Using a DVMS® to Operationalize and Measure Digital Business Governance, Resilience, and Assurance Success
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction
In today’s complex digital ecosystems, organizations face increasing pressure to demonstrate that they are secure and that their digital business programs create measurable value. Traditional IT and security metrics often focus narrowly on technical outputs—patching rates, intrusion attempts, or compliance scores. While important, these measures rarely capture the broader business impact of digital business efforts. A Digital Value Management System (DVMS) offers a more holistic approach, aligning digital business with governance, resilience, and assurance. To fully leverage the DVMS, organizations must adopt new ways of measuring digital business success that reflect cultural change, strategic alignment, operational resilience, and value delivery.
Digital business in the DVMS Context
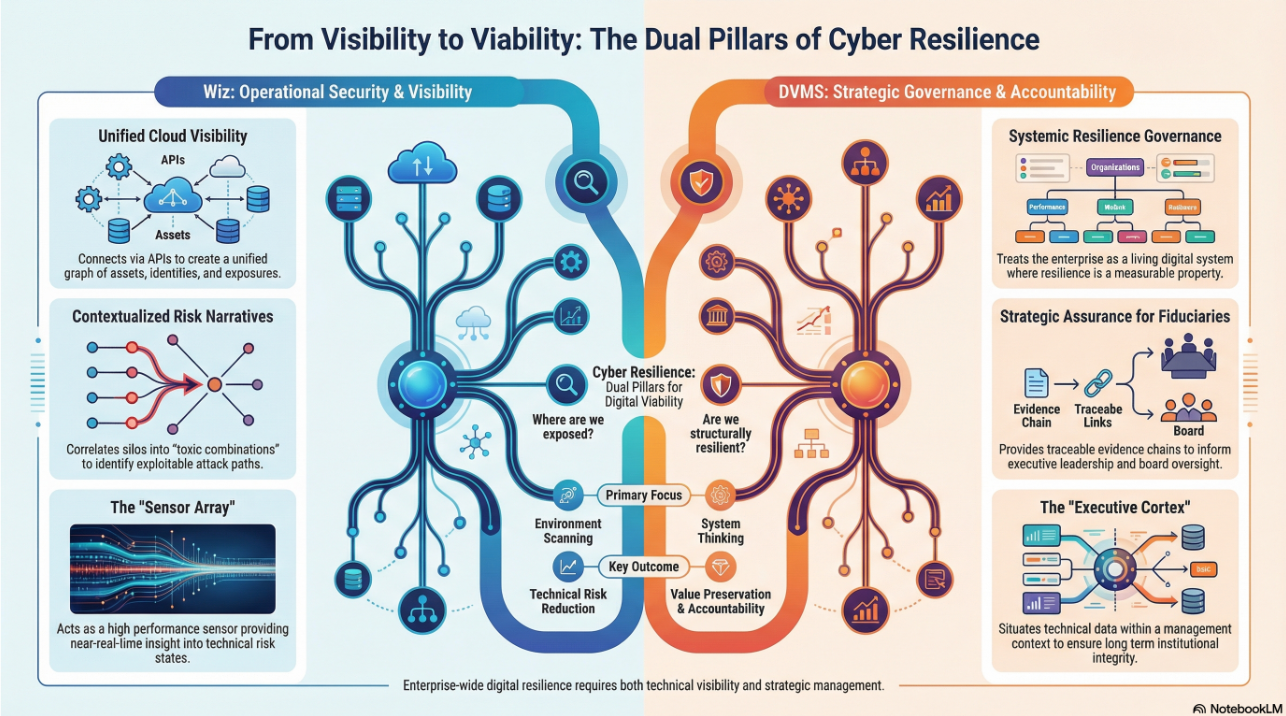
The DVMS operating system is built to unify governance, operational resilience, and assurance in digital enterprises. Unlike traditional siloed approaches, DVMS integrates digital business into a culture-driven system that links digital investments to value creation and protection. In this model, digital business is not an isolated function but an enabler of trust, adaptability, and sustainable performance. Measuring success, therefore, cannot rely solely on technical indicators. Instead, success is judged by how well the digital business supports digital value realization, maintains stakeholder confidence, and strengthens adaptive governance.
Shifting from Compliance to Value
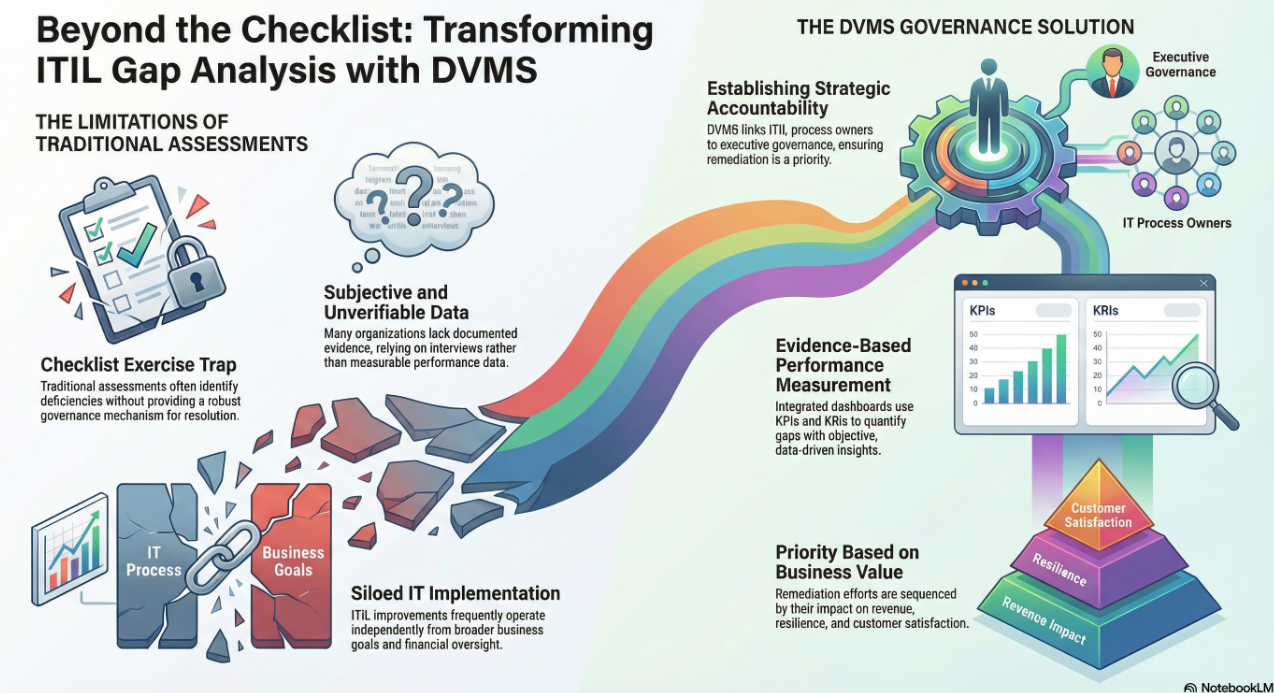
A key role of the DVMS is to move organizations beyond a compliance mindset. Traditional programs often measure success by regulatory alignment or audit results. While compliance remains essential, a DVMS-driven approach focuses on how digital business safeguards digital value and supports strategic objectives. For example, instead of merely reporting compliance with a data protection standard, a DVMS organization might measure how adequate those controls are in maintaining customer trust, reducing downtime, or accelerating recovery after incidents. This shift reframes digital business as a strategic enabler of value rather than a cost of doing business.
Core Dimensions of Digital Business Success in DVMS
Digital business success within a DVMS can be understood across several interconnected dimensions:
- Adaptive Governance – Success is measured by how well digital business decision-making is integrated into business governance, ensuring investments and risks are evaluated in value.
- Operational Resilience – Digital business outcomes are assessed by the ability to withstand, respond to, and recover from cyber disruptions with minimal impact on critical operations.
- Embedded Assurance – Assurance is measured by the degree to which confidence in digital operations is built into processes, reducing the need for after-the-fact verification.
- Cultural Integration—Success is also cultural, as measured by how deeply digital business practices are embedded into daily operations and embraced by employees as part of value delivery.
Metrics for Adaptive Governance
Measuring governance requires evaluating how digital business is incorporated into strategic decision-making. Key indicators include:
- Alignment of digital business investments with business outcomes, tracked by mapping spending to value at risk or value gained.
- Board-level engagement, measured by the frequency and quality of digital business discussions at executive and governance forums.
- Risk-informed decision-making, demonstrated by evidence that digital business risks are considered in portfolio management and digital initiatives.
By embedding digital business into governance, organizations ensure that it is not seen as an isolated IT issue but as a driver of strategic confidence.
Metrics for Operational Resilience
Operational resilience is a cornerstone of DVMS-driven digital business. Success here is measured less by the absence of incidents and more by the ability to continue delivering value despite them. Useful measures include:
- Mean time to detect (MTTD) and respond (MTTR) for cyber incidents.
- System availability and uptime of critical services, even during attacks or outages.
- Business continuity test outcomes, showing how well digital services can be restored within acceptable recovery objectives.
- Resilience exercises and simulations, with lessons learned tracked and improvements implemented.
These measures ensure that resilience is treated as an ongoing capability rather than a one-time benchmark.
Metrics for Embedded Assurance
In a DVMS, assurance is not an external audit function but a built-in quality of digital operations. Success in assurance can be measured by:
- Continuous control monitoring, tracking real-time compliance with critical security requirements.
- Reduction in audit findings or exceptions, showing that assurance is embedded, not reactive.
- Third-party trust indicators include independent certifications, customer confidence scores, or reduced contractual penalties.
By embedding assurance, organizations gain confidence in their digital operations without relying solely on external validation.
Cultural Indicators of Digital Business Success
Perhaps the most distinctive aspect of DVMS is the role of culture in driving sustained success. Cultural metrics may include:
- Employee engagement in digital business programs, measured through participation rates in training, simulations, and awareness campaigns.
- Behavioral compliance, such as reductions in phishing click rates or policy violations.
- Cross-functional collaboration, evidenced by joint ownership of digital business goals across IT, business, and governance teams.
Culture ensures digital business becomes part of “how things are done,” making it resilient to leadership changes, new threats, or shifting regulations.
Linking Digital Business Metrics to Business Value
The ultimate measure of success in a DVMS is the degree to which digital business contributes to value creation and protection. Key value-based measures include:
- Reduced financial losses from cyber incidents relative to peers or industry averages.
- Improved customer trust and retention, measured through satisfaction surveys or net promoter scores linked to security confidence.
- Faster innovation adoption, with digital business embedded into DevSecOps pipelines to reduce delays in bringing new products to market.
- Market and regulatory recognition, with digital business strength enhancing brand reputation and compliance positioning.
This linkage ensures that digital business metrics are not isolated but directly tied to business outcomes.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptive Measurement
A DVMS emphasizes adaptability, meaning that digital business success is never static. Measurement must evolve as threats, technologies, and business objectives change. Organizations should adopt feedback loops where metrics drive continuous improvement—feeding lessons learned into governance, resilience planning, and cultural development. This adaptive approach ensures that measures remain relevant and actionable, avoiding the trap of measuring what is easy instead of what matters.
Conclusion
Measuring digital business success in a DVMS requires a shift from narrow technical metrics to comprehensive indicators that span governance, resilience, assurance, culture, and business value. By reframing success in digital value delivery, organizations transform digital business from a compliance exercise into a strategic enabler of trust and resilience. In a world where digital ecosystems are increasingly complex and fragile, this approach strengthens security and embeds it as an integral part of sustainable business performance. The result is an organization that can anticipate, withstand, recover, and adapt to survive and thrive in the digital age.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
DVMS Institute®
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NISTCSF) Cyber Resilience Certified Training Solutions
The DVMS Institute assists organizations in operationalizing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NISTCSF) or any best practice framework (ITSM, GRC, ISO, etc.) by utilizing a Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) to transform it from a static compliance reference framework into a culture-driven adaptive overlay system of Governance, Resilience, and Assurance.
The Institute’s Accredited Publications and Certified Training Courses offer a structured pathway for mastering the integration of governance intent, operational execution, and assurance evidence, enabling organizations to demonstrate measurable resilience, regulatory alignment, and stakeholder confidence in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.

Digital Value Management System® (DVMS)
A Digital Value Management System (DVMS) transforms systemic cyber risk into operational resilience by uniting Fragmented Frameworks and Standards, such as NIST, ITSM, GRC, and ISO, into a holistic, adaptive, and culture-driven Governance, Resilience, and Assurance (GRA) overlay system that keeps your digital business running, no matter the disruption.
The DVMS doesn’t replace existing frameworks—it connects, contextualizes, and amplifies them, transforming compliance requirements into actionable intelligence that drives and ensures sustained digital operations and performance.
By adopting a DVMS, organizations are positioned to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Deliver Digital Value and Trust Across A Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
For the CEO, the DVMS provides a clear line of sight between digital operations, business performance, and strategic outcomes—turning governance and resilience into enablers of growth and innovation rather than cost centers.
For the Board of Directors, the DVMS provides ongoing assurance that the organization’s digital assets, operations, and ecosystem are governed, protected, and resilient—supported by evidence-based reporting that directly links operational integrity to enterprise value and stakeholder trust.
For the CIO, the DVMS provides a structured way to align technology investments and operations with measurable business outcomes.
For the CRO, the DVMS provides a way to embed risk and resilience directly into operational processes, turning risk management into a driver of performance and adaptability.
For the CISO, the DVMS provides a continuous assurance mechanism that demonstrates cyber resilience and digital trust across the enterprise and its supply chain.
For Internal and External Auditors, the DVMS provides verifiable proof that the enterprise can maintain operational continuity under stress.
DVMS Explainer Videos
- Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- MVC ZX Model – Powers the CPD
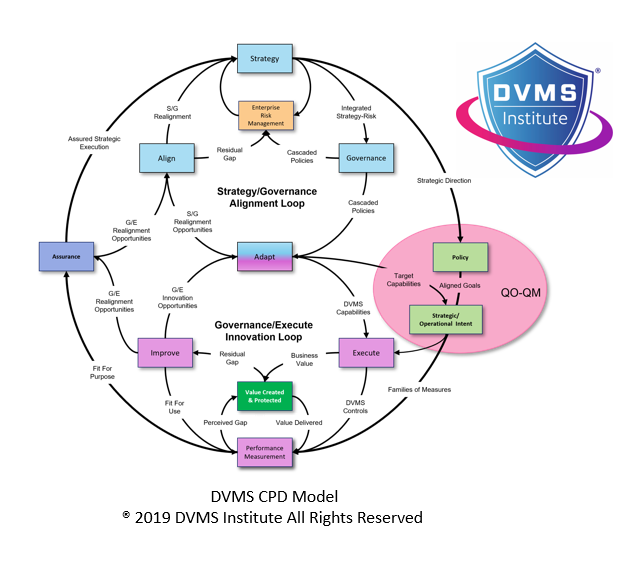
- CPD Model – Powers DVMS Operations
- 3D Knowledge Model – Powers the DVMS Culture
- FastTrack Model – Enables A Phased DVMS Adoption
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved