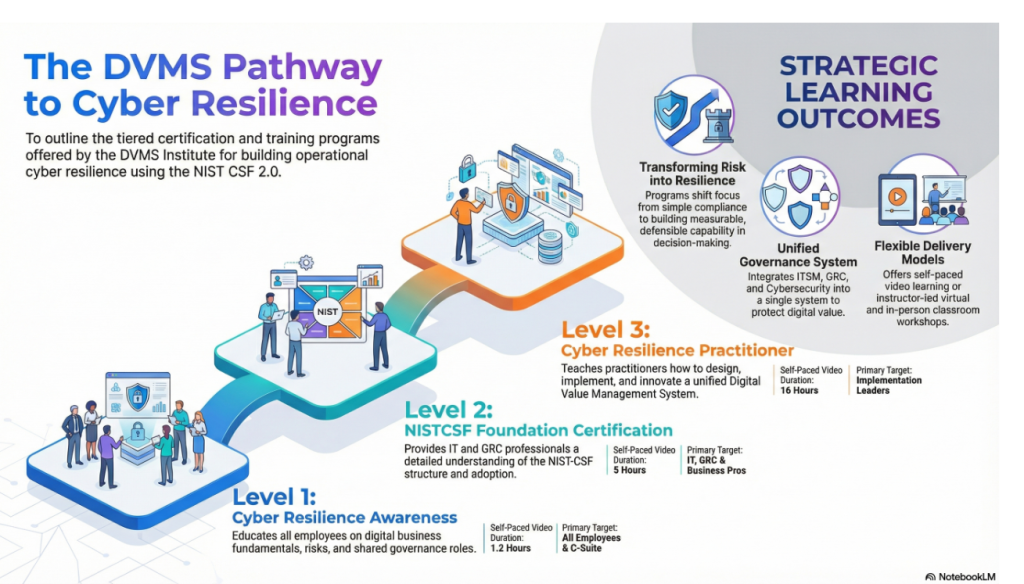
DVMS Cyber Resilience Awareness Training
The DVMS Cyber Resilience Awareness course and its accompanying body of knowledge publication educate all employees on the fundamentals of digital business, its associated risks, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and their role within a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
DVMS NISTCSF Cyber Resilience Foundation Certification Training
The DVMS NISTCSF Cyber Resilience Foundation certification training course and its accompanying body of knowledge publications provide ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business professionals with a detailed understanding of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and its role in a shared model of governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability for creating, protecting, and delivering digital value.
DVMS Cyber Resilience Practitioner Certification Training
The DVMS Practitioner certification training course and its accompanying body of knowledge publications teach ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and Business practitioners how to elevate investments in ITSM, GRC, Cybersecurity, and AI business systems by integrating them into a unified governance, resilience, assurance, and accountability system designed to proactively identify and mitigate the cyber risks that could disrupt operations, erode resilience, or diminish client trust.
A FastTrack Approach to Launching Your DVMS Program
Explainer Video – Scaling a DVMS Program
The DVMS FastTrack approach is a phased, iterative approach that helps organizations mature their DVMS over time, rather than trying to do everything simultaneously.
This approach breaks the DVMS journey into manageable phases of success. It all starts with selecting the first digital service you want to make cyber resilient. Once that service becomes resilient, it becomes the blueprint for operationalizing cyber resilience across the enterprise and its supply chain.
Company Brochures and Presentation
Explainer Videos
- DVMS Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- DVMS Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- DVMS Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- DVMS MVC ZX Model – Powers the CPD
- DVMS CPD Model – Powers DVMS Operations
- DVMS 3D Knowledge Model – Powers the DVMS Culture
- DVMS FastTrack Model – Enables A Phased DVMS Adoption
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved