Enhancing the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) for Culture-Powered, Adaptive, and Resilient Outcomes
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction: A New Perspective on Risk Management
In the digital transformation era, organizations must move beyond traditional security postures and adopt a comprehensive approach to managing cyber risk as part of broader enterprise risk. While thorough, the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) has historically been perceived as control-centric and compliance-driven.
On the other hand, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0, especially when operationalized through the DVMS Institute Digital Value Management System® (DVMS), provides a governance-oriented, outcome-focused, and adaptive lens that can elevate RMF implementations to a new level of resilience.
Organizations can reframe cybersecurity risk as an enterprise enabler by integrating the RMF with the NIST-CSF and DVMS. This blog explores how this combination can help RMF evolve into a dynamic mechanism for delivering cyber resilience through continuous improvement, organizational learning, and strategy-risk alignment.
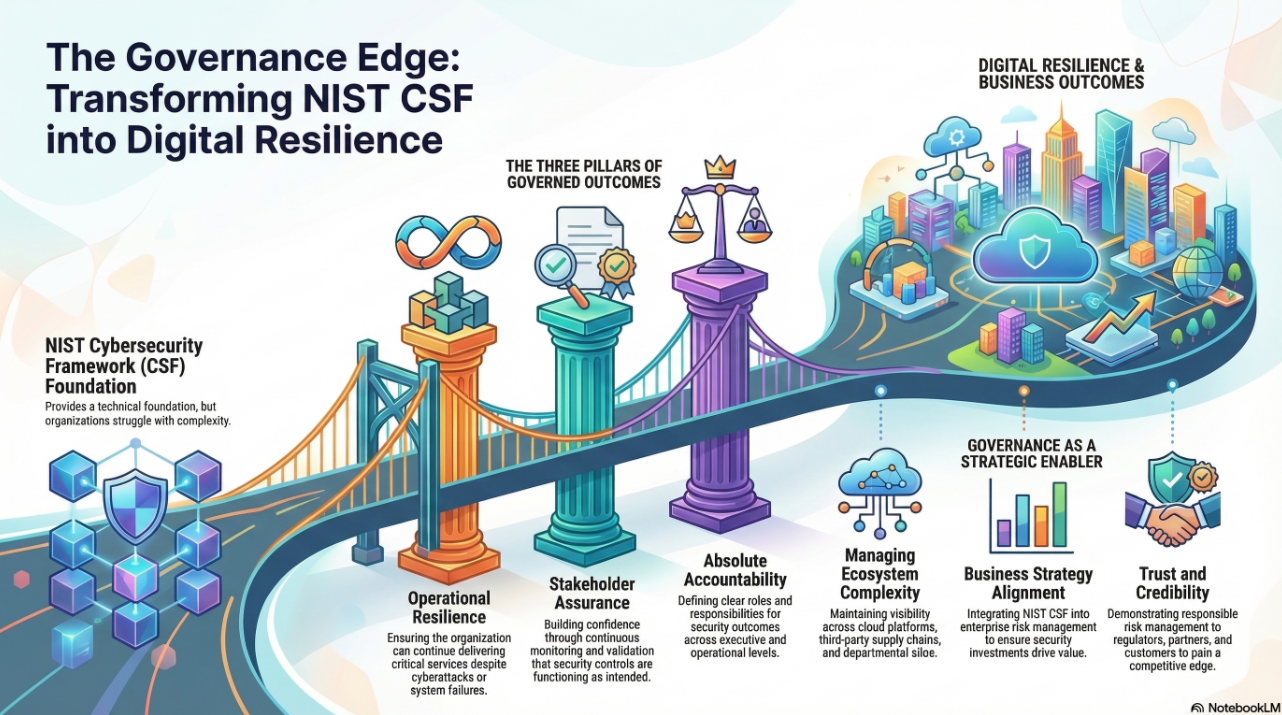
NIST-CSF 2.0: A Governance-Driven, Outcome-Focused Framework
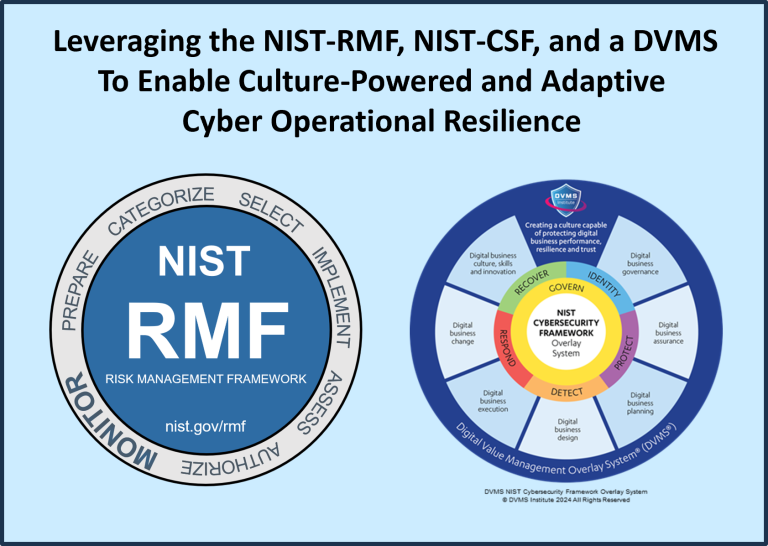
NIST-CSF 2.0 introduces six core Functions—Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. The addition of the “Govern” Function shifts the framework toward enterprise-wide cyber risk governance, emphasizing alignment with mission priorities, risk appetite, and stakeholder expectations.
These Functions are not just technical processes but strategic outcomes that integrate with enterprise risk management (ERM). They prompt organizations to consider cybersecurity in terms of value creation, not just threat mitigation.
The DVMS Overlay: From Cybersecurity to Strategy-Risk and Resilience
The DVMS complements and operationalizes the NIST-CSF as an adaptable overlay that integrates existing frameworks, standards, and methods. It introduces a systems thinking model to address cyber risk as a function of organizational behavior, leadership, culture, and value delivery.
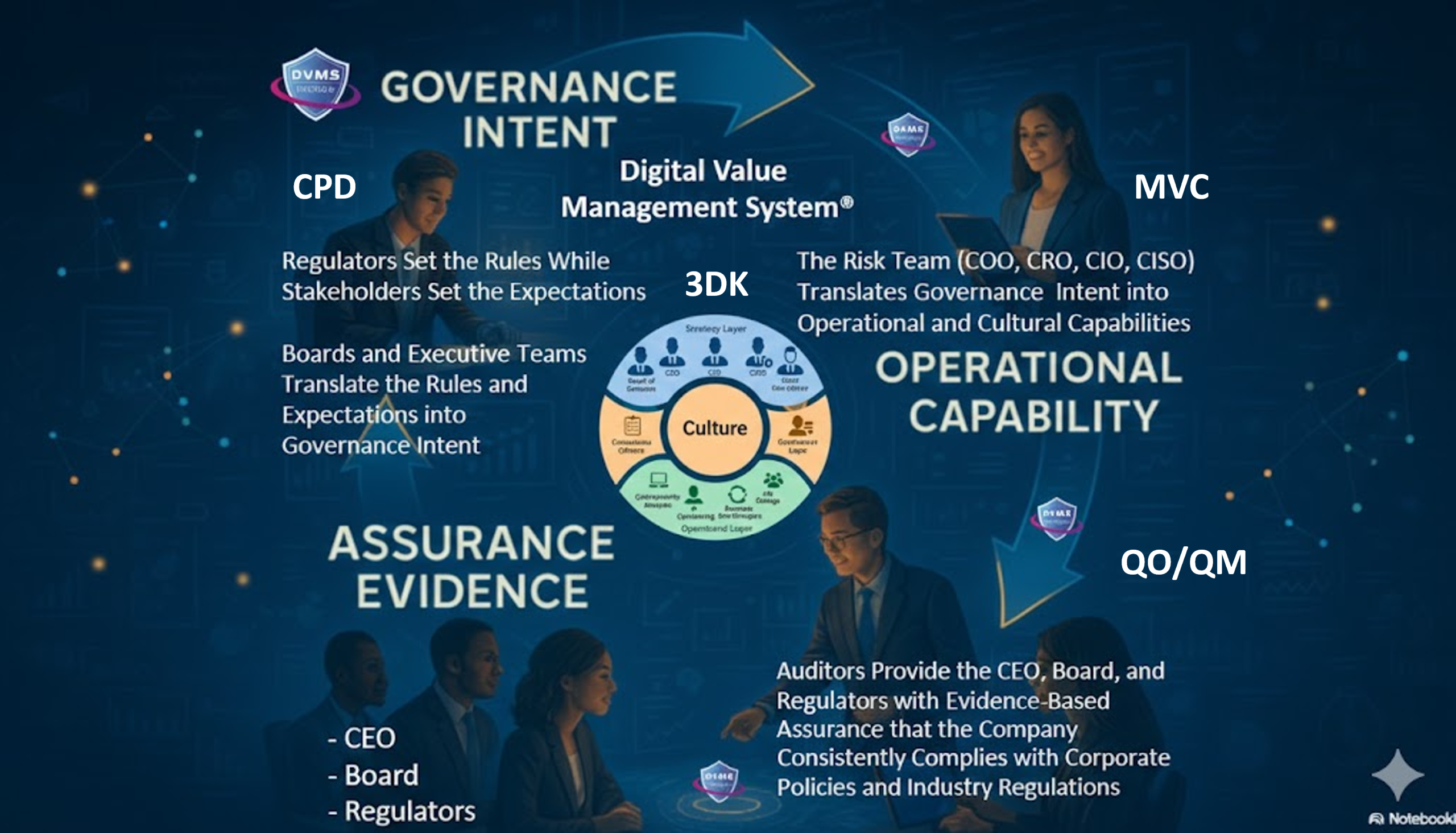
The DVMS is structured around seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs): Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate. These MVCs form the DVMS Z-X Model, which maps to all organizational functions and ensures that cybersecurity initiatives are aligned with operational and strategic goals. By aligning cybersecurity with business value through the Create–Protect–Deliver (CPD) model, DVMS enables adaptive and resilient systems that continuously improve based on internal performance and external threats.
RMF and Its Traditional Challenges
The NIST RMF provides a structured process for integrating security and risk management activities into the system development lifecycle. It consists of seven steps:
- Prepare
- Categorize
- Select
- Implement
- Assess
- Authorize
- Monitor
While thorough, RMF has been criticized for its static, checklist-like nature. Without adaptive feedback mechanisms and business alignment, organizations often struggle to maintain resilience in the face of emerging threats.
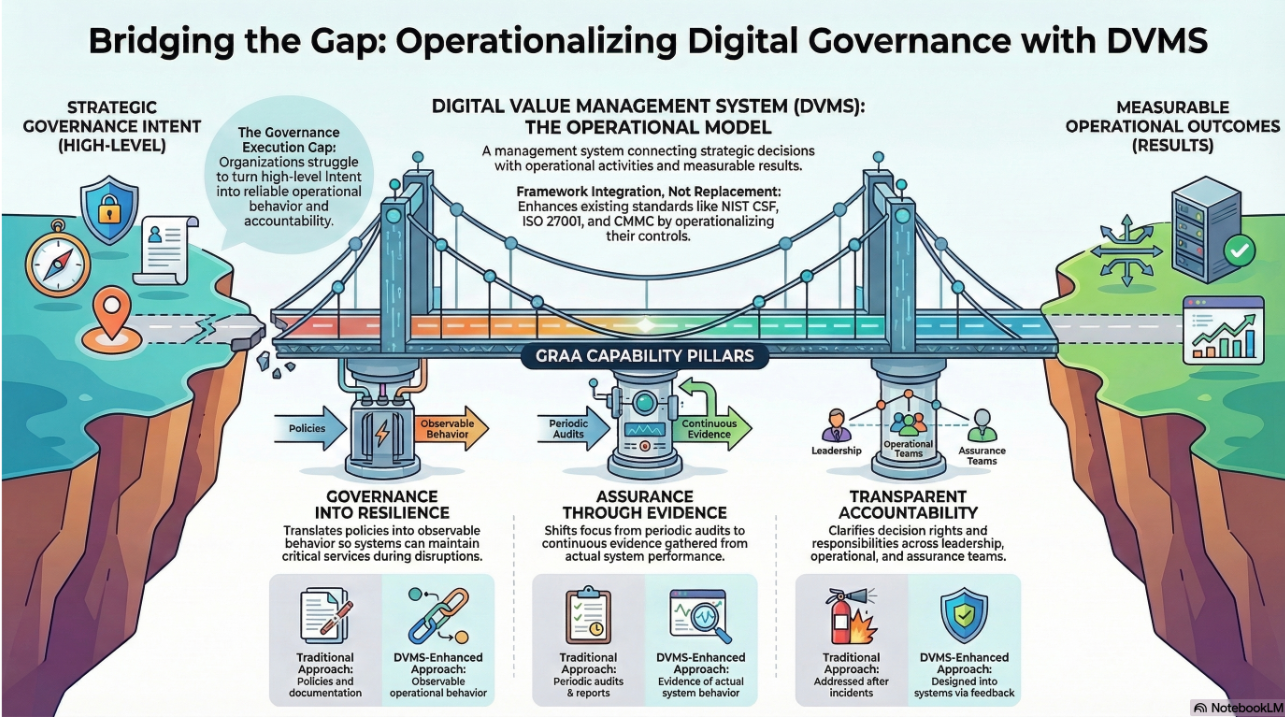
Bridging the Gap: CSF_DVMS as a Strategic Accelerator for RMF
Integrating CSF_DVMS into RMF transforms the latter from a compliance exercise into a resilience-driven capability. Here’s how:
- Governance and Strategy-Risk Alignment
The CSF’s “Govern” Function, when supported by the DVMS’s Govern and Assure capabilities, establishes cybersecurity as a board-level concern. It ensures that risk decisions are grounded in mission outcomes, not just technical control effectiveness. This alignment helps RMF’s “Prepare” step move from static documentation to a dynamic process that captures real-time strategy-risk inputs.
- Operational Profiles and Maturity
The CSF’s Organizational Profiles and Tiers enable organizations to assess their current and target states of maturity. The DVMS uses these profiles as diagnostic tools for gap analysis and roadmap development, reinforcing RMF’s “Monitor” and “Categorize” steps with an enterprise-wide view of control effectiveness.
- Adaptive Implementation and Innovation
DVMS’s phased FastTrack™ approach (Initiate, Basic Hygiene, Expand, Innovate) offers a maturity path that mirrors RMF’s continuous monitoring ethos. Organizations can evolve from basic compliance (e.g., Tier 2 Risk-Informed) to a culture of innovation and agility (e.g., Tier 4 Adaptive), which is essential in a VUCA (Volatile, Uncertain, Complex, Ambiguous) cyber environment.
- Systems Thinking and Resilience Engineering
The DVMS’s emphasis on systems thinking helps organizations identify interdependencies across people, processes, and technology. This aligns with RMF’s “Assess” and “Monitor” phases by ensuring that risk decisions account for direct and cascading effects, essential for resilience engineering.
Organizational Culture and Continuous Learning
A key differentiator of DVMS is its focus on culture. Culture is seen not as a soft artifact but a critical strategic asset, enabling or impeding cyber resilience. The cultural web model, introduced in the DVMS guidance, shows how structures, symbols, rituals, and stories reinforce (or undermine) desired security behaviors.
By embedding a learning culture and using models like GQM (Goal–Question—Metric) and QO-QM (Question–Outcome–Question Metric), organizations institutionalize feedback loops that inform RMF’s continuous monitoring efforts. This approach shifts resilience from reactive to proactive.
The 3D Knowledge Model: Enhancing Team and Strategic Alignment
The Practitioner’s Guide introduces the 3D Knowledge Model to map team behavior (x-axis), collaboration (y-axis), and strategic alignment (z-axis). This multidimensional lens ensures RMF activities are not siloed but interwoven with broader business goals. When combined with the DVMS CPD Model, organizations can better link each control or safeguard to the value it protects and the risks it mitigates.
Case Example: From Control to Capability
Consider a federal agency tasked with implementing RMF across a hybrid cloud environment. By using CSF_DVMS:
- GOVERN drives policy creation tied to mission outcomes.
- IDENTIFY and PROTECT align asset inventories with risk registers and value chains.
- RESPOND and RECOVER focus not just on business continuity but on restoring stakeholder trust.
Each step of RMF is enriched with metrics, cultural context, and systems awareness—allowing the agency to move from Tier 2 to Tier 4 in a much shorter timeframe.
Conclusion: From Compliance to Competence
The integration of NIST-CSF with the DVMS overlay empowers the Risk Management Framework to shift from a compliance-centered activity to an enterprise enabler of adaptive resilience. Through strategy-risk integration, systems thinking, cultural alignment, and phased capability development, organizations can ensure that every risk decision contributes to the secure creation, protection, and delivery of digital business value.
This is not merely a change in tools—it’s a transformation in mindset.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
In today’s digitally driven economy, cyber disruptions are no longer an “if” but a “when.”
The DVMS Institute’s Certified Training Programs teach organizations the skills to build and operate a Holistic, Adaptive, and Culture Aligned System capable of coordinating Cyber Resilience actions across an enterprise’s Digital Supply Chain.
True cyber resilience requires the seamless alignment of Strategy, Governance, and Operations (SGO) across the enterprise digital supply chain, supported by a culture committed to creating, protecting, and sustaining resilient digital value.
The DVMS training programs position cyber resilience not as a technical function but as a strategic, supply-chain-wide organizational capability.
This systems-based approach, powered by the DVMS CPD, Z-X, 3D Knowledge models, supported by a Culture that mandates engagement from Leadership, Employees, and Supply Chain partners, each fulfilling distinct responsibilities to enable cyber resilience.
This adaptive, forward-looking approach to Governance, Resilience, and Assurance (GRA) positions your business to:
- Maintain Operational Stability Amidst Constant Digital Disruption
- Drive Agility and Trust Across Your Digital Ecosystem
- Satisfy Critical Regulatory and Certification Requirements (SEC, NIS2, DORA, etc.)
- Leverage Cyber Resilience as a Competitive Advantage
-
DVMS Module Explainer Videos
- DVMS Architecture Video: David Moskowitz explains the DVMS System
- DVMS Case Study Video: Dr. Joseph Baugh Shares His DVMS Story.
- Overlay Model – Using existing systems to power operational resilience
- ZX Model – The business capabilities that power operational resilience
- CPD Model – Adaptable governance & assurance across the enterprise
- 3D Knowledge Model – Enabling holistic organizational learning
- FastTrack Model – A phased approach to adapting a NIST-CSF-DVMS
Digital Value Management System® is a registered trademark of the DVMS Institute LLC.
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved