How the DVMS Builds a Learning System that Measures, Adapts, and Innovates Over Time
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction: From Compliance to Continuous Learning
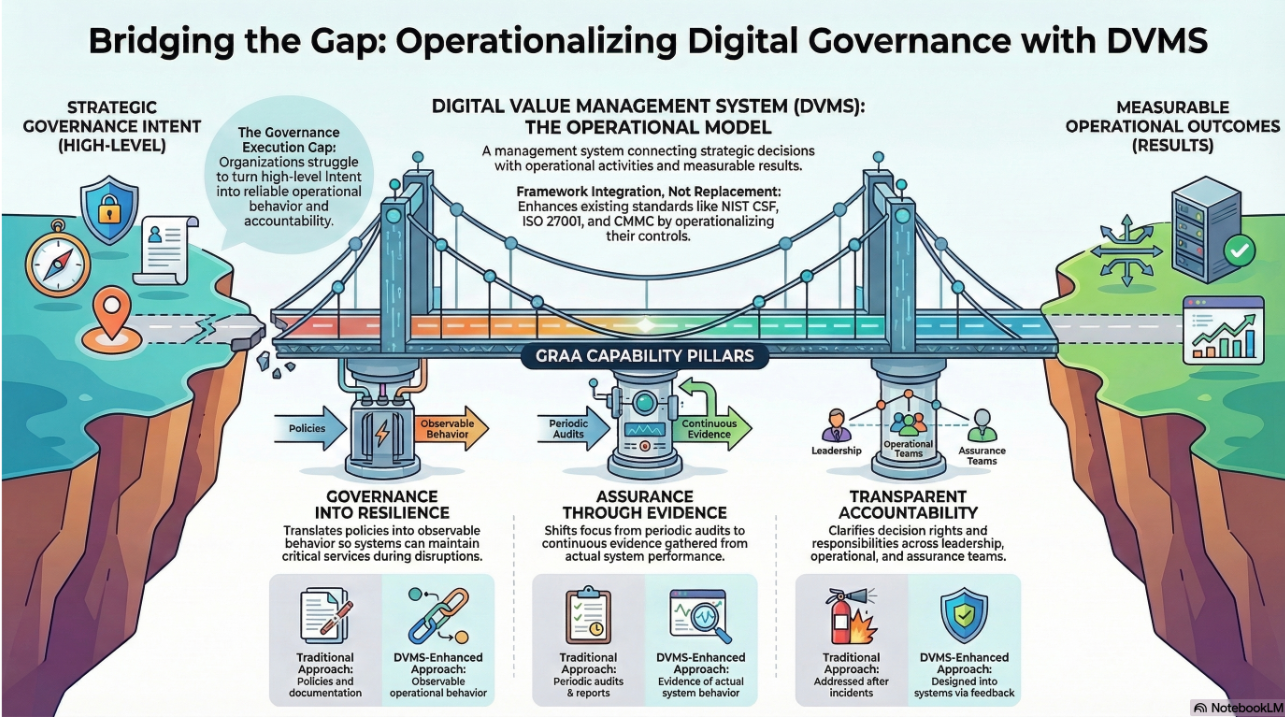
Modern organizations operate in environments defined by volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity (VUCA). Traditional governance and risk models, anchored in static compliance and periodic review, cannot keep pace with this rate of change. To thrive, organizations must evolve into learning systems that continuously measure, adapt, and innovate. The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS), developed by the DVMS Institute, provides such a mechanism. It transforms governance from a set of controls into a dynamic feedback system—a self-improving, culture-driven architecture capable of converting every action, failure, and discovery into knowledge that enhances performance and resilience.
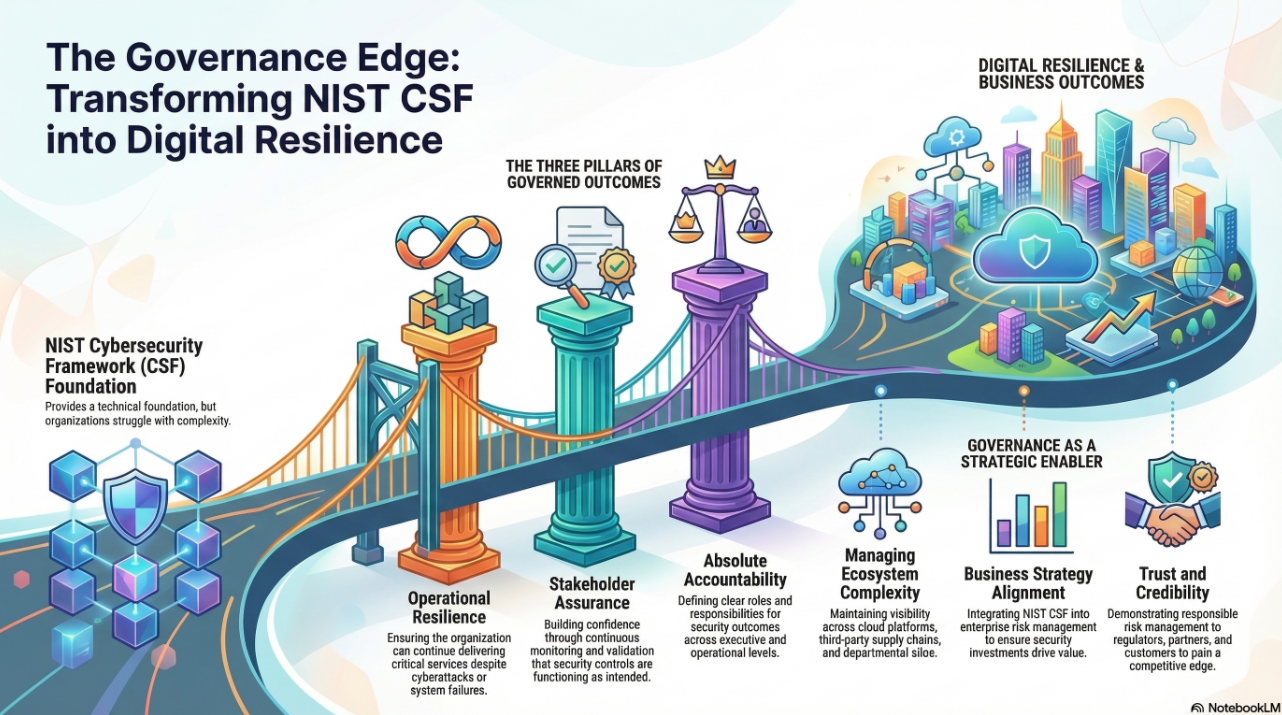
Drawing on the principles of systems thinking, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0, and the DVMS’s own Create–Protect–Deliver (CPD) and Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVC) models, this essay explores how the DVMS builds a learning system that measures, adapts, and innovates over time.
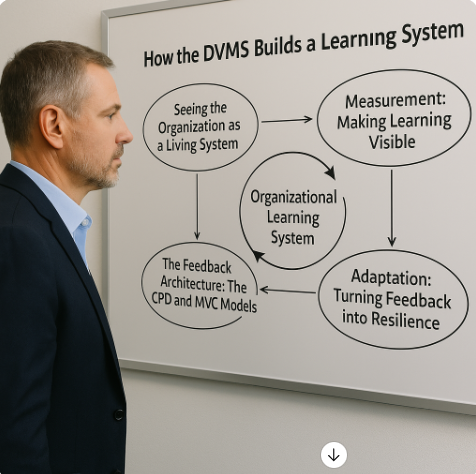
Seeing the Organization as a Living System
At its core, the DVMS begins with a profound shift in perspective: organizations are complex adaptive systems (CAS)—networks of interdependent human and technical elements that evolve through feedback and interaction. In such systems, cause and effect are nonlinear, and small changes can lead to significant, often unpredictable outcomes.
The DVMS recognizes that learning is the behavior that sustains equilibrium within this complexity. To “learn,” an organization must measure how its structures and behaviors interact, assess the effects of change, and use those insights to adapt future action. This understanding drives the DVMS architecture: rather than a fixed framework, it is an overlay system that sits atop the existing frameworks (e.g., NIST CSF, ISO 27001, COBIT, or ITIL), linking them into a continuous flow of feedback, measurement, and improvement.
This systems-based overlay reframes risk and governance not as isolated control functions but as dynamic, interconnected feedback loops—an essential characteristic of any proper learning system.
Measurement: Making Learning Visible
The first principle of the DVMS learning system is measurement—the ability to observe, quantify, and interpret performance over time. Measurement transforms abstract ideas, such as culture, assurance, and resilience, into actionable data that drives improvement.
The DVMS introduces structured measurement methodologies—particularly the Goal–Question–Metric (GQM) and Question-Outcome–Question-Metric (QO–QM) approaches—to help organizations ask the right questions, define meaningful goals, and build quantifiable evidence for decision-making.
These techniques are grounded in systems thinking, emphasizing that every measurement exists within a context and that metrics must connect strategic intent (goals) with observable behavior (outcomes). For example:
- Goal: Improve digital value protection.
- Question: How do teams verify that value is protected during development?
- Metric: Frequency and accuracy of concurrent assurance reviews within projects.
This closed-loop structure transforms passive measurement reporting into an active learning function. When combined with NIST’s Govern Function—which requires organizations to define, communicate, and monitor cybersecurity risk strategies—the DVMS creates a measurement ecosystem that spans from boardroom strategy to operational execution.
Measurement, therefore, is not just about counting incidents or compliance scores; it is about quantifying learning velocity—how quickly the organization detects variance, applies corrective action, and integrates new knowledge into its systems.
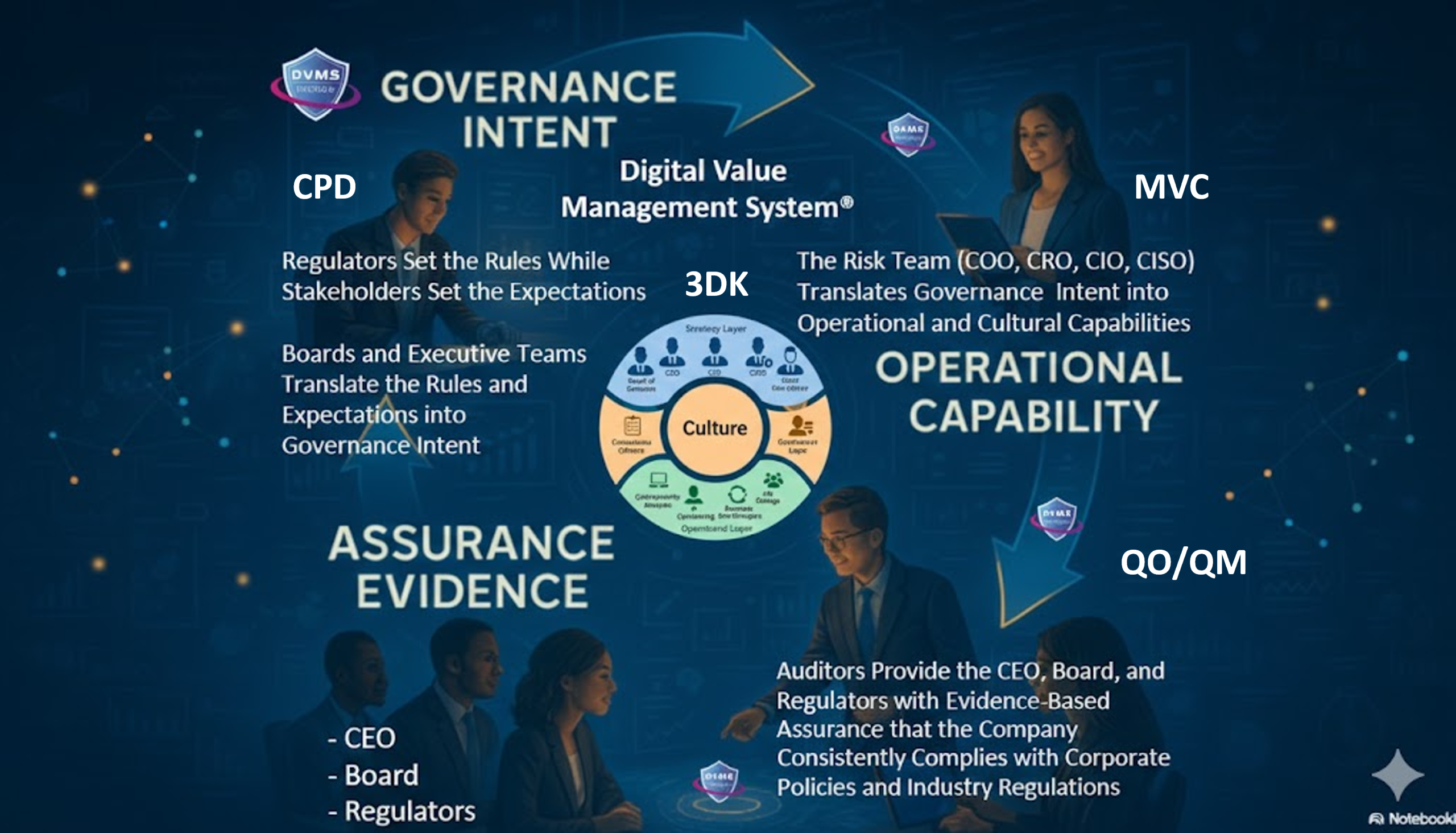
The Feedback Architecture: The CPD and MVC Models
To operationalize learning, the DVMS connects measurement to action through two complementary models: the Create–Protect–Deliver (CPD) Model and the Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVC) framework.
The CPD Model defines the flow of digital business value as a continuous loop where value is created, protected, and delivered concurrently, not sequentially. This structure transforms every cycle of activity into an opportunity for reflection and learning.
- Create focuses on design and planning—generating new value.
- Protect embeds assurance and measurement—verifying alignment with governance and risk appetite.
- Deliver completes the loop—executing, observing, and feeding insights back into the governance process.
The MVC Model—Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate—defines the minimum set of organizational capabilities necessary to sustain that loop. Each capability represents both a structural and behavioral component of learning:
- Govern sets direction and defines what success looks like.
- Assure measures performance and ensures alignment.
- Plan and Design to translate strategic learning into operational systems.
- Change and Execute turn learning into action.
- Innovate ensures the cycle never stops.
Together, the CPD and MVC form the feedback engine that allows the DVMS to measure behavior, adapt systems, and institutionalize innovation.
Adaptation: Turning Feedback into Resilience
A learning system’s true power lies in its ability to adapt—to modify behavior based on measurement. The DVMS achieves this through the integration of feedback at every level of the organization.
Drawing inspiration from Donella Meadows’s work on leverage points in systems, the DVMS applies change strategically rather than reactively. Adaptation is not about adding more controls but about changing the mental models that drive decisions. The DVMS employs techniques such as the Iceberg Model, which examines events, patterns, structures, and underlying beliefs, to help teams look beyond the surface of incidents and identify their root causes.
Adaptation is also embedded structurally through the FastTrack™ approach, which progresses through four iterative phases:
- Initiate – establish baseline governance and measurement systems.
- Basic Hygiene – stabilize and correct systemic weaknesses.
- Expand – scale adaptation to new domains and partners.
- Innovate – embed continuous improvement into culture and leadership.
At each phase, measurement informs action, and adaptation improves performance. As the organization navigates these cycles, it transitions from reactive problem-solving to proactive anticipation—what the DVMS refers to as learning to see differently.
This process aligns with the adaptive tier of the NIST CSF 2.0, where governance and risk management are continually improved through learning and integration.
Culture as the Catalyst for Learning
A system can only adapt if its culture supports inquiry, transparency, and psychological safety. The DVMS treats organizational culture not as an intangible variable but as a measurable component of system behavior.
Using the Cultural Web framework (symbols, power structures, rituals, and control systems), leaders can assess how values and assumptions shape organizational learning. Culture, in the DVMS model, functions as both a sensor and an actuator, detecting environmental signals (risk, disruption, and opportunity) and translating them into collective action.
Leadership plays a pivotal role. As the DVMS authors note, culture “cascades from the very top of the organization through every management layer to every person”. Leaders model the learning behaviors they expect from others—such as curiosity, humility, and accountability—turning culture into the human engine of adaptation.
By integrating cultural measurement into its assurance loops, the DVMS ensures that learning is not episodic but continuous and distributed—embedded in daily decisions and team interactions.
Innovation: The Regenerative Core of Learning
The DVMS defines innovation as the highest order of learning—where the organization not only adapts to change but generates it. Innovation in the DVMS framework is not confined to technology; it encompasses behavioral and structural innovation—new ways of working, governing, and collaborating.
The system recognizes four innovation types:
- Incremental (minor improvements),
- Sustaining (refining existing systems),
- Adaptive (changing policy or behavior), and
- Disruptive (strategic transformation).
These innovation levels correspond to different layers of learning maturity. The more frequently the organization measures and adapts, the faster it moves from incremental to disruptive innovation. This reflects a core principle of the NIST CSF: the journey from Risk-Informed to Adaptive tiers is one of progressive learning and refinement.
Through innovation, the DVMS ensures that the learning system regenerates rather than decays. Each feedback cycle strengthens the organization’s ability to create, protect, and deliver value under new conditions.
The DVMS as a Learning Ecosystem
Taken together, the DVMS forms a learning ecosystem—a network of governance, assurance, culture, and operations that measure, adapt, and innovate as one system of systems.
- Measurement provides visibility into behavior and performance.
- Adaptation transforms feedback into change.
- Innovation turns change into sustained advantage.
By aligning these forces through systems thinking and cultural engagement, the DVMS transforms organizations into learning entities that can evolve faster than their environments. It bridges the “knowing–doing gap” that plagues many governance models, ensuring that every metric feeds improvement, every adaptation informs policy, and every innovation reinforces purpose.
The result is a system that embodies the NIST CSF 2.0’s ideal of governance-driven resilience—an enterprise that learns continuously, not episodically, and treats uncertainty as a catalyst for growth rather than a constraint.
Conclusion: Learning as the Architecture of Resilience
The DVMS does not simply teach organizations to comply; it teaches them to learn. By embedding measurement into every process, connecting that data to adaptive feedback, and institutionalizing innovation, the DVMS builds a living, breathing learning system. It replaces rigid governance with dynamic assurance, transforms culture into a measurable asset, and converts risk into the raw material of resilience.
Over time, this system achieves what few organizations manage: a state of strategic self-awareness. The enterprise knows not only what it is doing but how well it is learning from what it does. That self-awareness—the ability to measure, adapt, and innovate—is the true definition of resilience in the digital age.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2026 All Rights Reserved