U.S. Department of Energy C2M2 Maturity Model and the DVMS Institute NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System®
Rick Lemieux – Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
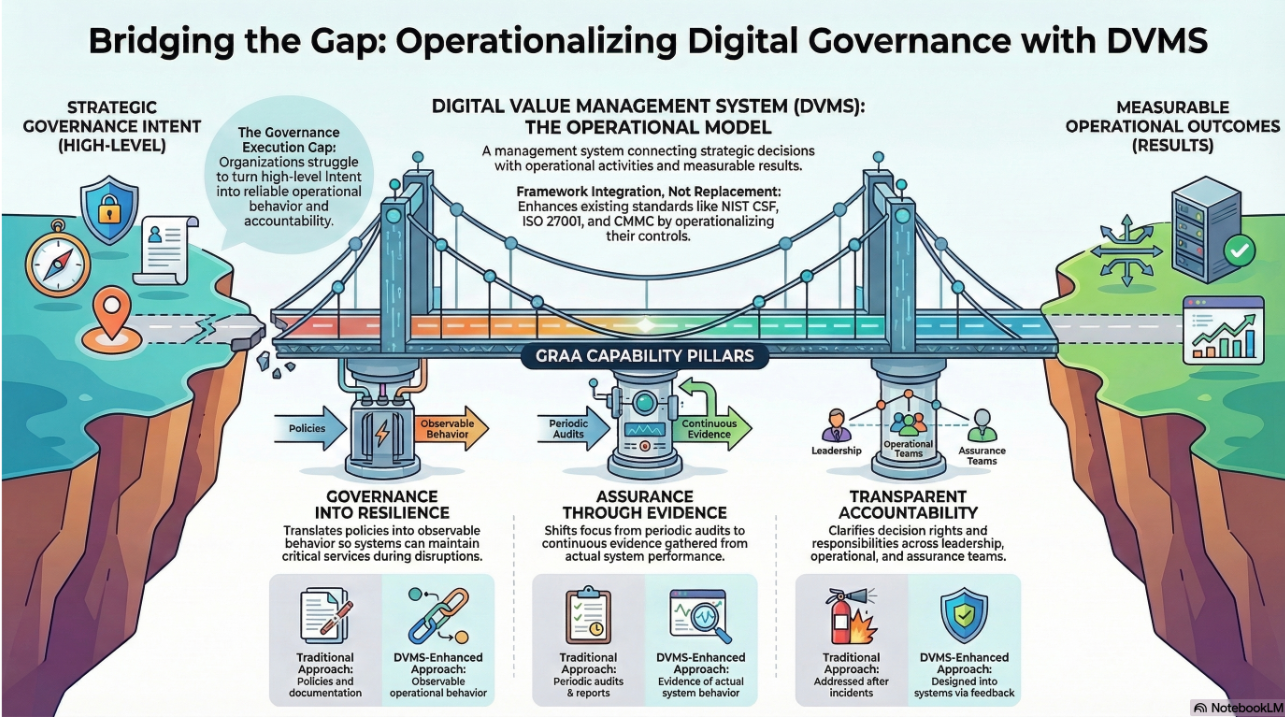
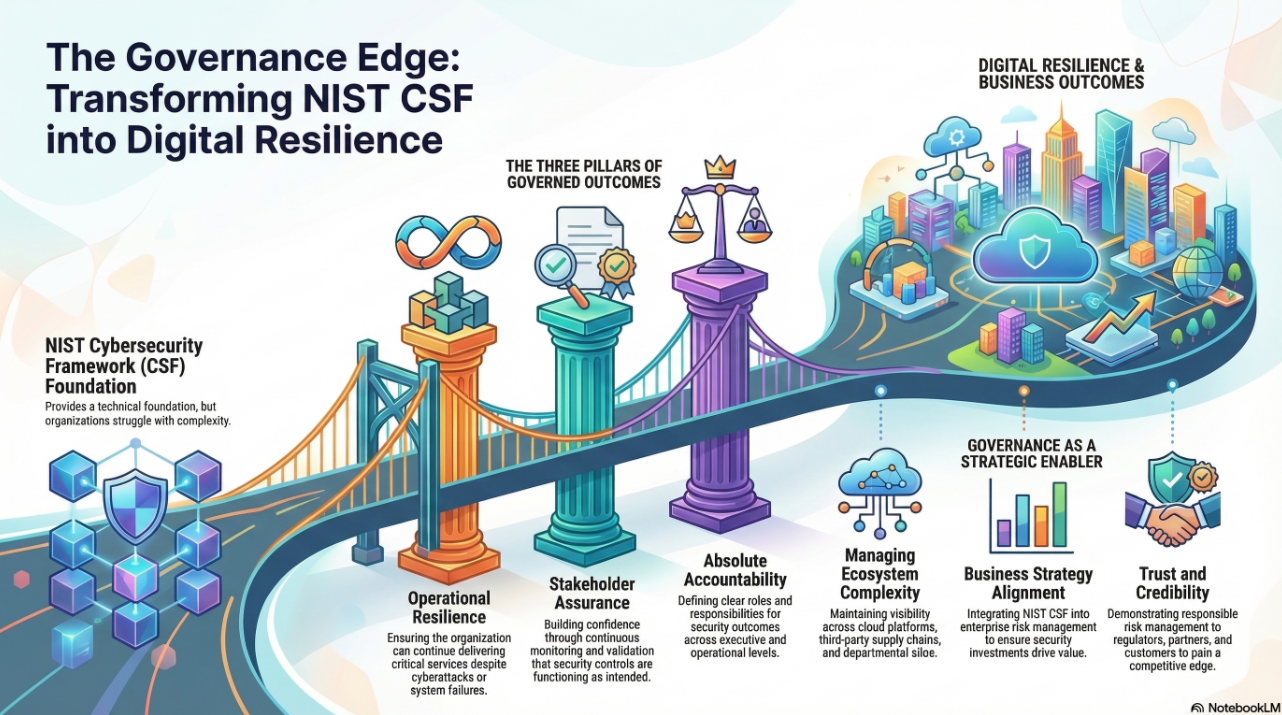
Organizations are expected to achieve measurable progress in cybersecurity capability in an era of escalating cyber threats and increasing reliance on digital infrastructure. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2) provides a comprehensive roadmap for organizations—particularly in critical infrastructure sectors—to assess, enhance, and institutionalize their cybersecurity capabilities. The C2M2 defines maturity across increasing sophistication levels, from informal, ad hoc practices to governed, measured, and continuously improved cybersecurity programs. However, while the C2M2 outlines “what” must be achieved, many organizations struggle with the “how.” Enter the Digital Value Management System (DVMS) and its core component, the Digital Value Capability Maturity Model (DVCMM)—a system developed by the DVMS Institute to operationalize both the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST-CSF) and the outcomes prescribed in the C2M2.
The DVCMM is purpose-built to enable organizations to achieve the maturity indicators defined by C2M2, focusing on technical compliance and integrated business value delivery. Unlike traditional maturity models that are narrowly focused on controls or technology, the DVCMM is rooted in a systems-thinking approach. It links cybersecurity maturity directly to the organization’s ability to create, protect, and deliver digital business value, integrating governance, risk, performance, and cultural adaptation. This holistic model addresses a core limitation of many C2M2 initiatives: the difficulty in translating high-level domains and maturity indicators into organizational behaviors and sustainable practices.
The C2M2 model defines three maturity indicator levels (MILs): MIL1 (Initial practices), MIL2 (Documented and consistently performed), and MIL3 (Institutionalized and adaptive). The DVCMM aligns tightly with these levels through its four maturity stages: Level 0 (Unmanaged), Level 1 (Defined), Level 2 (Managed), and Level 3 (Governed and Measured). These levels are explicitly designed to map to the C2M2’s increasing rigor, structure, and integration progression. By providing a clear and actionable model, DVCMM helps organizations understand what maturity looks like in practice, how to measure it, and what capabilities must be in place at each level.
Organizations begin formalizing their cybersecurity practices at Level 1 (Defined) of the DVCMM. These are typically reactive and fragmented but represent an awareness of the need for structure. This aligns with C2M2’s MIL1, where organizations exhibit some level of cybersecurity activity, albeit inconsistently. The DVCMM’s FastTrack™ framework, introduced at this stage, helps organizations stabilize their efforts by providing structured guidance across core capability domains. It ensures that organizations establish a foundation for cybersecurity governance that reflects their operational reality rather than adopting one-size-fits-all controls.
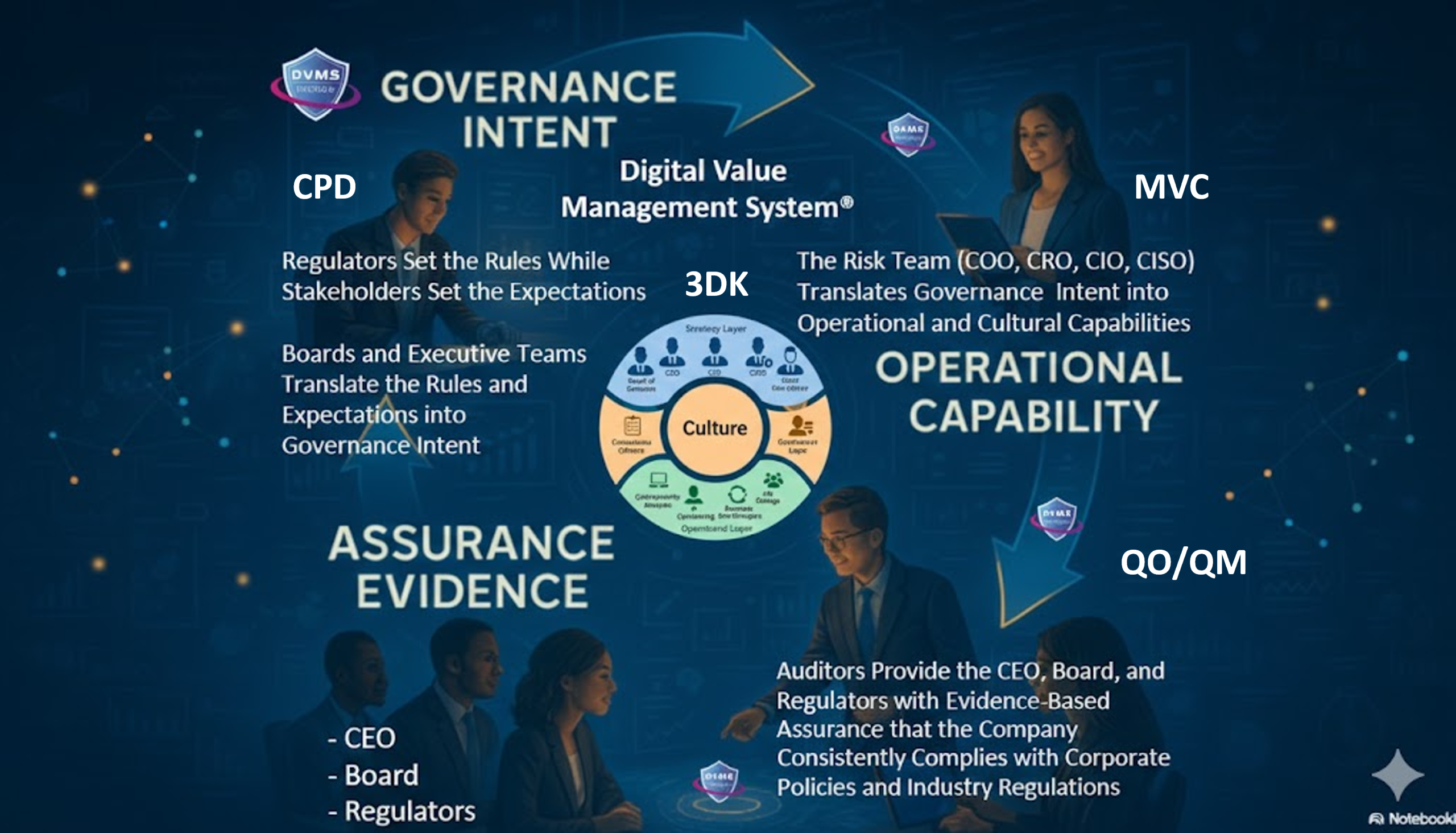
Moving to Level 2 (Managed) in the DVCMM, the model introduces repeatable and monitored practices across all capability areas. These capabilities are managed using feedback loops, stakeholder-driven metrics, and continuous performance assessments. This directly mirrors the C2M2 MIL2, which calls for documented, consistently performed practices across the enterprise. The DVCMM supports this by embedding its Z-X Model—a framework that defines seven Minimum Viable Capabilities (MVCs): Govern, Assure, Plan, Design, Change, Execute, and Innovate12603 DVMS Thriving on …. Each capability supports distinct operational domains and ensures cybersecurity is integrated into every aspect of the organization—from strategic planning to system execution.
The Govern capability, for example, supports C2M2 domains related to risk management, asset management, and cybersecurity program management. Organizations are taught to treat strategy and risk as inseparable, crafting strategy-risk-informed policies that align cybersecurity goals with business objectives. This governance alignment is critical for reaching C2M2’s higher maturity levels, where decisions must be guided by risk-informed, strategic oversight.
In the Assure capability, the DVCMM enables organizations to instrument their cybersecurity performance, establish metrics tied to stakeholder outcomes, and track effectiveness over time. The C2M2 MIL3 maturity indicators emphasize the need for performance management systems that use data to inform decisions and drive improvement. DVCMM supports this through structured questioning methodologies such as Goal-Question-Metric (GQM) and Question–Outcome–Question–Metric (QO-QM), which ensure that metrics are tied not only to technical controls but to the outcomes they are intended to deliver.
At the highest level of maturity—DVCMM Level 3—the system fully delivers the institutionalization outcomes of C2M2’s MIL3. Here, cybersecurity practices are standardized and measured, governed, optimized, and continuously improved. The DVCMM enables this by creating feedback loops between strategic goals, operational execution, and assurance functions. Cybersecurity becomes a strategic capability—integrated into culture, decision-making, and innovation. This level also focuses on adaptive resilience, a key outcome for critical infrastructure operators under C2M2. The DVCMM’s “Innovate” capability empowers organizations to embed cybersecurity considerations into change initiatives and digital transformation efforts, ensuring that maturity is sustainable, not static.
The CPD Model—the core execution framework of the DVMS—ensures these maturity levels are embedded in value-creating workflows. The CPD Model represents three continuous loops: Create, Protect, and Deliver digital business value. It serves as a connective tissue across governance and operational activities, ensuring that every cybersecurity decision is contextualized by the digital assets and business outcomes it supports. This model addresses C2M2’s demand for cybersecurity to be integrated with enterprise functions, not isolated within technical teams. It supports organizational performance management, incident response, situational awareness, and stakeholder engagement—the very capabilities C2M2 aims to strengthen.
Notably, the DVCMM is not an abstract theoretical model. It is tied to practical tools, performance assessments, and training programs that guide organizations through maturity. The DVMS Institute teaches the model through real-world narratives, practitioner-led simulations, and governance scenarios. As a result, the DVCMM is a living model—it evolves with the organization and can be customized for different sectors, regulatory requirements, and risk profiles. This adaptability is especially crucial for organizations in critical infrastructure sectors, which often operate in hybrid environments with overlapping compliance obligations.
Culturally, the DVCMM addresses another often-overlooked aspect of cybersecurity maturity: the human and organizational dimensions. By integrating models like the 3D Knowledge Model, the DVMS teaches teams to understand how knowledge flows across the enterprise, how mental models influence decisions, and how culture impacts capability development. These lessons help organizations embed cybersecurity into team behavior, leadership practices, and operational rituals—key ingredients for achieving institutionalization at C2M2 MIL3.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System (DVMS) and its embedded Digital Value Capability Maturity Model (DVCMM) provide a robust, adaptive, and measurable roadmap for achieving the outcomes called out in the U.S. Department of Energy’s C2M2. By operationalizing NIST-CSF principles through system-wide governance, stakeholder alignment, and performance-driven capability development, the DVCMM supports and accelerates an organization’s journey toward institutionalized cyber resilience. It is a model not of compliance but of competence—a transformative approach that enables cybersecurity to become a driver of trust, innovation, and strategic value.
About the Author

Rick Lemieux
Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer of the DVMS Institute
DVMS Institute is a renowned provider of accredited (APMG International), Assured (NCSC-GCHQ-UK), and Recognized (DHS-CISA-NICCS-USA) NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Digital Value Management System® body of knowledge publications, certification trainings, assessment platforms and real-life desktop simulation trainings.
The Institute’s NIST Cybersecurity Framework Digital Value Management System® certified training programs teach businesses of any size, scale, or complexity the skills to build a Performance Driven Overlay System for Cyber Resilience capable of anticipating and mitigating the systemic risk digital businesses face today.
By embedding systemic risk management into strategic decision-making and aligning it with employee cultural values, organizations can build resilience—a dynamic capability to withstand digital business disruption and comply with any cybersecurity regulation (SEC, UK, DORA, NIS2, SAMA, SOCI, IMO, etc.) or maturity model mandates (HITRUST, CMMC, C2M2 etc.).
® DVMS Institute 2024 All Rights Reserved