How A DVMS® Empowers GRC Professionals to Engage with Executive Leadership and the Board
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) professionals face increasing pressure to effectively communicate cybersecurity risks and compliance obligations to executive leadership and boards of directors.
These stakeholders often prioritize business performance, growth, and shareholder value, while perceiving GRC concerns as compliance hurdles or cost centers. Bridging this communication gap requires a paradigm shift that reframes cybersecurity risk as an integral component of business value and strategic decision-making.
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS), developed by the DVMS Institute, provides a comprehensive overlay model that enables this shift. It empowers GRC professionals to connect cybersecurity risk management to strategic outcomes, thus fostering more meaningful engagement with leadership and boards.
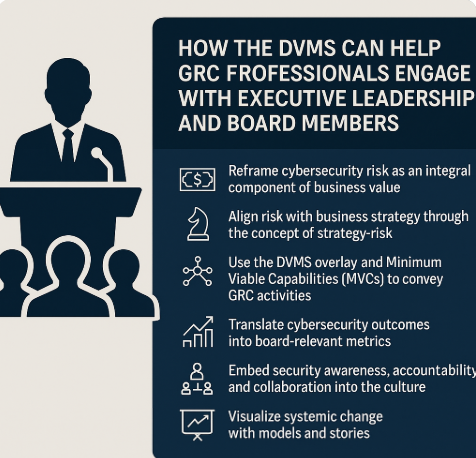
Reframing the GRC Narrative: From Compliance to Strategic Enablement
The DVMS reconceptualizes cybersecurity as an essential component of digital business value rather than a technical or compliance-centric issue. This perspective is foundational for GRC professionals who need to articulate the strategic significance of cybersecurity initiatives. Rather than presenting risk in technical language, such as vulnerabilities, attack vectors, or control deficiencies, the DVMS encourages translation into business outcomes: operational resilience, customer trust, revenue protection, and regulatory readiness.
Using the DVMS, GRC professionals can present cybersecurity activities as mechanisms that safeguard the organizational ability to create, protect, and deliver value. This narrative aligns more naturally with board-level concerns and reinforces GRC’s role as a strategic enabler rather than a regulatory watchdog.
Bridging Communication Gaps Through Strategy-Risk
A key innovation in the DVMS is the concept of “strategy-risk”—the inseparability of business strategy and risk management. Traditional approaches often treat strategy and risk as parallel, loosely connected disciplines. The DVMS integrates them into a single conceptual framework, asserting that every strategic objective inherently carries risk, and that managing that risk is vital to realizing business goals.
GRC professionals leveraging the DVMS can frame conversations around strategy-risk to show how risk mitigation enhances the likelihood of strategic success. For example, instead of stating that “vendor access needs tighter controls,” the message becomes “our digital supply chain needs assurance to preserve operational continuity and avoid reputational damage.” This alignment helps executives understand risk in the context of opportunity, growth, and innovation, which are central to their agenda.
The DVMS Overlay and Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs)
DVMS is not a standalone framework but an overlay that integrates seamlessly with existing governance models, standards, and methods. Its strength lies in its seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs): Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate. These capabilities structure an organizational approach to managing digital business value and risk.
For GRC professionals, the MVCs offer a structured narrative for how their activities contribute to broader organizational health. For instance:
- Govern and Assure provide a foundation for executive visibility and oversight.
- Plan and Design translate policy into operational risk strategies.
- Execute and Innovate demonstrate how risk mitigation drives business adaptability and value creation.
This systemic framing is more relatable for executives and board members accustomed to portfolio-level thinking rather than siloed control implementations.
Making Cybersecurity Outcomes Board-Relevant
One of the core challenges for GRC professionals is the misalignment of metrics. Boards focus on KPIs tied to business performance, such as revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and brand equity. In contrast, GRC often reports on audit findings, closed control maturity scores, or number of vulnerabilities patched metrics that are abstract or irrelevant to executive concerns.
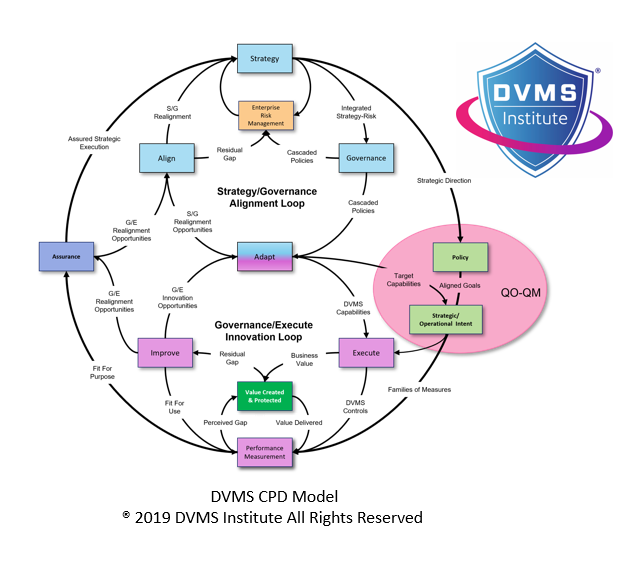
The DVMS addresses this disconnect through its CPD (Create, Protect, Deliver) model and strategy-driven metrics framework (QO–QM). GRC professionals can reframe cybersecurity metrics in terms of value delivery. For example:
- Instead of “incident response time,” report “time to restore customer-facing services post-incident.”
- Instead of “policy adherence,” report “reduction in potential regulatory penalties avoided.”
This metric translation ensures that board members understand the impact of risk management in business terms.
Enhancing Cultural Alignment and Accountability
Executive boards play a pivotal role in shaping organizational culture. However, cultural transformation must cascade through all layers to be effective. The DVMS incorporates cultural awareness as a foundational principle, recognizing that cybersecurity outcomes are as much about behaviors and mindsets as about technology or policy.
GRC professionals can use DVMS principles to advocate for cultural change by embedding security awareness, accountability, and collaboration into existing workflows. For example, instead of mandating annual security training as a checkbox exercise, they can engage leadership to model desired behaviors and make security a shared responsibility. The DVMS emphasizes that policies must be accompanied by leadership accountability, helping GRC professionals reposition themselves as catalysts for long-term cultural resilience.
Tying in the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0
DVMS is designed to complement NIST CSF 2.0, which has expanded its scope to include the “Govern” function. This addition highlights governance’s centrality to cybersecurity outcomes, including oversight, roles and responsibilities, and enterprise risk alignment.
Using DVMS alongside NIST CSF 2.0 enables GRC professionals to align tactical activities (e.g., implementing controls) with strategic governance outcomes (e.g., defining risk tolerances, enabling business decisions). Using NIST’s language of Profiles, Tiers, and desired outcomes, GRC leaders can tailor communications to show how their cybersecurity initiatives directly contribute to organizational priorities.
Visualizing Systemic Change with Models and Stories
Boards often respond more favorably to narratives and visual tools than dense reports or technical dashboards. DVMS provides several conceptual tools, such as the Z-X Model and CPD Model, that help visualize how different elements of the organization interact and evolve. These models demonstrate the flow of value and risk, making it easier for leadership to grasp system-wide impacts of localized decisions.
Storytelling based on real scenarios—especially those demonstrating how proactive risk management preserved customer trust or averted reputational loss—can be far more persuasive than abstract metrics. DVMS encourages this narrative approach, enabling GRC professionals to be storytellers of resilience.
GRC as Strategic Partner, Not Compliance Enforcer
To secure a permanent seat at the executive table, GRC professionals must transcend the limitations of traditional, siloed reporting. The Digital Value Management System provides the scaffolding needed to transform GRC from a back-office function into a strategic business partner.
Using DVMS, GRC professionals can translate complex cybersecurity issues into strategic outcomes, align metrics with business value, foster a culture of shared responsibility, and demonstrate how governance and risk enable innovation and resilience. When GRC leaders use the DVMS to shift their role from compliance enforcer to value enabler, they create the conditions for enduring engagement with executive leadership and the board.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
In today’s digitally driven economy, cyber disruptions are no longer an “if” but a “when.”
The DVMS Institute’s Certified Training Programs teach organizations the skills to build a Holistic and Culture-Aligned Overlay System capable of coordinating Adaptive, Cyber Operations Governance, Resilience, and Assurance across a Complex Digital Ecosystem.
Achieving true cyber resilience across a complex digital ecosystem requires seamless alignment between organizational Strategy, Governance, and Operations, underpinned by a culture dedicated to sustaining and continuously innovating organizational digital value.

The DVMS positions cyber resilience as a strategic, enterprise-wide capability powered by the Institute’s CPD, Z-X, and 3D Knowledge models.
This systems-based approach to cyber operational resilience demands active engagement from all members of the Digital Ecosystem, with each member playing a distinct role in proactively identifying and mitigating the systemic risks that threaten digital business operations.
This adaptive, forward-looking approach to Governance, Resilience, and Assurance (GRA) positions businesses to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Drive Agility and Trust Across Your Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
DVMS Explainer Videos
- Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- ZX Model – The MVC’s that power operational resilience
- CPD Model – Adaptable governance and assurance
- 3D Knowledge Model – Enabling holistic organizational learning
- FastTrack Model – A phased approach to cyber resilience
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved