Using A NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management® System To Enable Performance Driven Cyber Resilience
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
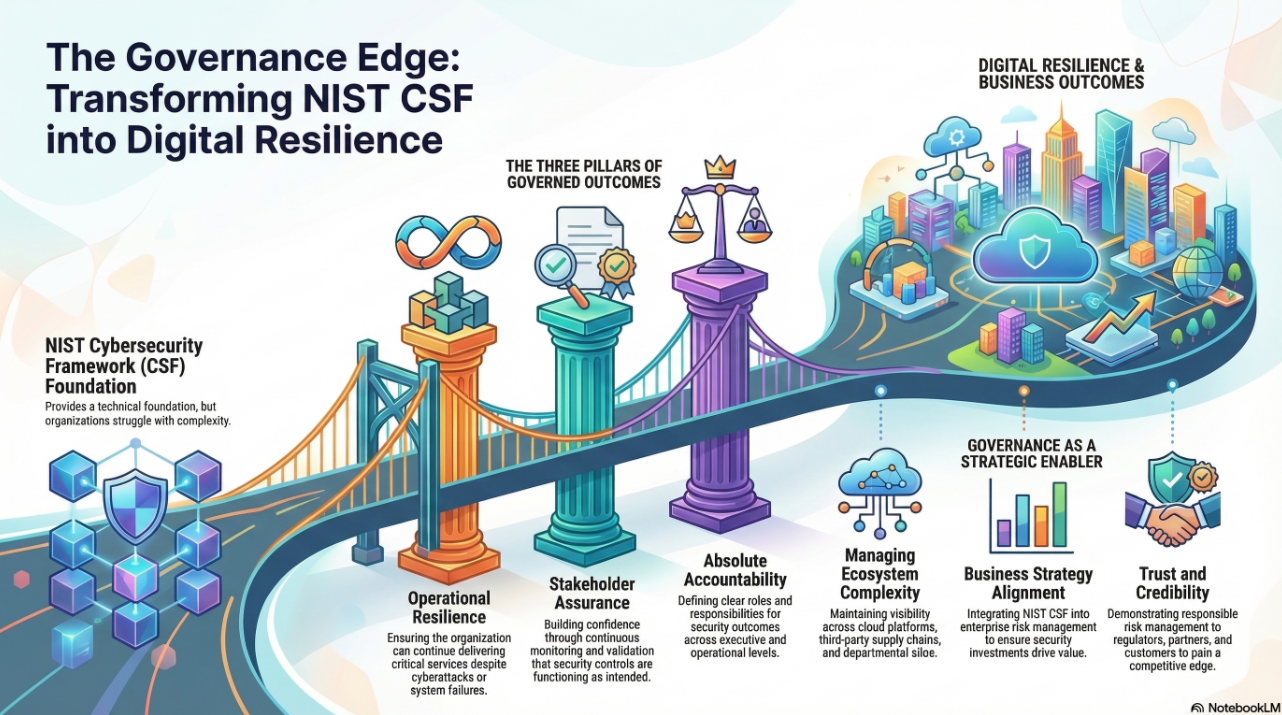
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF), when integrated through the Digital Value Management Overlay System (DVMS), becomes a transformative approach that enables organizations to not only manage cyber risk but to build enduring organizational cyber resiliency. Cyber resiliency, in the context of a digitally dependent enterprise, is no longer simply the ability to defend against threats; it is the capacity to adapt to changing conditions, recover rapidly from disruptions, and continue delivering value in the face of adversity.
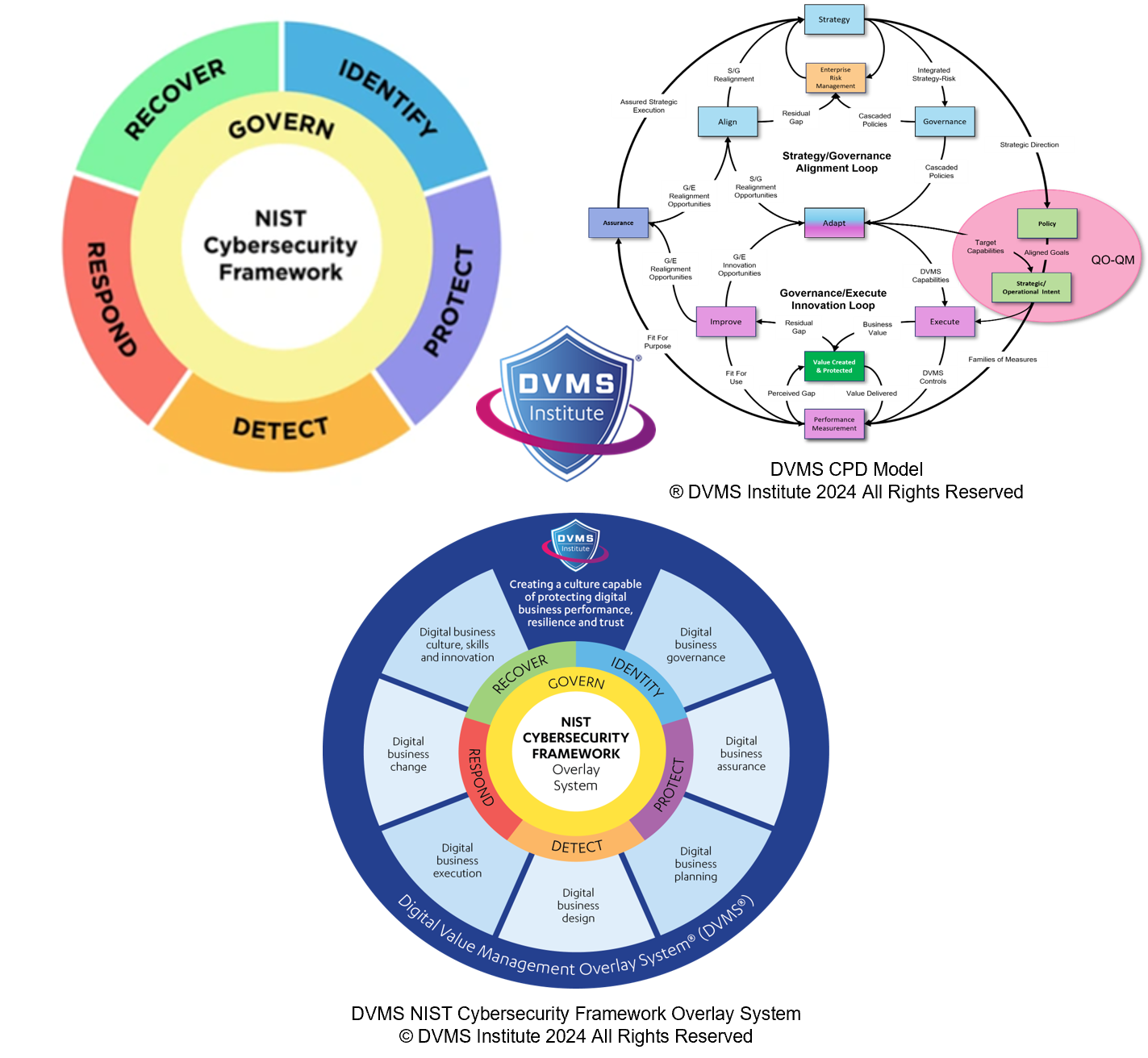
While the NIST CSF is widely recognized for its functional structure—Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—it is through the DVMS that these abstract functions become operationalized, integrated with enterprise strategy, and embedded within the day-to-day behaviors of the organization.
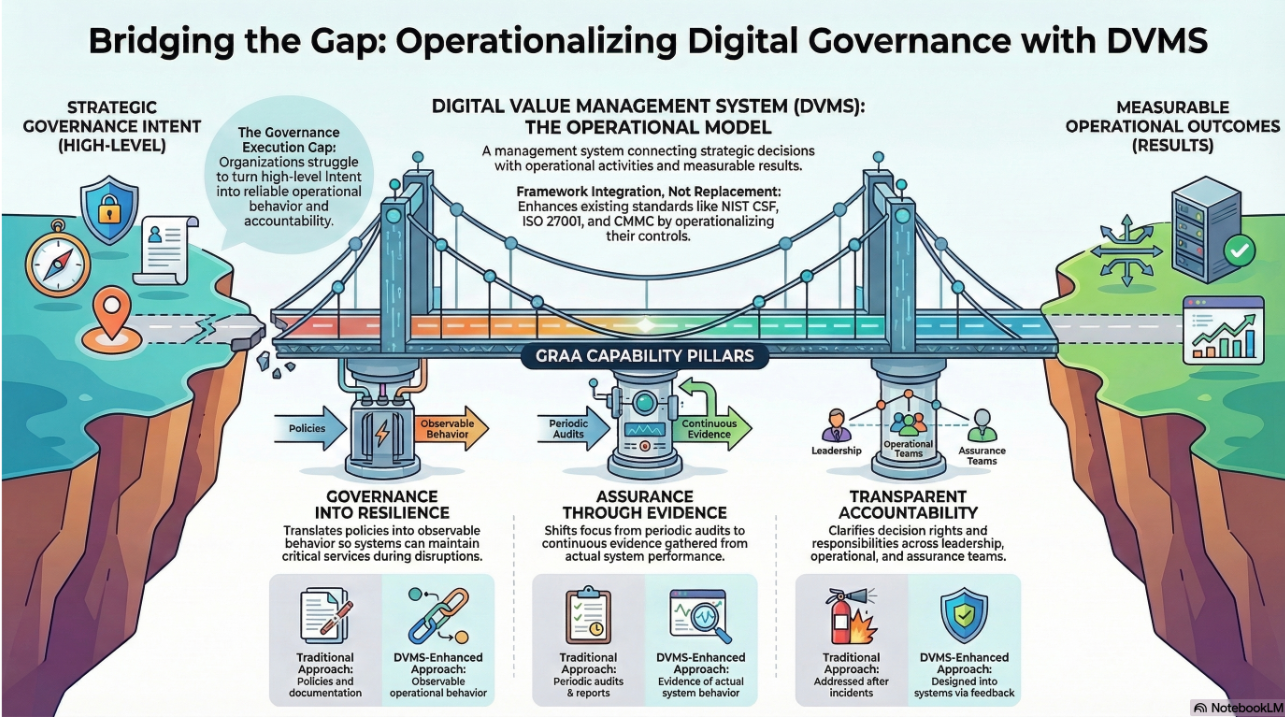
The DVMS views cyber resilience not as a function of technology alone but because of systemic alignment between strategy, governance, operations, and culture. It approaches cybersecurity through a systems-thinking lens, allowing organizations to see beyond silos and understand how digital risk management is interwoven with every aspect of value creation and delivery. At the core of the DVMS is the understanding that digital value cannot be sustained unless it is appropriately protected. The traditional model of “create first, protect later” leaves organizations vulnerable to breaches, disruptions, and loss of stakeholder trust.
The DVMS shifts this paradigm by embedding protection into the value creation process itself. Through the CPD Model (Create, Protect, Deliver), organizations are guided to develop capabilities that ensure digital services and assets are continuously assessed for their value, exposure, and risk, and that mechanisms are in place to ensure these assets are delivered securely and reliably. This model ensures that security is no longer an afterthought but a continuous process that evolves alongside business objectives and digital transformations. By linking cybersecurity with organizational purpose and performance, the DVMS enables leaders to make risk-informed decisions that enhance both resilience and agility.
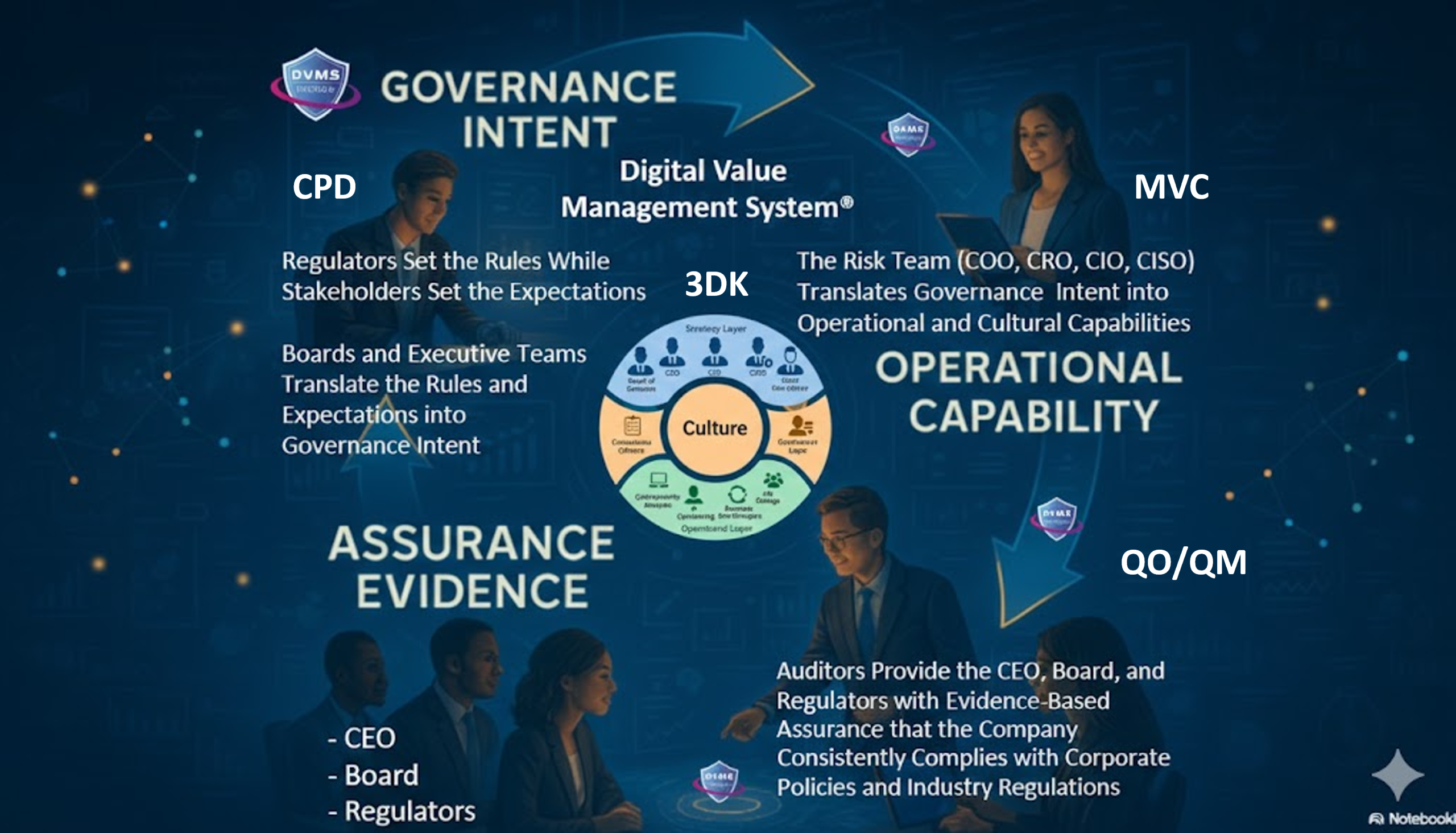
To bring this vision into practice, the DVMS introduces the Z-X Model, which defines seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs) every organization must master to achieve cyber resilience: Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate. These capabilities are not rigid departments or technical functions; they are dynamic capabilities that span the entire organization and guide how digital value is governed, protected, and evolved. For example, Govern and Assure set the foundation for leadership accountability, policy formation, and risk oversight. Plan and Design focus on aligning strategic goals with cybersecurity controls, ensuring that new services or technologies are architected with protection in mind. Change and Execute operationalize protection by managing transitions, deploying safeguards, and delivering services within defined risk thresholds. Innovate ensures the organization continuously adapts, evolves, and learns from past performance. Each MVC is supported by a set of sub-practice areas that guide organizations in identifying gaps, measuring progress, and maturing their capabilities over time. This layered approach is critical for cyber resilience, as it enables organizations to align cybersecurity with broader enterprise architecture and business continuity planning.
Another key element of how the DVMS enhances organizational cyber resilience is its emphasis on systems thinking and the integration of feedback loops. Cybersecurity is not static; threats evolve, technologies change, and business needs shift. The DVMS encourages organizations to move away from linear, checklist-based approaches and instead adopt a mindset of continuous learning, adaptation, and improvement. This is operationalized through the 3D Knowledge Model, which frames organizational dynamics across three axes: past-present-future knowledge (X-axis), team collaboration and interdependence (Y-axis), and alignment with strategic and operational intent (Z-axis). By viewing cybersecurity through this multidimensional lens, organizations can better understand how their knowledge flows, where bottlenecks exist, and how misalignments between teams or systems might create hidden vulnerabilities. This visibility is essential for building the kind of situational awareness and responsiveness that defines true cyber resilience.
DVMS also incorporates powerful tools for measurement and governance, such as the Question-Outcome–Question-Metric (QO-QM) framework. Cyber resiliency cannot be achieved without clear metrics, but traditional cybersecurity metrics often fail to communicate meaningful outcomes to business stakeholders. QO-QM closes this gap by tying every cybersecurity action to a defined outcome, and every outcome to a set of strategically framed questions and metrics. This approach allows organizations to link security investments to value delivery, operational performance, and resilience outcomes. It also supports the shift from compliance-driven cybersecurity to performance-driven cyber resilience. For example, instead of measuring how many patches were deployed (an activity), the organization might measure how effectively those patches reduced exposure to critical vulnerabilities in systems that support revenue generation or public trust (an outcome). This reframing of metrics from technical to strategic is critical for engaging leadership and building a culture where cybersecurity is seen as a value enabler, not a cost center.
Culture is another cornerstone of the DVMS and its impact on cyber resilience. Resilience is not just about systems; it is also about people. The DVMS recognizes that leadership behavior, organizational norms, communication patterns, and trust are all part of the resilience equation. Through capabilities like Leadership and Culture, Tone at the Top, Crisis Coordination, and Knowledge Management, the DVMS ensures that cybersecurity is embedded into the organizational culture and not left solely to technical teams. It promotes behaviors such as proactive risk identification, open reporting of vulnerabilities, and collaborative response to incidents. These cultural traits are essential for detecting threats early, minimizing impact, and recovering quickly. Furthermore, DVMS empowers leaders to take ownership of cybersecurity by aligning it with enterprise risk, strategy, and mission. This alignment ensures that resilience is viewed as a strategic priority and that resources, policies, and talent development efforts support that priority.
Operationally, the DVMS helps organizations adopt and scale cybersecurity capabilities through its FastTrack Phased Approach. This model divides implementation into four iterative phases—Initiate, Basic Hygiene, Expand, and Innovate—each designed to meet organizations where they are in their maturity journey and guide them toward higher levels of resilience. The Initiate phase focuses on defining mission clarity, setting governance foundations, and identifying critical assets. Basic Hygiene introduces essential protections such as access control, configuration management, and awareness training. Expand scales capabilities across systems, supply chains, and business units, integrating detection, response, and continuous monitoring. Innovate brings in advanced practices like red teaming, automation, AI-based threat intelligence, and business-aligned risk quantification. By guiding organizations through these phases, the DVMS ensures that cyber resilience is not achieved through one-time projects but through continual investment, iteration, and evolution.
Crucially, the DVMS is framework-agnostic and adaptable to any regulatory or operational context. Whether an organization is subject to national mandates like the Uruguay Cybersecurity Framework (MCU), regional regulations like GDPR, or sector-specific standards like HIPAA or NERC CIP, the DVMS provides the scaffolding to integrate those requirements within the broader goal of resilience. It acts as a harmonizing layer that connects strategy with compliance, operations with oversight, and people with process. This adaptability is what makes the DVMS such a powerful enabler of organizational cyber resilience. It allows each organization to tailor its security journey based on mission, risk appetite, maturity, and resource availability while ensuring alignment with best practices and measurable outcomes.
The NIST CSF provides the directional compass for managing cybersecurity risk, but it is through the Digital Value Management System that this guidance becomes actionable, measurable, and sustainable. DVMS enables organizations to embed security into the architecture of digital business, transform compliance into performance, and build the adaptive capacity required to weather today’s complex threat environment. In doing so, it empowers organizations to go beyond defense and embrace cyber resilience as a strategic capability that protects value, sustains trust, and fuels innovation. Through its integrated models, performance frameworks, cultural enablers, and phased implementation pathways, the DVMS turns the principles of the NIST CSF into a living system of continuous protection and organizational learning—exactly what is needed in a world where digital resilience is foundational to operational success.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
DVMS Institute is a renowned provider of accredited (APMG International), Assured (NCSC-GCHQ-UK), and Recognized (DHS-CISA-NICCS-USA) NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Digital Value Management System® body of knowledge publications, certification trainings, assessment platforms and real-life desktop simulation trainings.
The Institute’s NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System® certified training programs teach businesses of any size, scale, or complexity the skills to build a Performance Driven Overlay System for Cyber Resilience capable of anticipating and mitigating the systemic risk digital businesses face today.
By embedding systemic risk management into strategic decision-making and aligning it with employee cultural values, organizations can build resilience—a dynamic capability to withstand digital business disruption and comply with any cybersecurity regulation (SEC, UK, DORA, NIS2, SAMA, SOCI, IMO, etc.) or maturity model mandates (HITRUST, CMMC, C2M2 etc.).
® DVMS Institute 2024 All Rights Reserved