How the Digital Value Management System (DVMS) Provides a Standardized Approach to Global Cyber Operational Resilience
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
The DVMS: A Standardized Approach to Global Cyber Operational Resilience for the IIF
Introduction
Operational resilience has emerged as a foundational pillar in the governance of global financial systems. The Institute of International Finance (IIF), a global association of financial institutions, has emphasized the urgent need for a coherent, standardized framework to address increasingly complex operational risks—particularly those related to cyber threats, technological dependencies, and third-party vulnerabilities. Within this context, the Digital Value Management System (DVMS) provides a timely, robust, and globally harmonized solution to cyber operational resilience. By aligning governance, risk management, compliance, and performance oversight into an integrated model, the DVMS empowers the IIF and its global members to meet the challenges of an interconnected digital economy with agility and consistency.
The Urgency of Operational Resilience
Over the past decade, operational disruptions such as the COVID-19 pandemic, cyberattacks, financial market instabilities, geopolitical events, and supply chain vulnerabilities have dramatically underscored the need for operational resilience across the financial sector. The IIF has documented how these disruptive forces exposed gaps in the ability of financial institutions to continue delivering critical operations under duress. Operational resilience—defined by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) as “the ability to deliver critical operations through disruption”—has moved from being a theoretical ideal to a regulatory imperative. However, while regulatory interest has intensified, the global landscape remains fragmented. Jurisdictional variations in policy definitions, testing requirements, and third-party oversight continue to generate complexity for multinational institutions.
Fragmentation in Global Regulatory Frameworks
Despite common objectives, regulatory approaches to operational resilience diverge sharply across regions. The United Kingdom’s focus on “important business services,” the European Union’s DORA framework emphasizing “critical or important functions,” and the United States’ preference for “critical operations and core business lines” all reflect different interpretations of what constitutes a resilience-relevant function. This misalignment has forced global financial institutions to maintain multiple, overlapping resilience frameworks that differ by geography, compliance scope, and enforcement standards. The result is a convoluted risk management environment that is not only costly but often counterproductive. In contrast, the DVMS offers a unifying framework that aligns with the IIF’s call for global interoperability and consistent resilience outcomes.
The DVMS Architecture: An Overview
The Digital Value Management System (DVMS) is a comprehensive enterprise governance and value management model specifically designed to help organizations manage digital business value, cyber risk, operational performance, and regulatory compliance in an integrated manner. Unlike siloed risk management approaches that treat cybersecurity, business continuity, and operational assurance separately, the DVMS adopts a systems-based structure that enables organizations to align their business objectives with operational capabilities in a dynamic digital environment. It does this through four core layers: Governance, Enablement, Integration, and Assurance. Each layer supports distinct but interrelated capabilities that drive operational resilience outcomes.
Harmonization Through Governance and Policy Alignment
At its core, the DVMS provides a governance framework that helps institutions align their strategic objectives with operational execution. For the IIF and its member institutions, this governance capability is critical. It ensures that resilience efforts are not simply compliance-driven but strategically integrated across the organization. By defining governance in terms of policy harmonization, oversight responsibilities, stakeholder engagement, and decision rights, the DVMS supports the IIF’s vision of a globally consistent approach to resilience that respects local requirements without duplicating effort. This alignment is especially important when balancing firm-specific risk appetites with jurisdictional impact tolerance thresholds as discussed in the BCBS and UK frameworks.
Operationalizing Resilience Through Risk Enablement
One of the DVMS’s most significant contributions to global cyber operational resilience lies in its Enablement Layer. This layer is responsible for ensuring that organizations have the capabilities, knowledge, and resources to manage operational and cyber risks effectively. Drawing upon established risk management disciplines, such as those prescribed by the BCBS (e.g., business continuity planning, ICT risk management, and third-party risk management), the DVMS ensures that these functions are integrated and mutually reinforcing. This is especially valuable in an international context where operational resilience may be unevenly understood or executed. By providing standard operating models, maturity benchmarks, and resilience capability maps, the DVMS allows institutions to scale resilience efforts across diverse operating environments.
Third-Party Risk Management and Digital Supply Chains
Third-party dependencies represent one of the most significant risk vectors in the global financial ecosystem. The IIF has repeatedly emphasized the systemic risks that arise from the interconnectedness of cloud providers, fintech vendors, and ICT subcontractors. The DVMS directly addresses this challenge through its integrated third-party risk management capability. It enables organizations to assess, monitor, and control third-party services based on criticality to operations, rather than just contractual obligations. This approach aligns with the Financial Stability Board’s guidance on third-party oversight and supports the IIF’s call for consistent and scalable third-party registers. Moreover, the DVMS supports resilience testing across supply chains and provides a structured methodology for mapping interdependencies and escalation paths in case of failure.
Integrated Resilience Testing and Continuous Improvement
The IIF has highlighted the growing importance of resilience testing, scenario planning, and impact analysis. However, it also notes the risk of misaligned testing strategies—where institutions test for improbable catastrophes at the expense of likely scenarios. The DVMS addresses this by offering a multi-tiered testing framework that combines scenario-based exercises with control testing, notification validation, recovery rehearsal, and stakeholder response assessments. This ensures that testing is not only aligned with operational reality but also helps institutions remain within their defined tolerance for disruption. Importantly, the DVMS embeds a feedback loop for continuous improvement, ensuring that lessons learned are codified into process enhancements, training protocols, and future testing cycles.
Enabling Cross-Jurisdictional Interoperability
For the IIF, international interoperability is a baseline principle. As financial institutions operate across borders, their ability to implement a unified resilience framework is often compromised by conflicting local regulations. The DVMS solves this by enabling cross-jurisdictional interoperability through its abstraction of operational resilience principles from compliance specifics. Rather than tailoring separate frameworks for every market, institutions using the DVMS can maintain a central model of operational resilience and then “localize” it through modular adaptations. This harmonized-yet-flexible structure supports the IIF’s vision of a globally coordinated resilience model that avoids regulatory duplication and enhances operational efficiency.
Aligning with Macroprudential and Systemic Risk Objectives
In recent years, authorities such as the Bank of England and the European Systemic Risk Board have begun taking a macroprudential view of operational resilience—seeking to understand how systemic interdependencies might magnify the impact of a local failure. The DVMS is uniquely positioned to support this evolution. Its Assurance Layer not only monitors internal performance but also enables firms to map and model ecosystem-wide dependencies, including financial market infrastructures, critical third parties, and peer organizations. This systems-thinking approach equips institutions with the analytical tools to engage with regulatory expectations around systemic tolerance levels and to participate in sector-wide contingency planning efforts.
Addressing Observed Challenges and Limitations
The IIF has identified several barriers that undermine effective operational resilience implementation. These include over-expansive definitions of critical assets, impractical expectations for recovery timelines (e.g., the controversial two-hour RTO), and administrative overload from maintaining duplicative third-party registers. The DVMS mitigates these pain points by offering pragmatic guidance on criticality assessment, proportional testing, and automated third-party governance. Its use of materiality thresholds ensures that resilience efforts are focused on assets and services that truly matter to financial stability. Additionally, the DVMS supports resilience prioritization based on actual risk exposure rather than regulatory abstraction—thereby aligning investment with impact.
Fostering Public-Private Collaboration
Perhaps one of the most valuable contributions the DVMS offers to the IIF community is its role in enabling collaboration. Operational resilience cannot be achieved in isolation. It requires coordinated response strategies, shared threat intelligence, and joint recovery mechanisms between financial institutions, regulators, third-party providers, and even customers. The DVMS facilitates this through its integrated stakeholder engagement model, which includes communication planning, coordinated testing, and cross-sectoral policy alignment. This mirrors the IIF’s call for collaborative efforts between public and private actors to build resilience at the systemic level.
Future Outlook and Strategic Imperative
As the nature of risk continues to evolve—driven by AI, quantum computing, geopolitical realignments, and climate disruptions—the ability to maintain operational resilience will become even more critical. The IIF anticipates that future resilience frameworks will require adaptive planning, dynamic monitoring, and digital twin modeling to simulate and respond to real-time operational threats. The DVMS is designed for this future. Its modularity, scalability, and data-driven architecture position it as a future-proof platform capable of evolving in step with both regulatory expectations and operational complexity.
Conclusion
The Digital Value Management System (DVMS) provides a timely, robust, and globally harmonized solution to cyber operational resilience within this context. By aligning governance, risk management, compliance, and performance oversight into an integrated model, the DVMS empowers the IIF and its global members to meet the challenges of an interconnected digital economy with agility and consistency. The DVMS provides the IIF and its global membership with more than just a compliance tool—it offers a standardized, strategic, and scalable approach to cyber operational resilience. Integrating governance, risk enablement, resilience testing, third-party oversight, and continuous improvement into a cohesive model, the DVMS responds directly to the fragmented regulatory landscape and mounting operational challenges identified by the IIF.Its alignment with international principles, ability to scale across jurisdictions, and focus on systems-thinking make it an indispensable framework for building a secure, agile, and resilient global financial system.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
In today’s digitally driven economy, cyber disruptions are no longer an “if” but a “when.”
The DVMS Institute’s Certified Training Programs teach organizations the skills to build a Holistic and Culture-Aligned Overlay System capable of coordinating Cyber Operational Resilience actions across a Complex Digital Ecosystem.
Achieving true cyber operational resilience requires seamless alignment between organizational Strategy, Governance, and Operations, underpinned by a culture dedicated to sustaining and continuously innovating the Creation, Protection And Delivery of organizational digital value.

The DVMS positions cyber resilience as a strategic, enterprise-wide capability powered by your best practice systems (ERM, ITSM, GRC, NISTCSF) and the DVMS MVC, CPD, and 3D Knowledge models.
This systems-based approach to cyber operational resilience demands active engagement from all members of the Digital Ecosystem. Each member plays a distinct role in proactively identifying and mitigating the systemic risks that threaten digital business operations.
This forward-looking approach to adaptive Governance, Resilience, and Assurance (GRA) positions businesses to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Drive Agility and Trust Across Your Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
DVMS Explainer Videos
- Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- ZX Model – The MVC’s that power operational resilience
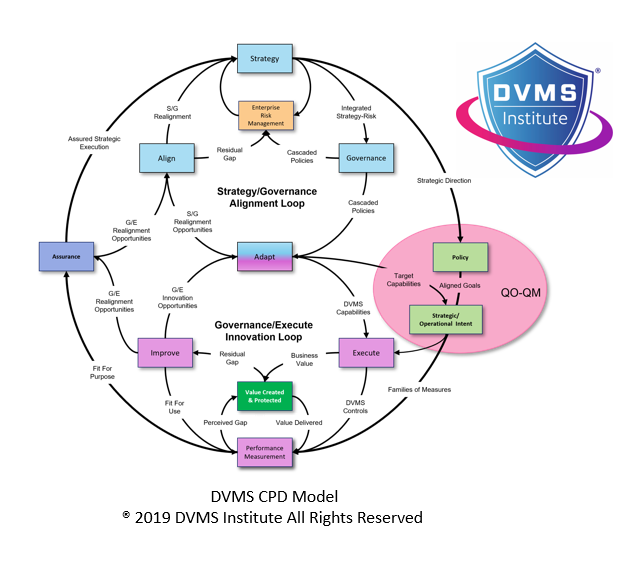
- CPD Model – Adaptable governance and assurance
- 3D Knowledge Model – Enabling holistic organizational learning
- FastTrack Model – A phased approach to cyber resilience
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved