Using a Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) to Enable ISACA’s® Digital Trust Ecosystem Framework (DTEF) Outcomes
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Enabling Digital Trust Through Systems Thinking
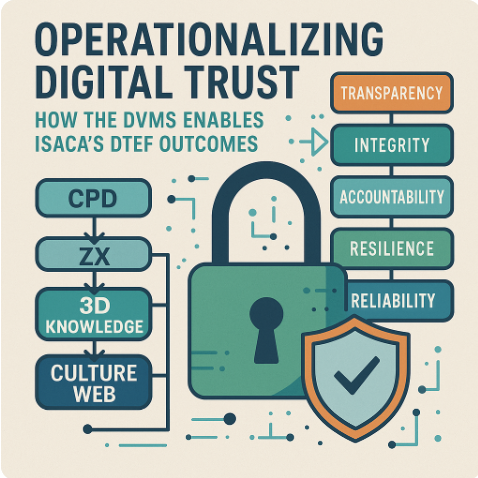
The Digital Trust Ecosystem Framework (DTEF), introduced by ISACA®, outlines essential outcomes organizations must pursue to foster digital trust in a complex, interconnected world. These include transparency, integrity, accountability, resilience, and reliability across digital systems and processes.
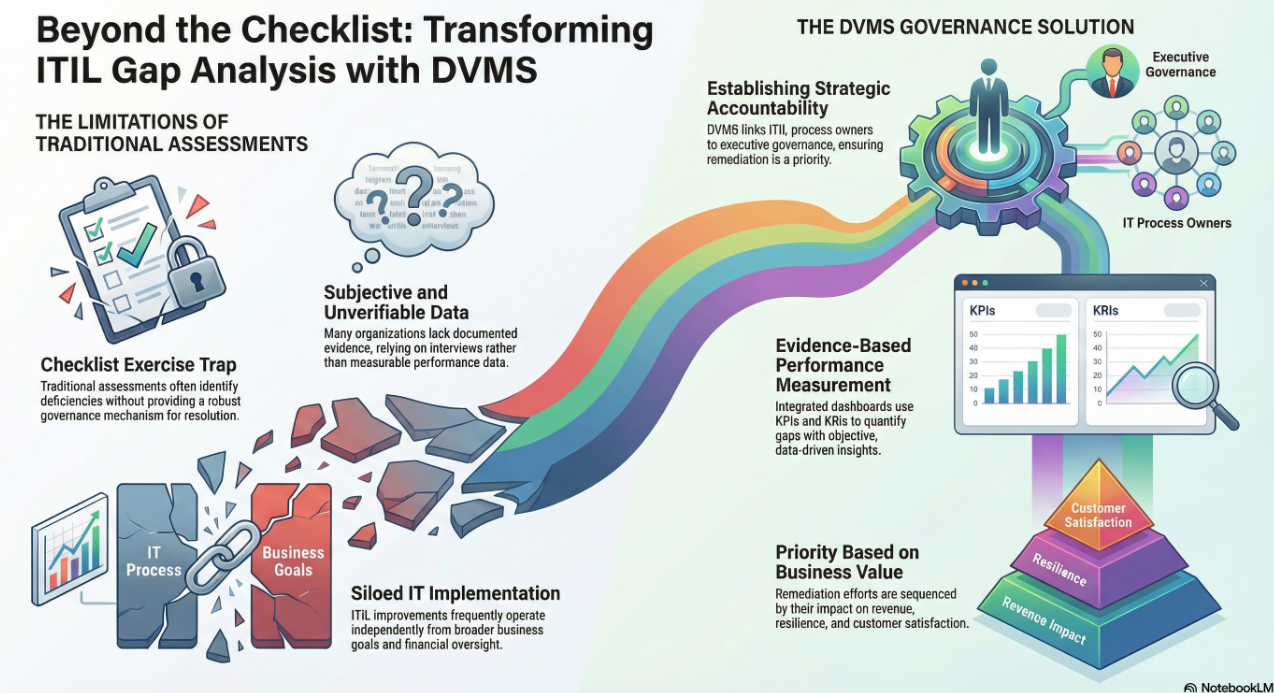
The Digital Value Management System® (DVMS) provides a holistic, culture-aligned overlay system for adaptive governance, resilience, and assurance that empowers organizations to realize these outcomes systematically. Unlike static frameworks or technical checklists, the DVMS enables a shift in perception: it repositions cybersecurity and trust not as isolated controls, but as intrinsic, strategic capabilities of the business model itself. The DVMS achieves this transformation by enabling organizations to think in systems and align value creation and protection as concurrent rather than sequential activities. This approach supports the DTEF’s focus on embedding trust into digital value chains and stakeholder interactions. The DVMS becomes a vehicle for translating digital trust objectives into tangible operational practices through integrated governance, cross-functional accountability, and adaptive learning.
Strategy-Risk: The Foundation of Trust and Performance
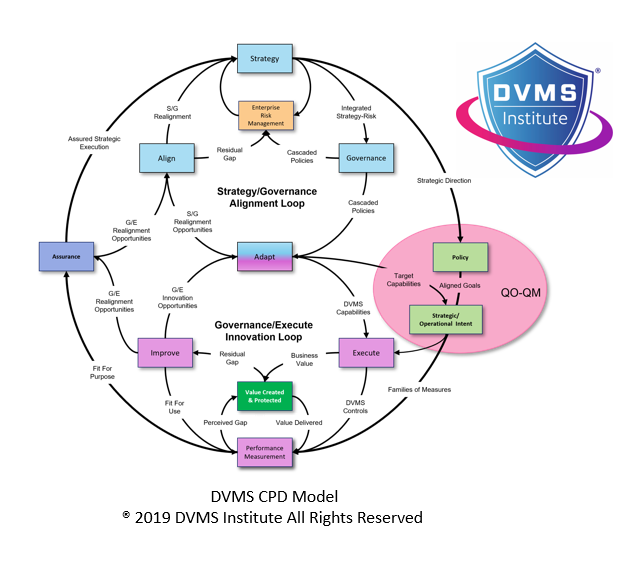
One of the DVMS’s unique contributions is the concept of “strategy-risk”—a paradigm that treats strategy and risk as a single entity rather than separate management concerns. This directly supports DTEF’s emphasis on strategic integration and the alignment of digital trust with enterprise value delivery. Organizations adopting the DVMS learn to assess and manage digital risks not as side concerns, but as fundamental elements of strategy formulation, execution, and assurance.
The CPD Model—Create, Protect, and Deliver Digital Business Value—is the DVMS’s operational core. It reinforces that unprotected value has no enduring worth, and therefore, digital trust must be built into all business processes. Through this model, the organization begins to view cybersecurity as a quality attribute of digital value, rather than a cost center or compliance obligation. This is key to achieving trust outcomes such as reliability and resilience, which the DTEF associates with sustained stakeholder confidence.
The Z-X Model and Minimum Viable Capabilities
The DVMS provides the Z-X Model to operationalize these strategic concepts. The model defines seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs): Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate. Each of these capabilities directly supports one or more DTEF outcomes.
- Govern and Assure map closely to DTEF outcomes around accountability and integrity. These capabilities ensure that enterprise policies, risk thresholds, and performance expectations align with digital initiatives.
- Plan and Design support transparency and reliability by embedding trust considerations into the architecture and strategy of digital products and services.
- Change and Execute ensure continuous alignment between operational execution and the evolving risk and value environment.
- Innovate promotes adaptability and responsiveness, essential to sustaining trust over time amid volatility.
This integrated capability model provides the structure needed to institutionalize DTEF outcomes across the enterprise. Instead of overlaying trust as an afterthought, the DVMS enables organizations to build it into their cultural and operational DNA.
Organizational Culture and the Learning Enterprise
A central tenet of the DVMS, and a shared principle with DTEF, is that trust must be cultivated through culture. The DVMS explicitly treats culture as an expression of system behavior. It employs the Cultural Web model and systems thinking (e.g., the Iceberg Model) to help organizations reveal the mental models, assumptions, and practices that enable or inhibit trust-building behaviors.
DVMS practitioners can challenge outdated beliefs and replace them with strategic clarity and trust-oriented actions by fostering a learning organization that embraces transparency, accountability, and systems awareness. Cultural integration is especially critical for outcomes like transparency and assurance, two of the cornerstones of ISACA’s DTEF.
DVMS’s structured approaches, like the 3D Knowledge Model and QO–QM (Question Outcome–Question Metric), allow organizations to quantify cultural and trust-related performance factors, creating a feedback loop for continuous improvement.
The FastTrack™ Approach to Resilience and Maturity
To help organizations scale their trust and resilience capabilities, the DVMS incorporates an iterative, phased methodology called FastTrack™, which aligns closely with DTEF’s emphasis on adaptive maturity models. FastTrack is broken into four non-linear phases:
- Phase 0: Initiate—Identify foundational capabilities and address the most critical gaps. Focus on understanding the organizational system and its digital assets.
- Phase 1: Basic Hygiene – Establish foundational controls and reinforce governance and assurance practices. This phase operationalizes DTEF’s core trust-building requirements.
- Phase 2: Expand – Broaden capabilities and integrate trust and resilience across business units and supply chains.
- Phase 3: Innovate – Embed continual innovation and trust-driven transformation into strategy and operations.
The model allows organizations to increase their trust posture while iteratively aligning with business outcomes. Importantly, each phase prioritizes culture, risk, and value and drives cross-functional learning—essential elements of the DTEF.
Profiles, Tiers, and Measurable Progress
The DVMS approach aligns with the NIST CSF 2.0’s use of Organizational Profiles and Tiers, valuable tools for aligning with DTEF outcomes. Current and Target Profiles help organizations articulate their trust capabilities and define their desired future state. The Tier system—from Partial (Tier 1) to Adaptive (Tier 4)—offers a maturity gradient for trust governance, echoing DTEF’s requirement for accountability and oversight.
Through DVMS, organizations use these structures not just for compliance, but for ongoing performance improvement. They allow trust to be evaluated, communicated, and improved through metrics, strategies, and stakeholder engagement—core values of the DTEF.
DVMS as an Adaptive Overlay
The DVMS distinguishes itself by functioning as an overlay rather than a replacement. It integrates seamlessly with existing frameworks—ITIL, COBIT, ISO, or DTEF. This flexibility ensures that organizations can adapt the DVMS to their context while aligning with the overarching goals of trust, performance, and resilience. This adaptability is especially critical in today’s volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) digital environments.
The DVMS is more than a cybersecurity management system—it is a strategic and operational compass that aligns directly with the ISACA® DTEF’s vision for digital trust. By adopting DVMS, organizations can ensure they meet digital trust expectations and embed them as integral components of how they create, protect, and deliver value.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
In today’s digitally driven economy, cyber disruptions are no longer an “if” but a “when.”
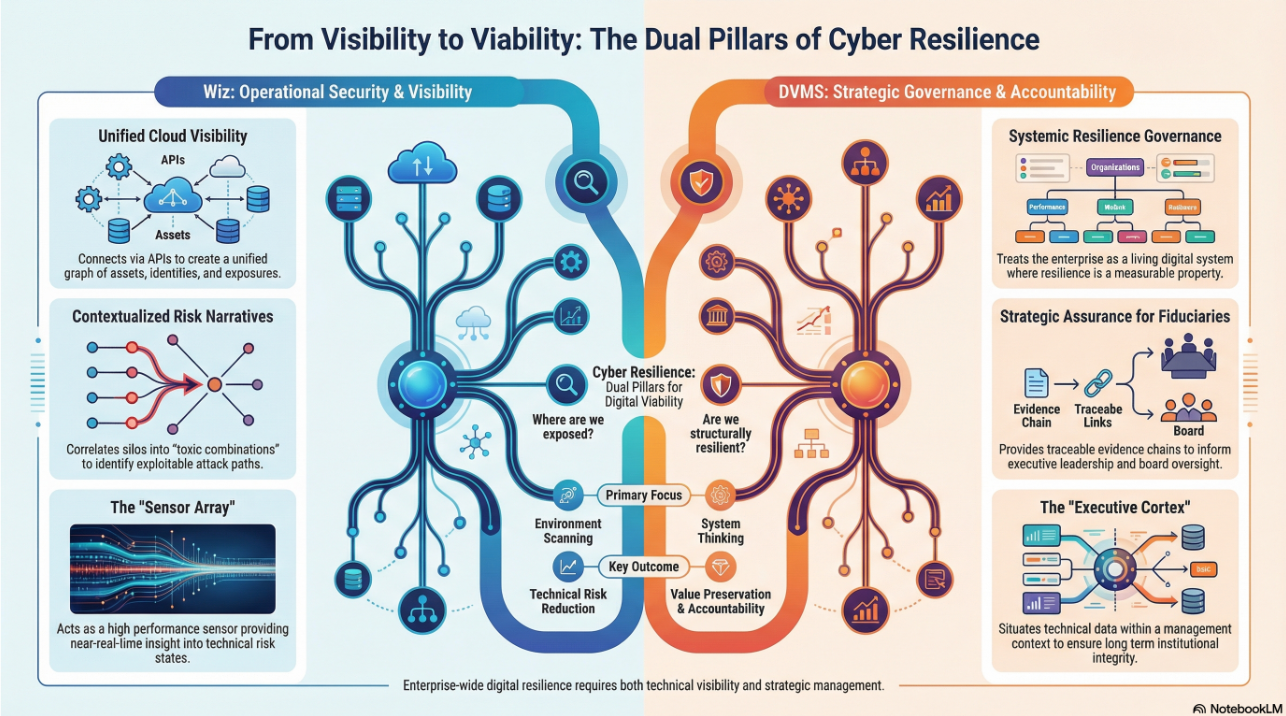
The DVMS Institute’s Certified Training Programs teach organizations the skills to build a Holistic and Culture-Aligned Overlay System capable of coordinating Adaptive, Cyber Operations Governance, Resilience, and Assurance across a Complex Digital Ecosystem.
Achieving true cyber resilience across a complex digital ecosystem requires seamless alignment between organizational Strategy, Governance, and Operations, underpinned by a culture dedicated to sustaining and continuously innovating organizational digital value.

The DVMS positions cyber resilience as a strategic, enterprise-wide capability powered by the Institute’s CPD, Z-X, and 3D Knowledge models.
This systems-based approach to cyber operational resilience demands active engagement from all members of the Digital Ecosystem, with each member playing a distinct role in proactively identifying and mitigating the systemic risks that threaten digital business operations.
This adaptive, forward-looking approach to Governance, Resilience, and Assurance (GRA) positions businesses to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Drive Agility and Trust Across Your Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
DVMS Explainer Videos
- Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- Overlay Model – What is an Overlay Model
- ZX Model – The MVC’s that power operational resilience
- CPD Model – Adaptable governance and assurance
- 3D Knowledge Model – Enabling holistic organizational learning
- FastTrack Model – A phased approach to cyber resilience
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved