How a Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) Solves Your Cyber Resilience, Compliance, and Trust Problem
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction: The Challenge of Fragmentation
Organizations have invested heavily in Information Technology Service Management (ITSM), Governance, Risk, Compliance (GRC), and cybersecurity programs. While each is valuable, when pursued in isolation, these programs often result in duplication of effort, gaps in protection, and confusion around accountability. Siloed approaches are costly and can leave organizations vulnerable.
A Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) offers a transformative solution by uniting these programs into a cohesive, adaptive system. The DVMS overlays existing frameworks and methods, enabling them to work together as an integrated whole. This approach ensures resilient, compliant, and trusted digital business operations that continually adapt to today’s volatile threat and regulatory landscape.
From Compliance to Value Protection
Traditional cybersecurity and compliance programs are often reactive, focusing narrowly on passing audits or meeting regulatory demands. However, unprotected value has no value: a product, service, or process cannot deliver stakeholder trust if it is not secure and resilient.
The DVMS reframes ITSM, GRC, and cybersecurity as value protection disciplines. By embedding the principle that value creation and protection must occur concurrently, the DVMS turns fragmented controls into a holistic capability that preserves trust, reputation, and operational stability. Compliance becomes an outcome of doing the right things right, rather than the sole objective.
The Overlay Concept: Making Investments Work Together
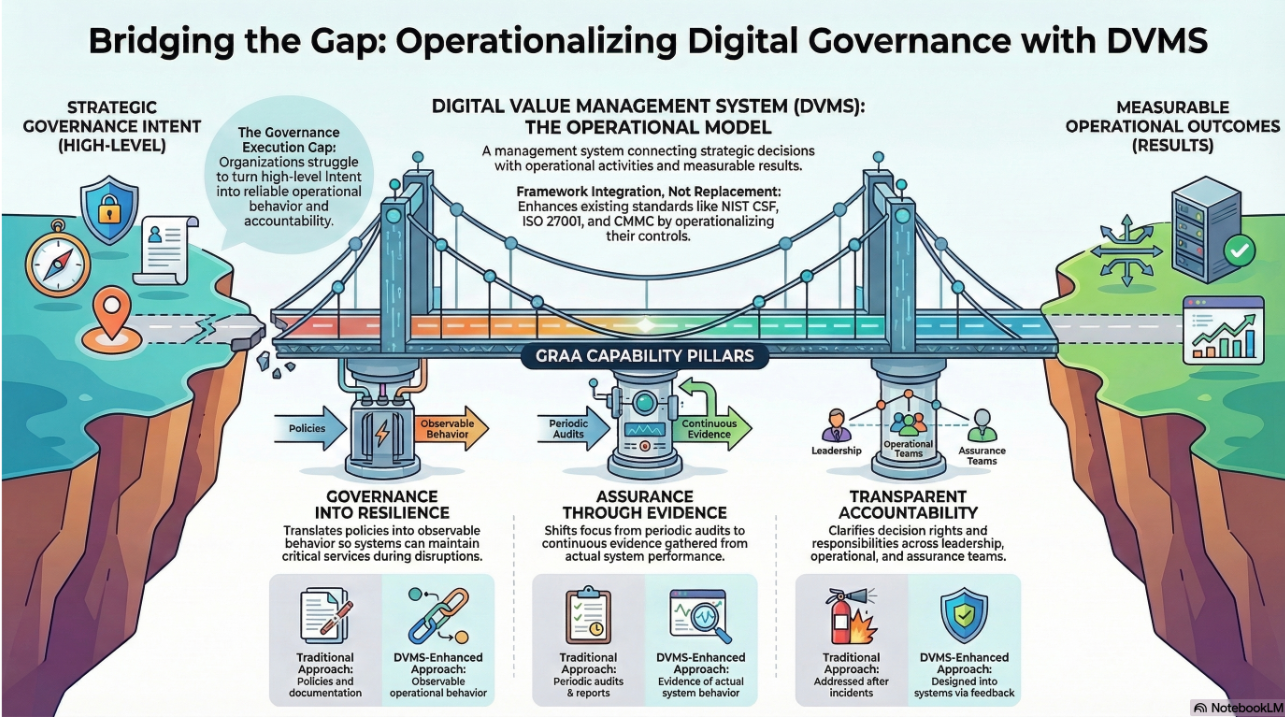
The DVMS is not a new framework to replace existing systems but an overlay that integrates them. This distinction is crucial. ITSM ensures reliable services, GRC aligns business processes with regulations, and cybersecurity safeguards assets from threats. Yet without an overlay, organizations struggle with misaligned priorities and conflicting practices. The DVMS harmonizes these investments by mapping them onto its seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate). These capabilities provide a single organizing lens, ensuring that ITSM processes, GRC requirements, and cybersecurity controls reinforce rather than contradict one another.
Driving Resilience Through Systems Thinking
Modern enterprises are complex adaptive systems. Risks and outcomes are interconnected, and changes in one area often have unintended consequences elsewhere. The DVMS applies systems thinking, helping leaders see “the whole, not the hole”. By treating ITSM, GRC, and cybersecurity as interdependent subsystems of digital value, the DVMS enables proactive governance and risk management. This approach prevents organizations from chasing isolated fixes and promotes resilience as a continuous, organization-wide capability. In practice, incident response, regulatory reporting, and service continuity are not separate workflows but integrated expressions of the same resilient system.
Alignment with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
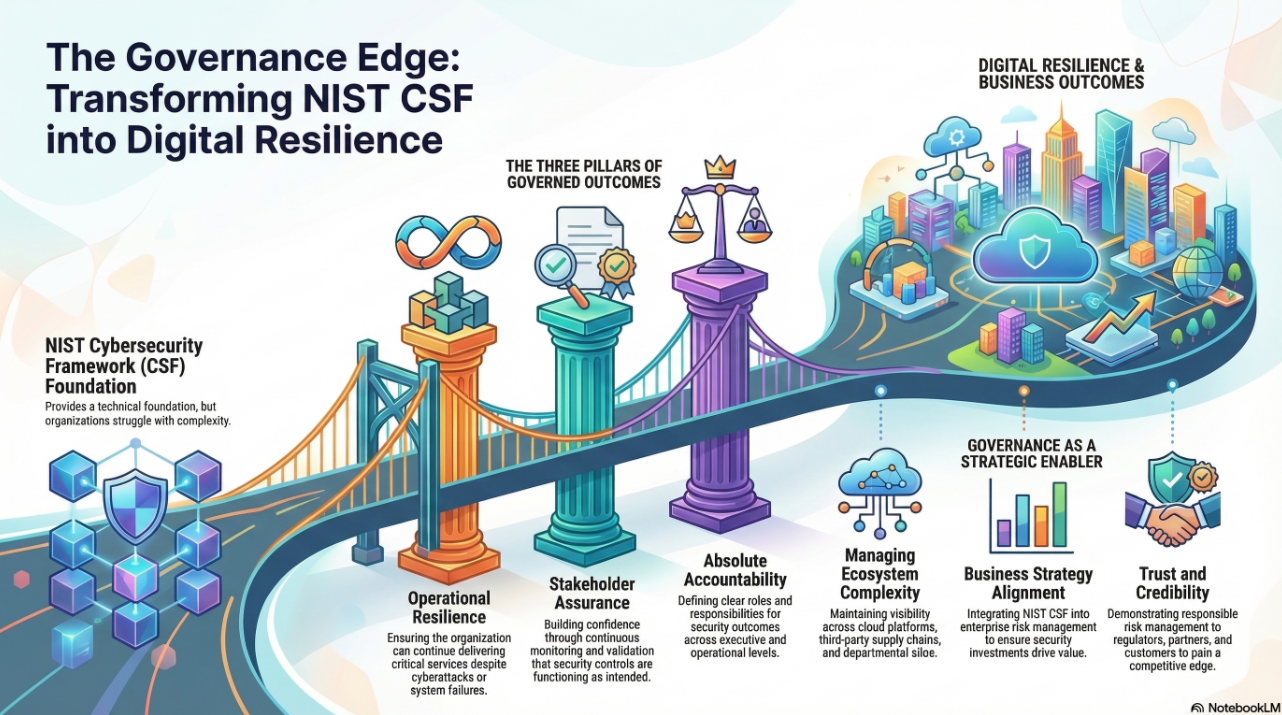
The DVMS aligns naturally with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0, which emphasizes governance, adaptability, and outcomes. NIST CSF’s six Functions—Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—mirror the DVMS model. For example, the DVMS “Govern” and “Assure” capabilities correspond to CSF’s GOVERN and IDENTIFY Functions, ensuring strategic intent cascades into risk-informed actions. Meanwhile, “Execute” and “Recover” align with PROTECT and RESPOND, delivering operational resilience. Organizations can use the DVMS as an overlay to translate NIST CSF outcomes into day-to-day business practices, turning frameworks into lived resilience.
Strengthening Culture and Accountability
A common weakness of ITSM, GRC, and cybersecurity initiatives is their focus on process at the expense of culture. Tools and policies cannot succeed without accountable leadership and risk-aware employees. The DVMS emphasizes culture as both a source of risk and a lever of resilience. Its models encourage boards and executives to treat cybersecurity as an enterprise risk issue, not a technical one. At the same time, the DVMS fosters a learning organization where teams continually adapt, innovate, and embed security-conscious behavior into everyday operations. This cultural integration transforms compliance from a checklist into a natural expression of organizational values.
The CPD Model: Creating, Protecting, and Delivering Value
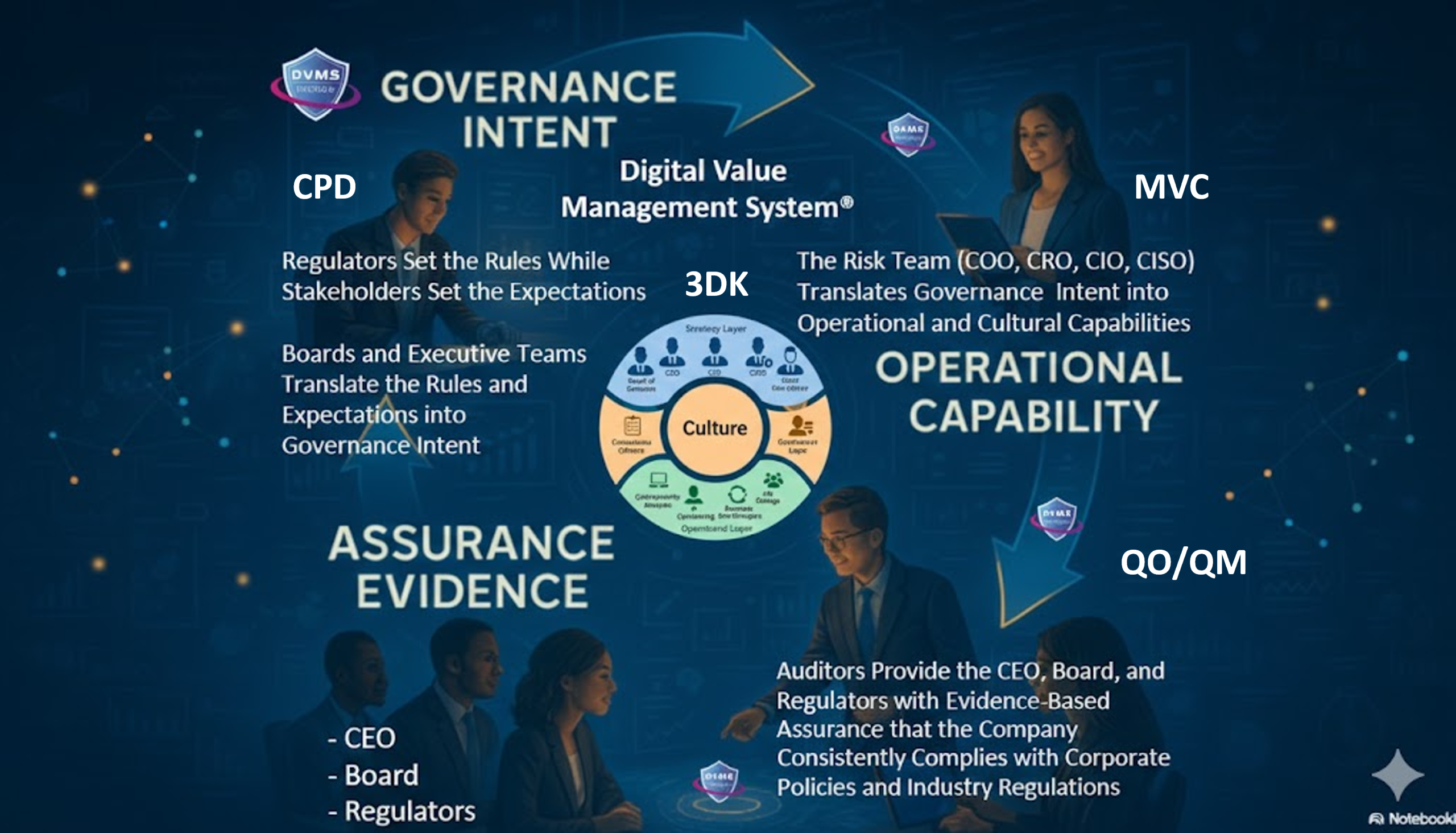
At the heart of the DVMS is the CPD (Create, Protect, Deliver) Model, which operationalizes the principle that unprotected value is worthless. ITSM primarily supports the creation and delivery of services, GRC ensures delivery meets obligations, and cybersecurity protects assets from compromise. The CPD Model weaves these strands together, ensuring that creation, protection, and delivery are not sequential activities but concurrent ones. For example, when an IT service is designed, resilience and compliance are built in from the outset, rather than bolted on afterward. This integration eliminates costly rework and enhances stakeholder confidence.
The 3D Knowledge Model: Making Expertise Actionable
Even with strong processes and controls, organizations often struggle with fragmented knowledge. The DVMS incorporates a 3D Knowledge Model that aligns team knowledge (past, present, future), collaboration across functions, and strategic alignment with enterprise goals. This model ensures that ITSM, GRC, and cybersecurity expertise do not remain in silos but flow across the enterprise. The result is a shared understanding of digital risks and opportunities, enabling faster, better decisions. For instance, a compliance team’s insights into regulatory changes can immediately inform ITSM design choices and cybersecurity risk assessments.
Assurance and Continuous Improvement
A key promise of the DVMS is auditable assurance. By uniting ITSM, GRC, and cybersecurity under one system, the DVMS provides a transparent evidence trail of how resilience, compliance, and trust are achieved. This makes audits more efficient while reducing costs associated with redundant reporting. Beyond audits, the DVMS emphasizes continual improvement. Through its FastTrack™ approach, organizations stabilize their environment, expand capabilities, and embed innovation into their DNA. This ensures ITSM, GRC, and cybersecurity investments continue to deliver value in the face of evolving technologies, threats, and regulations.
Realizing Trusted Digital Operations
Trust is the currency of the digital economy. Customers, partners, and regulators demand assurance that organizations can protect data, maintain service continuity, and comply with obligations. A DVMS enables this by turning ITSM, GRC, and cybersecurity into a single trust-building system. Instead of separate initiatives competing for budget and attention, the DVMS ensures every investment contributes to the same outcome: resilient, compliant, and trusted operations. This trust protects reputation and enables growth, as organizations with stronger resilience and compliance capabilities gain a competitive advantage.
Conclusion: A Strategic Imperative
Organizations cannot afford fragmented approaches to digital risk in today’s environment of expanding attack surfaces, rising regulatory expectations, and complex supply chains. A Digital Value Management System® maximizes ITSM, GRC, and cybersecurity investments by uniting them into a cohesive, adaptive overlay system. By aligning with NIST CSF outcomes, applying systems thinking, embedding cultural resilience, and operationalizing value protection through the CPD and 3D Knowledge Models, the DVMS delivers on the promise of resilient, compliant, and trusted digital business operations. Far from being an optional enhancement, the DVMS is a strategic imperative for any organization seeking to thrive on the edge of digital chaos.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
Traditional best-practice approaches to IT Service Management (ITSM), Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC), and Cybersecurity are insufficient to manage the resilience, compliance, and trust requirements of today’s complex digital ecosystems.
The DVMS Institute Certified Training programs and publications provide detailed guidance on evolving any best-practice program into an integrated, adaptive, and culture-driven Digital Value Management Governance and Assurance System® (DVMS) capable of ensuring resilient, compliant, and trusted digital business outcomes.
For ITSM
The DVMS elevates ITSM from a process-aligned service-delivery program into an integrated, adaptive, and culture-driven governance and assurance overlay system, ensuring the delivery of high-performance and resilient digital business outcomes.
For GRC
The DVMS elevates GRC from a compliance checklist activity to an integrated, adaptive, and culture-driven governance and assurance overlay system, ensuring the resilient, compliant, and trusted digital business outcomes regulators expect.
For Cybersecurity
The DVMS elevates a cybersecurity program from a control-centric defense approach into an integrated, adaptive, and culture-driven governance and assurance overlay system, transforming systemic cyber risk into compliant and trusted operational resilience.
By adopting a DVMS, organizations are positioned to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Deliver Digital Value and Trust Across A Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage

DVMS Explainer Videos
- Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- MVC ZX Model – Powers the CPD
- CPD Model – Powers DVMS Operations
- 3D Knowledge Model – Powers the DVMS Culture
- FastTrack Model – Enables A Phased DVMS Adoption
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved