The Role of the DVMS in Delivering NIST Cybersecurity Framework Outcomes
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
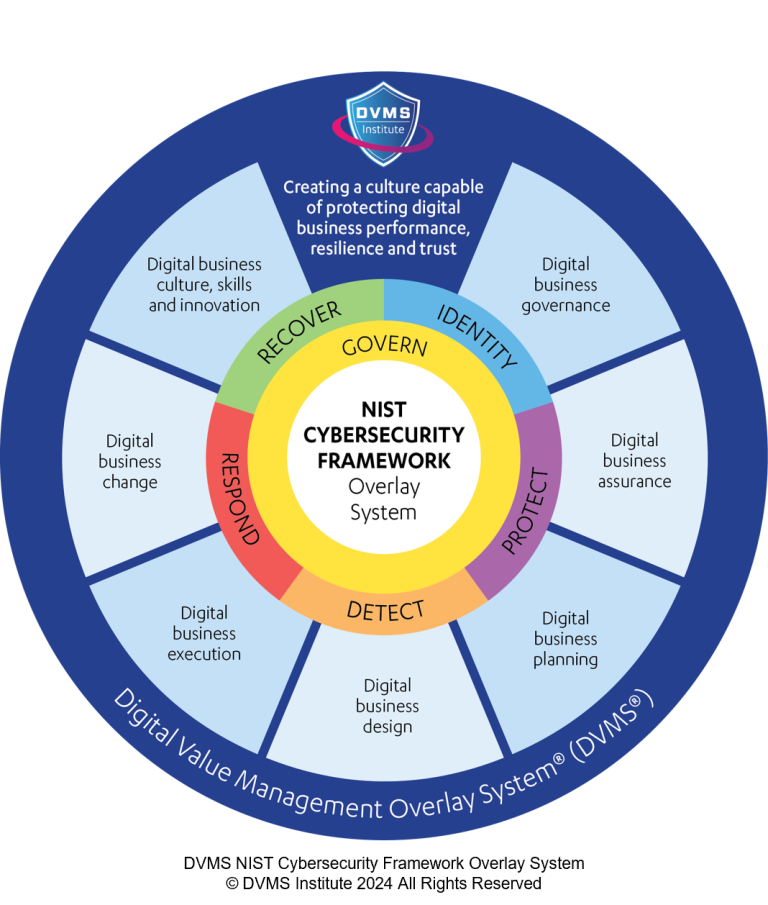
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) has evolved into a globally respected guide for managing digital risk. While it offers a set of desired outcomes organized under six core Functions—Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—it does not dictate how these outcomes will be achieved.
This is where the Digital Value Management System® (DVMS), developed by the DVMS Institute, becomes instrumental. The DVMS provides a scalable, adaptive overlay that organizations can use to operationalize and institutionalize the CSF that aligns with business strategy, culture, and desired outcomes. This essay explores how the DVMS enables and enhances the achievement of the business outcomes defined in the NIST CSF.
Embedding Risk-Based Thinking in Decision-Making
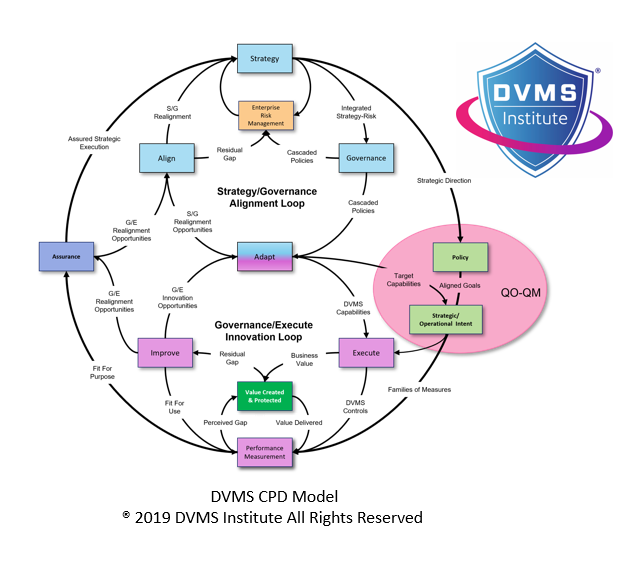
The DVMS is designed around the CPD Model—Create, Protect, and Deliver digital business value—and treats risk as an intrinsic element of strategy. This aligns directly with the CSF’s emphasis on risk-informed governance. The DVMS’s Z-X Model defines seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs): Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate. These capabilities enable a holistic, systems-thinking approach to embedding cybersecurity into enterprise-wide decision-making processes.
For example, the DVMS approach to “Govern” includes setting cybersecurity policies that reflect an organization’s strategic intent, risk tolerance, and compliance needs. This supports the CSF outcome of enabling executive leadership to make informed, balanced decisions that align security with operational priorities.
Strengthening Operational Resilience
The NIST CSF’s Recover Function emphasizes quick restoration of normal operations following a cyber event. The DVMS supports this through its “Change” and “Execute” capabilities, which ensure that incident response, continuity plans, and change management processes are integrated into operational workflows.
Moreover, the DVMS treats resilience as a dynamic capability. Its iterative FastTrack™ approach—Phase 0: Initiate, Phase 1: Basic Hygiene, Phase 2: Expand, and Phase 3: Innovate—enables organizations to mature their cyber resilience incrementally and systematically. This helps ensure recovery planning is not reactive but embedded in day-to-day operations.
Enabling Regulatory and Standards Alignment
The CSF is a harmonizing framework that maps to various legal and regulatory standards. Similarly, the DVMS is not a standalone method or framework, but a scalable overlay that can sit atop existing frameworks, including NIST-CSF, ISO, ITIL, CMMC, and others. By viewing cybersecurity as part of enterprise governance rather than a technical silo, the DVMS enables alignment with these standards in a business-centric manner.
For instance, its “Assure” capability ensures that compliance obligations are met and managed through transparent and adaptive governance mechanisms. This directly supports CSF outcomes related to external audit readiness and internal accountability.
Driving Performance and Continuous Improvement
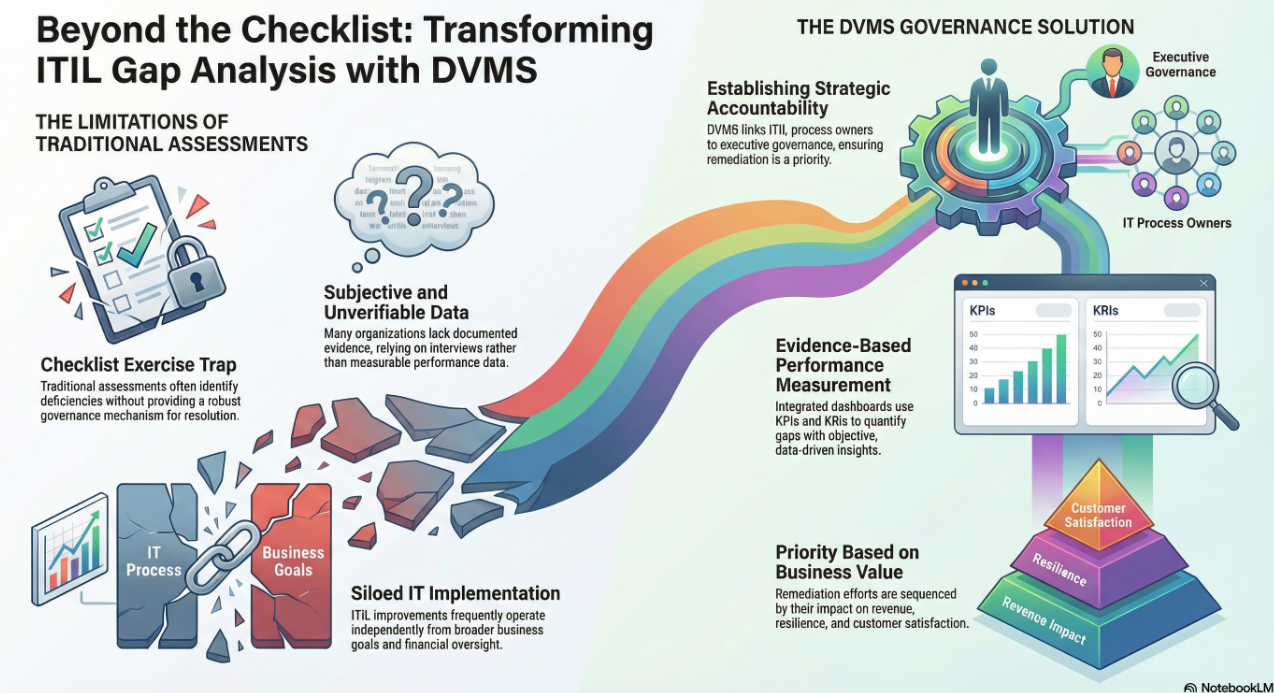
One of the core business outcomes of the CSF is fostering continuous improvement, supported by self-assessment and maturity measurement. The DVMS directly addresses this by embedding performance improvement into its operating model. It uses tools like the Digital Value Capability Maturity Model (DVCMM) and the Question Outcome–Question Metric (QO-QM) framework to tie strategic objectives to measurable results.
This approach allows for continuous tracking of key cybersecurity metrics—such as mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR)—while aligning them with broader business performance indicators. In doing so, the DVMS transforms cybersecurity from a cost center into a driver of value creation.
Facilitating Cross-Functional Collaboration
The CSF’s role in bridging the divide between technical and non-technical stakeholders is crucial for effective cybersecurity governance. The DVMS reinforces this by applying systems thinking to the entire organization, encouraging collaborative decision-making across silos.
The DVMS’s 3D Knowledge Model further enhances this by aligning team knowledge, collaboration, and strategic intent. This model ensures that cybersecurity initiatives are well-coordinated and aligned with the enterprise’s mission and stakeholder expectations. This directly supports the CSF’s vision of shared accountability and enterprise-wide engagement.
Enhancing Customer and Stakeholder Trust
Trust and transparency are recurring themes in the CSF. The DVMS supports this by embedding governance, assurance, and measurement into the organizational culture. It operationalizes CSF’s GOVERN and IDENTIFY functions by promoting visibility into how digital business value is created and protected.
The DVMS encourages organizations to document their cybersecurity capabilities through Organizational Profiles (aligned with CSF guidance) and maturity assessments. This not only aids in internal management but also serves as a trust signal to customers, investors, and partners.
Accelerating Innovation and Digital Transformation
The CSF emphasizes that cybersecurity should not hinder innovation but enable it. The DVMS reinforces this philosophy through its “Innovate” capability and adaptive design. By treating value protection as a concurrent—not sequential—activity to value creation, the DVMS ensures that cybersecurity is integrated early into the innovation lifecycle.
This approach supports secure-by-design principles, allowing digital transformation efforts to proceed without increasing risk. For example, as organizations move to the cloud or adopt AI-driven solutions, the DVMS ensures that cybersecurity requirements evolve with business innovation.
Improving Supply Chain Risk Management
Third-party risk is a growing concern across all sectors. The CSF addresses this by including outcomes related to supply chain visibility and control. The DVMS strengthens this through its governance overlay, ensuring cybersecurity requirements are integrated into procurement, vendor assessments, and contract management.
The DVMS also facilitates communicating CSF-aligned expectations to partners and suppliers through Target Profiles and standardized controls. This improves third-party accountability and reduces systemic supply chain risk.
Supporting Cyber Insurance Readiness
As insurers increasingly demand proof of cyber maturity, organizations need structured, demonstrable programs. The DVMS provides this structure through formal capabilities and maturity models that map directly to CSF outcomes. Its documentation and governance mechanisms allow organizations to demonstrate due diligence, risk controls, and incident response maturity—key elements in qualifying for cyber insurance and negotiating favorable terms.
Conclusion: DVMS as the CSF Delivery Engine
While the NIST CSF defines the “what” and “why” of cybersecurity risk management, the DVMS provides the “how.” It enables the business-aligned, outcome-driven application of the CSF across diverse organizational contexts. Through its holistic overlay, iterative improvement cycles, and alignment with enterprise strategy, the DVMS transforms the CSF from a framework into a dynamic engine for digital resilience, performance assurance, and sustainable value creation.
By integrating DVMS into their cybersecurity programs, organizations position themselves to manage digital risk effectively and use cybersecurity as a catalyst for innovation, trust, and competitive advantage.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
In today’s digitally driven economy, cyber disruptions are no longer an “if” but a “when.”
The DVMS Institute’s Certified Training Programs teach organizations the skills to build a Holistic and Culture-Aligned System capable of coordinating Adaptive, Governance, Resilience, and Assurance actions across a Complex Digital Ecosystem.
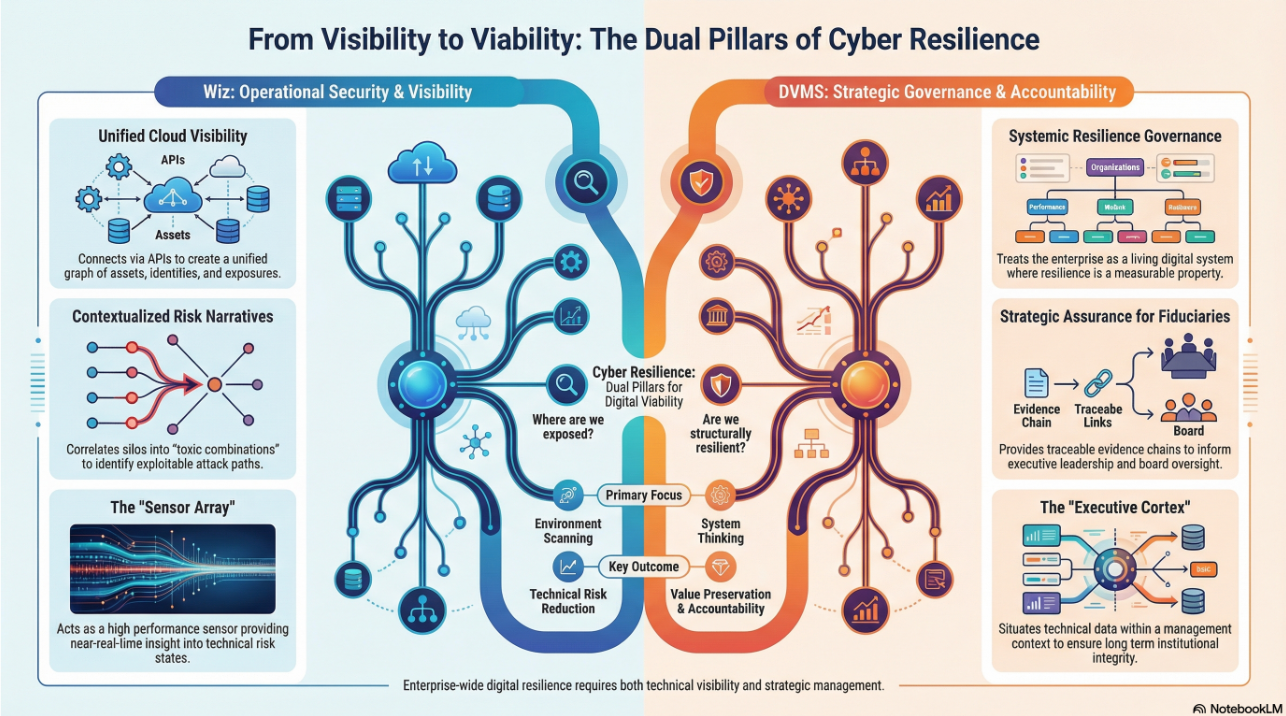
Achieving true cyber resilience across a complex digital ecosystem requires seamless alignment between organizational Strategy, Governance, and Operations, underpinned by a culture dedicated to sustaining and continuously innovating organizational digital value.

The DVMS positions cyber resilience as a strategic, enterprise-wide capability powered by the Institute’s CPD, Z-X, and 3D Knowledge models.
This systems-based approach to cyber operational resilience demands active engagement from all members of the Digital Ecosystem, with each member playing a distinct role in proactively identifying and mitigating the systemic risks that threaten digital business operations.
This adaptive, forward-looking approach to Governance, Resilience, and Assurance (GRA) positions businesses to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Drive Agility and Trust Across Your Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
DVMS Explainer Videos
- Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- ZX Model – The MVC’s that power operational resilience
- CPD Model – Adaptable governance and assurance
- 3D Knowledge Model – Enabling holistic organizational learning
- FastTrack Model – A phased approach to cyber resilience
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved