The NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System – The Industry’s First Cyber Resilience Operating System
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
Introduction
In today’s volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) digital landscape, organizations require more than compliance checklists to survive—they need a cyber resilience “operating system” that adapts, learns, and sustains value in the face of continuous disruption. Integrating the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 with the Digital Value Management System (DVMS) provides precisely that: a cyber resilience operating system that links strategy, risk, value, and culture into a unified, scalable system of systems.
This system transcends traditional cybersecurity approaches. It embeds cyber risk into enterprise strategy, operationalizes resilience, and enables the organization to continuously create, protect, and deliver digital business value. This system’s heart model combines the CSF’s risk-informed guidance with the DVMS’s systemic overlay, minimum viable capabilities, and adaptive feedback loops. These elements are orchestrated through the 3D Knowledge Model, which fosters collective awareness, collaboration, and strategic alignment.
NIST CSF 2.0: The Foundation for Cyber Risk Governance
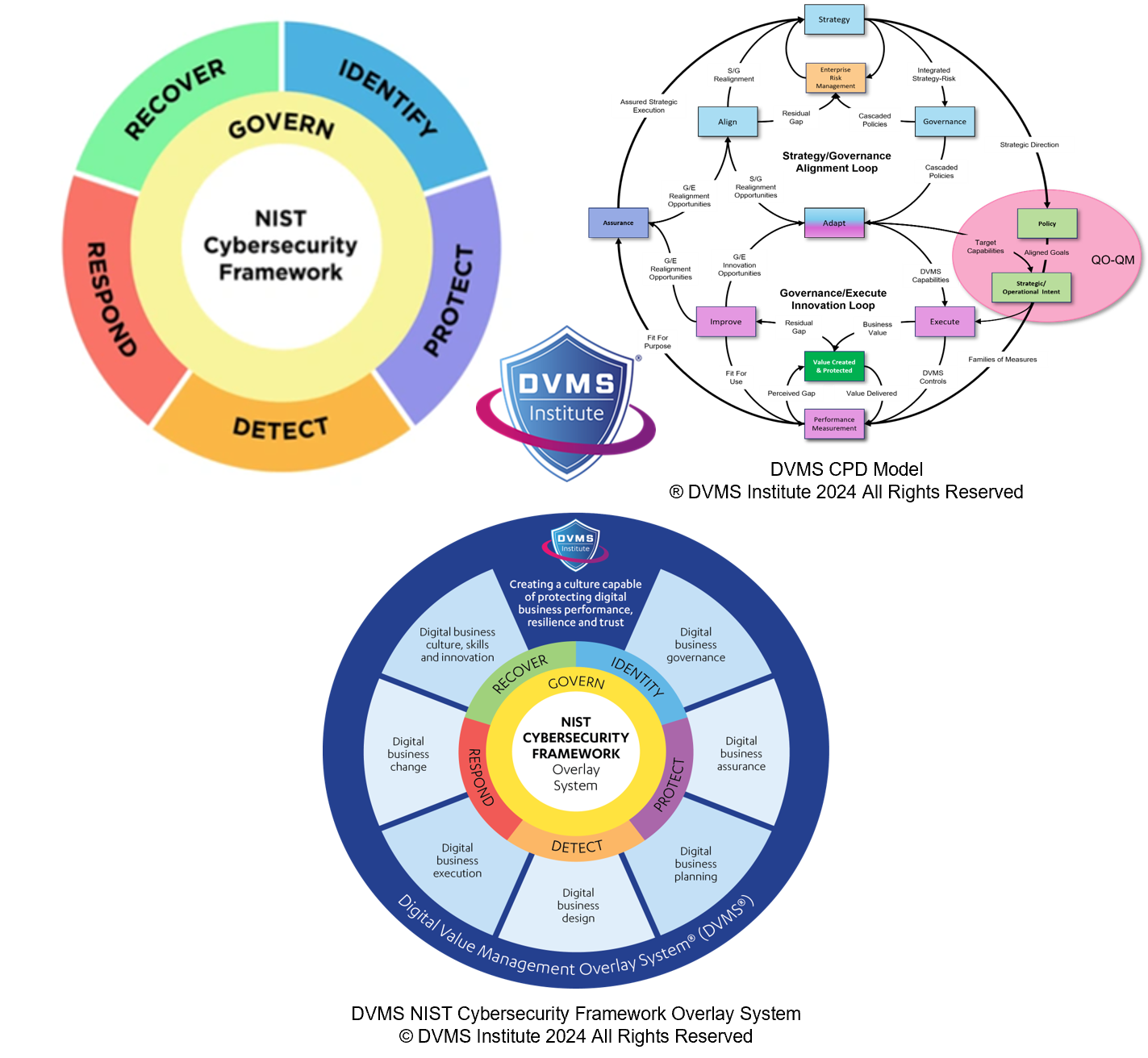
The NIST CSF 2.0 is a flexible, outcome-oriented framework structured around six key Functions:
- Govern
- Identify
- Protect
- Detect
- Respond
- Recover
It helps organizations of all sizes and sectors manage cybersecurity risks holistically. However, the CSF is not a how-to manual. It provides the “what” and the “why”—desired outcomes—but leaves the implementation (“how”) open-ended.
This is where the DVMS overlay comes in.
DVMS: The Implementation Overlay
The Digital Value Management System (DVMS) is not a new framework—it is a universal overlay that applies systems thinking to whatever frameworks, controls, or methods an organization already uses. It helps the organization achieve the CSF’s outcomes through a practical structure built on seven minimum viable capabilities (MVCs) arranged in the DVMS Z-X Model:
- Govern – Strategic direction and policy.
- Assure – Oversight and verification.
- Plan – Capacity and resource prioritization.
- Design – Structuring value creation and protection.
- Change – Organizational agility and adaptation.
- Execute – Operational value delivery.
- Innovate – Continuous improvement and experimentation.
Every part of an organization’s digital operations maps to one or more of these capabilities. These capabilities are not linear—they’re interdependent, forming a dynamic and adaptive operating structure.
The CPD Model: Creating, Protecting, and Delivering Value
The DVMS is operationalized through the CPD Model:
- Create – Initiatives to design or enhance digital business value.
- Protect – Embedding risk mitigation, security, privacy, and compliance.
- Deliver – Ensuring sustainable and trustworthy stakeholder value delivery.
This model reinforces the view that value protection and value creation are inseparable. They are two sides of the same coin. If value is not appropriately protected, it has no sustainable value.
The CPD Model also incorporates three feedback loops:
- Governance/Execution Loop – Connects oversight with day-to-day operations.
- Strategy/Governance Loop – Aligns leadership direction with risk and policy.
- Execution/Innovation Loop – Drives organizational learning and evolution.
These loops form the nervous system of the operating model—helping organizations sense, respond, and adapt.
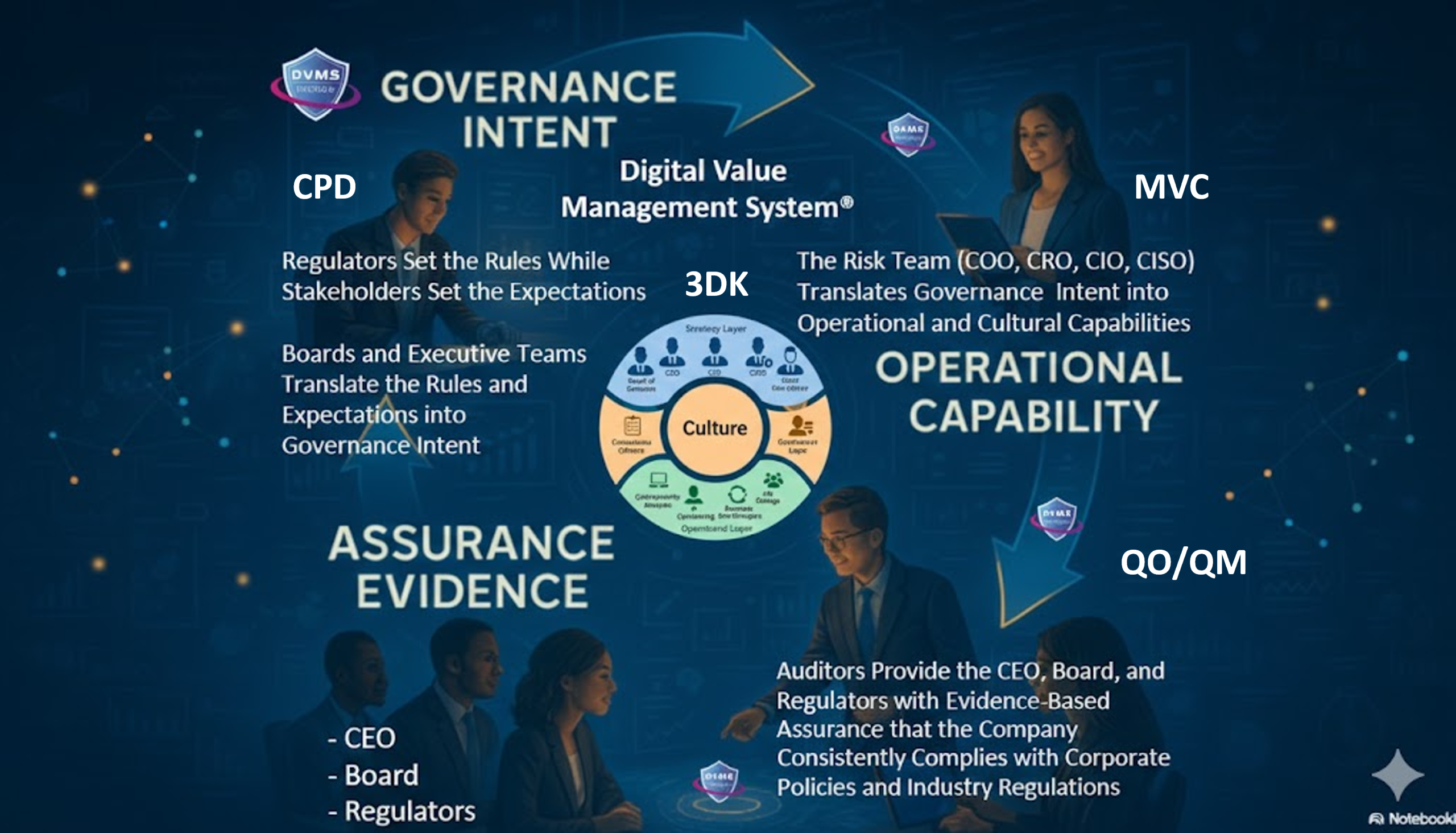
The 3D Knowledge Model: Intelligence Across Time, Teams, and Strategy
At the heart of the DVMS operating system lies the 3D Knowledge Model, a conceptual tool for creating organizational intelligence and proactive behavior.
The model visualizes knowledge and alignment across three dimensions:
- X-Axis: Knowledge over Time
- Past lessons, current practices, and future anticipations.
- Encourages continual learning from incidents and change.
- Y-Axis: Inter-Team Collaboration
- Understanding the ripple effects of decisions across teams.
- Breaks down silos and enables cross-functional cooperation.
- Z-Axis: Strategic and Operational Alignment
- Ensures that all cybersecurity and resilience efforts tie back to business value and mission.
These three axes together help surface context, capability, and maturity—core characteristics of resilient organizations.
For example, a security operations center (SOC) might analyze threat data (X-axis), coordinate with IT and HR during incident response (Y-axis), and report outcomes to executives for strategic investment decisions (Z-axis). In this way, the model ensures resilience isn’t just technical—it’s cultural and strategic.
From Cybersecurity to Cyber Resilience
Most traditional cybersecurity programs are reactive. The DVMS-CSF system redefines resilience as a proactive, systemic capability to adapt, learn, and restore value during adversity. This is accomplished through:
- Profiles and Tiers from the CSF 2.0 to define current and target states.
- QO–QM (Question-Outcome–Question Metric) and GQM (Goal-Question-Metric) methods to define, measure, and adapt outcomes.
- Cultural integration, recognizing that leadership, accountability, and norms must align with cyber risk priorities.
By blending strategic foresight (governance), structured adaptation (DVMS MVCs), and continuous learning (3D Knowledge Model), the DVMS-CSF system helps organizations thrive “on the edge of chaos.”
Conclusion: A Living Operating System for the VUCA Era
Cyber resilience isn’t just an outcome—it’s a continuous operating condition. The integration of the NIST CSF and DVMS equips organizations with a living operating system for risk-aware digital business value.
This system:
- Establishes common language across technical and non-technical teams.
- Scales with the organization’s complexity, size, and maturity.
- Enables cyber risk to be governed like any other business risk.
- Makes resilience a by-product of good business.
In a digital world where disruption is inevitable, the organizations that will survive—and thrive—are those that can see the whole, ask better questions, and continually learn. That’s the promise of a cyber resilience operating system powered by the NIST CSF and DVMS.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
DVMS Institute is a renowned provider of accredited (APMG International), Assured (NCSC-GCHQ-UK), and Recognized (DHS-CISA-NICCS-USA) NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Digital Value Management System® body of knowledge publications, certification trainings, assessment platforms and real-life desktop simulation trainings.
The Institute’s NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System® certified training programs teach businesses of any size, scale, or complexity the skills to build a Performance Driven Overlay System for Cyber Resilience capable of anticipating and mitigating the systemic risk digital businesses face today.
By embedding systemic risk management into strategic decision-making and aligning it with employee cultural values, organizations can build resilience—a dynamic capability to withstand digital business disruption and comply with any cybersecurity regulation (SEC, UK, DORA, NIS2, SAMA, SOCI, IMO, etc.) or maturity model mandates (HITRUST, CMMC, C2M2 etc.).
® DVMS Institute 2024 All Rights Reserved