Integrating ITSM Best Practices into the NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management Overlay System (DVMS)
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
In today’s interconnected and rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations are under immense pressure to manage cybersecurity not only as a technical concern but also as a core element of strategic business governance. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0, especially when integrated with the Digital Value Management System® (DVMS), represents a transformative model for managing cybersecurity risks while delivering digital value. Within this ecosystem, IT Service Management (ITSM) best practices play a pivotal role, serving as the operational foundation that ensures value-based service delivery and alignment with business goals.
ITSM: The Operational Backbone of Digital Governance
ITSM encompasses a set of well-established best practices for managing and delivering IT services that meet the needs of the business. Frameworks such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) guide organizations in creating repeatable, measurable processes for planning, delivering, operating, and improving IT services. These practices directly support the core aims of both the NIST CSF and DVMS—namely, to govern, protect, and deliver digital value through coordinated and accountable processes.
In the context of the NIST CSF, ITSM processes underpin the Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover functions. For instance:
- Govern: ITSM ensures that policies, roles, and responsibilities are clearly defined and enforced across the IT environment.
- Identify: Through asset management, configuration management, and service catalog practices, ITSM enables comprehensive visibility into digital and physical assets.
- Protect: ITSM change management and access control practices support the implementation of safeguards to secure critical infrastructure.
- Detect: Incident and event management functions within ITSM provide the mechanisms to identify cybersecurity events promptly.
- Respond and Recover: ITSM’s incident response, problem management, and business continuity practices form the backbone of response and recovery efforts.
In this way, ITSM acts as the process layer that operationalizes cybersecurity capabilities across the organization. Its structured methodologies ensure consistency, compliance, and continual improvement—aligning seamlessly with the CSF’s outcome-driven design.
The CSF-DVMS Fusion: Strategic Alignment Through Practice
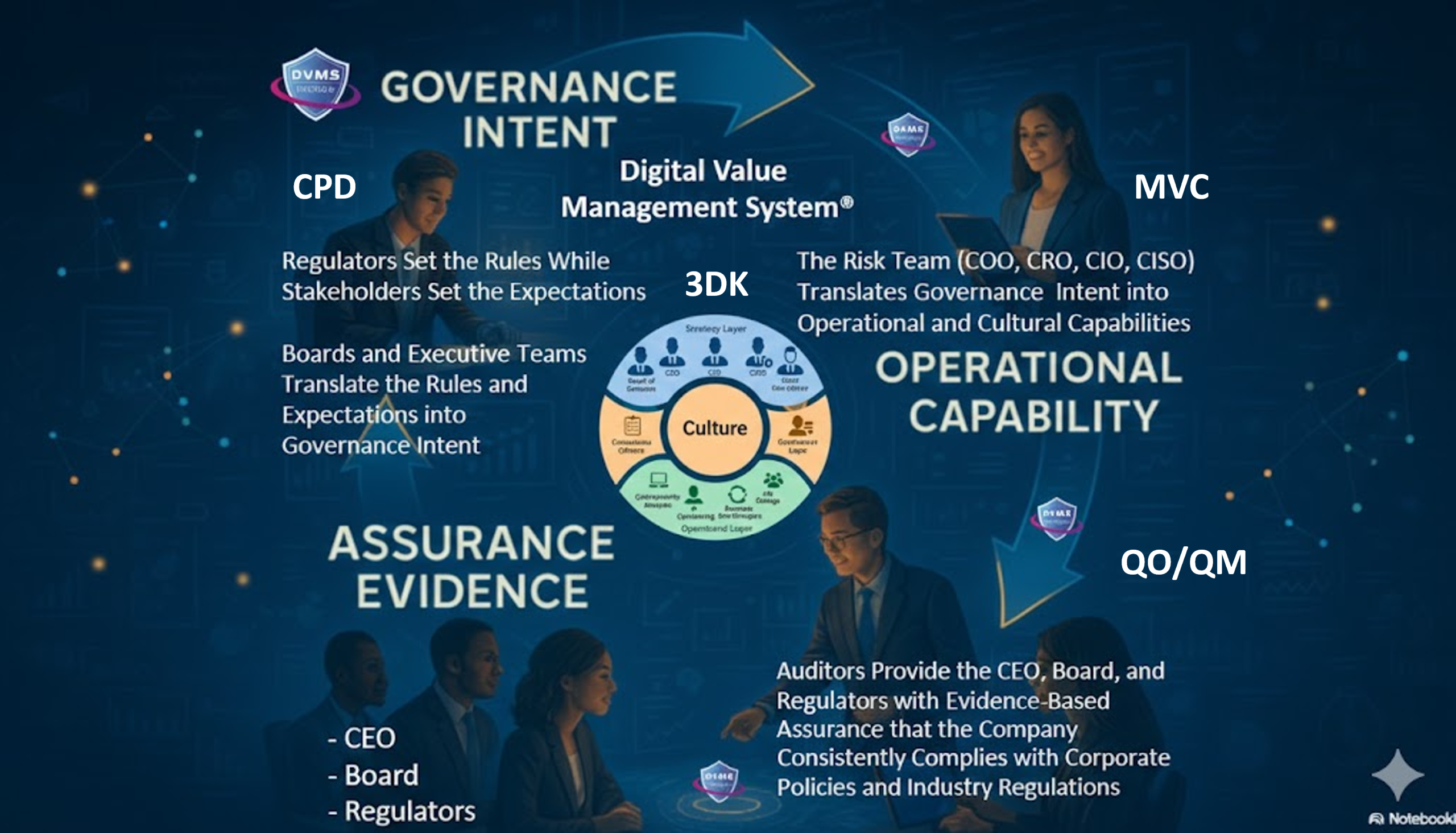
The integration of the CSF with DVMS elevates cybersecurity from a compliance-oriented activity to a core element of business value creation. The DVMS introduces a systems-thinking approach, embodied in the CPD Model—Create, Protect, Deliver—to link business strategy directly with operational execution.
Here, ITSM practices serve as the connective tissue between strategic intent and technical action. The DVMS outlines minimum viable capabilities—Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate—that parallel key ITSM disciplines. For example:
- Govern: ITSM’s governance practices (e.g., service level management, compliance audits) help institutionalize policies aligned with organizational priorities.
- Assure: Capacity, availability, and continuity management in ITSM validate that systems are reliable and capable of supporting business objectives.
- Plan & Design: ITSM’s service design and strategy processes ensure that services are designed with security, resilience, and stakeholder value in mind.
- Change & Execute: Change and release management practices control the transition of services into live operation without disrupting security postures.
- Innovate: Continual Service Improvement (CSI) in ITSM aligns with DVMS’s push for innovation through feedback loops and lessons learned.
Thus, ITSM best practices are not ancillary but central to executing the DVMS vision. They help embed cybersecurity into everyday business operations, ensuring that protective and resilient behaviors are woven into the fabric of service delivery.
Human-Centric Cybersecurity: People, Practice, and Process
One of the most critical contributions of ITSM to the CSF-DVMS framework is its focus on human-centric processes. The document emphasizes the importance of aligning People, Practice, and Process with technology—not as isolated elements, but as an integrated system that delivers value-based service outcomes.
- People: ITSM provides clearly defined roles and responsibilities, accountability mechanisms, and training programs that empower staff at all levels to act as stewards of digital value. This supports the CSF’s “Govern” function and DVMS’s emphasis on leadership and culture.
- Practice: ITSM frameworks codify daily routines and expected behaviors across IT operations. This consistency of action supports not only compliance but also a culture of reliability and security.
- Process: Structured processes within ITSM (incident, change, problem, knowledge management, etc.) enable repeatable and auditable execution of tasks. This aligns with both the CSF’s Organizational Profiles and Tiers for maturity and the DVMS phased roadmap (Initiate, Basic Hygiene, Expand, Innovate).
By operationalizing these elements, ITSM enables organizations to mature from reactive to proactive in their cybersecurity posture—progressing through the DVMS FastTrack stages with clear benchmarks and process maturity.
Technology as an Enabler, not a Crutch
The CSF-DVMS model highlights a crucial shift: technology is no longer the sole focus of cybersecurity but is framed as an enabler of broader organizational capabilities. ITSM reinforces this perspective by managing technology as a service—not an end.
For example, service asset and configuration management ensures that technology components are mapped to business services and understood in context. This visibility is essential for identifying vulnerabilities, planning mitigations, and responding effectively to incidents. Similarly, release and deployment practices ensure that new technologies are introduced safely and efficiently, minimizing risk while maximizing value.
ITSM ensures that technology investments are aligned with stakeholder expectations, regulatory compliance, and service outcomes—precisely the value-oriented focus that the DVMS model demands.
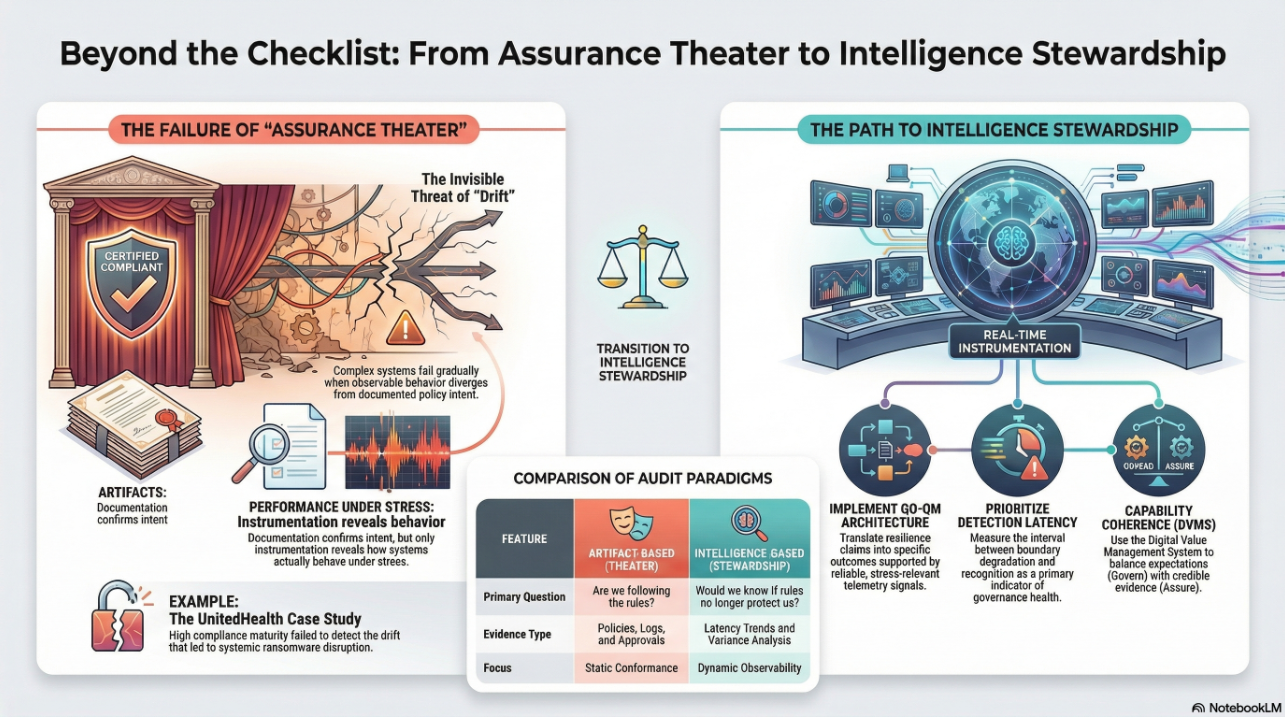
From Compliance to Resilience: Outcome-Driven Security
A key advantage of integrating ITSM into the CSF-DVMS framework is the shift from a compliance-centric approach to an outcome-driven model of cybersecurity. Rather than checking boxes, organizations using ITSM can measure success based on stakeholder satisfaction, service reliability, and business continuity.
The DVMS introduces a 3D Knowledge Model—team knowledge, inter-team collaboration, and strategic alignment—which maps directly to ITSM’s knowledge management and service integration principles. These human-centric dimensions emphasize that cyber resilience is not achieved through tools alone but through shared understanding, learning, and behavioral alignment.
This philosophy complements ITSM’s culture of continual improvement, where feedback from incident reviews, service performance, and stakeholder input drives enhancements to both technical and human systems.
Conclusion: Building Strategic Cyber Resilience with ITSM
ITSM best practices provide the essential mechanisms to embed cybersecurity into the daily operations of a digital enterprise. When integrated with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and the Digital Value Management System®, ITSM supports the transition from reactive cybersecurity compliance to proactive digital value management.
- At the tactical level, ITSM ensures consistent execution of cybersecurity controls.
- At the operational level, it connects strategy to execution through structured service management.
- At the strategic level, it reinforces stakeholder trust, business alignment, and digital resilience.
By integrating ITSM with the CSF and DVMS, organizations are equipped to deliver not only secure and resilient IT services, but also to transform cybersecurity into a source of competitive advantage and enduring stakeholder value.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Rick has 40+ years of passion and experience creating solutions to give organizations a competitive edge in their service markets. In 2015, Rick was identified as one of the top five IT Entrepreneurs in the State of Rhode Island by the TECH 10 awards for developing innovative training and mentoring solutions for boards, senior executives, and operational stakeholders.
The DVMS Institute’s NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System® certified training, assessment, and mentoring programs teach enterprises the skills to build a Holistic, Adaptive, and Culture-Powered Overlay System for internal, third-party, or hybrid cyber operations Governance, Resilience, and Assurance management
The NIST-CSF-DVMS positions cyber operations resilience not as a technical function but as a strategic, enterprise-wide cultural imperative that equips Leadership to Frontline Employees with the skills to Create, Protect, and Deliver (CPD) resilient digital business value.
Enabling cyber operations resilience also requires a coordinated effort across organizational Strategy, Governance, and Operational business layers. The NIST-CSF-DVMS 3D Knowledge Model ensures that each layer is aligned and operating cohesively as an integrated adaptive governance, resilience, and assurance overlay system, enabling enterprises to proactively identify, classify, and mitigate the systemic risks that could impact cyber operations.
This unique and innovative approach to Governance, Resilience, and Assurance enables enterprises to comply with any government-mandated cybersecurity regulation (SEC, DORA, NIS2, etc.) or maturity model program (SCF, HITRUST, CMMC, etc.).
® DVMS Institute 2025 All Rights Reserved